
A reference card or Romer [1] is a device for increasing the accuracy when reading a grid reference from a map.

A reference card or Romer [1] is a device for increasing the accuracy when reading a grid reference from a map.
Made from transparent plastic, paper or other materials, reference cards are found on most baseplate compasses. Essentially, they are a specially marked-out ruler which matches the scale of the map in use. The scales are laid out in reverse, such that by lining up the numbers given in the grid reference with the gridlines for the square in question, the corner of the Romer lies on the location the grid reference of which is being read. Some transparent versions have a small hole at the origin when this is not at the corner of the reference card. This allows access to the map such that the location could be marked with a pencil if using the reference card in reverse having been given a grid reference to start with. They are used in many types of land navigation and map reading, to give a more accurate grid reference than one just estimated by eye from the grid lines on the map.
While Romers of various designs are available commercially, they can easily be made by hand, by using a computer, or by finding a website [2] with instructions.
Invented in 1915 by Temporary Lieutenant (later Captain) Carrol Romer, M.C., R.E. (1883–1951), then "Maps", First Army: i.e. OC Maps and Printing Section, such reference cards were widely used by the British Army in World War I and after, being described in a Maps GHQ booklet Maps and Artillery Boards in December 1916. The name 'Romer' seems only to have been used officially from 1929. [3]
A version was later developed for car navigational rallies by car rally partners Eric Gardner and John Cridford during the early 1950s, the 'Garford Romer' was available for both imperial and metric Ordnance Survey maps and is still sold today. Although a registered design when it was first made and sold it was and still is much copied.

A personal digital assistant (PDA) is a multi-purpose mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. Following a boom in the 1990s and 2000s, PDA's were mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of more highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android in the late 2000s, and thus saw a rapid decline.

A punched card is a piece of card stock that stores digital data using punched holes. Punched cards were once common in data processing and the control of automated machines.

A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with magnetic north. Other methods may be used, including gyroscopes, magnetometers, and GPS receivers.

In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines, but historically using a variety of methods. Traditional definitions require a topographic map to show both natural and artificial features. A topographic survey is typically based upon a systematic observation and published as a map series, made up of two or more map sheets that combine to form the whole map. A topographic map series uses a common specification that includes the range of cartographic symbols employed, as well as a standard geodetic framework that defines the map projection, coordinate system, ellipsoid and geodetic datum. Official topographic maps also adopt a national grid referencing system.

In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically:
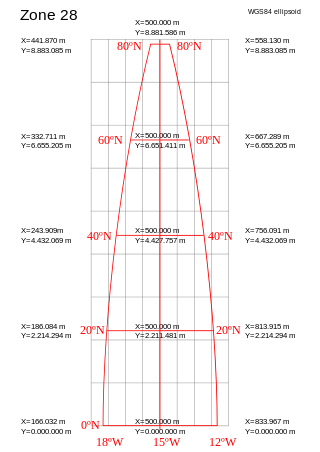
A projected coordinate system – also called a projected coordinate reference system, planar coordinate system, or grid reference system – is a type of spatial reference system that represents locations on Earth using Cartesian coordinates (x, y) on a planar surface created by a particular map projection. Each projected coordinate system, such as "Universal Transverse Mercator WGS 84 Zone 26N," is defined by a choice of map projection (with specific parameters), a choice of geodetic datum to bind the coordinate system to real locations on the earth, an origin point, and a choice of unit of measure. Hundreds of projected coordinate systems have been specified for various purposes in various regions.
QuickDraw was the 2D graphics library and associated application programming interface (API) which is a core part of classic Mac OS. It was initially written by Bill Atkinson and Andy Hertzfeld. QuickDraw still existed as part of the libraries of Mac OS X, but had been largely superseded by the more modern Quartz graphics system. In Mac OS X Tiger, QuickDraw has been officially deprecated. In Mac OS X Leopard applications using QuickDraw cannot make use of the added 64-bit support. In OS X Mountain Lion, QuickDraw header support was removed from the operating system. Applications using QuickDraw still ran under OS X Mountain Lion to macOS High Sierra; however, the current versions of Xcode and the macOS SDK do not contain the header files to compile such programmes.
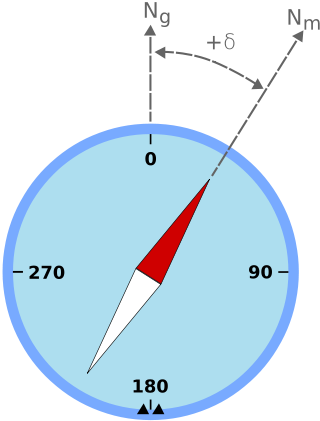
Magnetic declination is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB), also known as British National Grid (BNG), is a system of geographic grid references, distinct from latitude and longitude, whereby any location in Great Britain can be described in terms of its distance from the origin, which lies to the west of the Isles of Scilly.

An automotive navigation system is part of the automobile controls or a third party add-on used to find direction in an automobile. It typically uses a satellite navigation device to get its position data which is then correlated to a position on a road. When directions are needed routing can be calculated. On the fly traffic information can be used to adjust the route.

Intelligent Parking Assist System (IPAS), also known as Advanced Parking Guidance System (APGS) for Toyota models in the United States, is the first production automatic parking system developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in 1999 initially for the Japanese market hybrid Prius models and Lexus models. The technology assists drivers in parking their vehicle. On vehicles equipped with the IPAS, via an in-dash screen and button controls, the car can steer itself into a parking space with little input from the user. The first version of the system was deployed on the Prius Hybrid sold in Japan in 2003. In 2006, an upgraded version debuted for the first time outside Japan on the Lexus LS luxury sedan, which featured the automatic parking technology among other brand new inventions from Toyota. In 2009, the system appeared on the third generation Prius sold in the U.S. In Asia and Europe, the parking technology is marketed as the Intelligent Park Assist System for both Lexus and Toyota models, while in the U.S. the Advanced Parking Guidance System name is only used for the Lexus system.
The E6B flight computer is a form of circular slide rule used in aviation. It is an instance of an analog calculating device still being used in the 21st century.

The VAXBI bus is a computer bus designed and sold by the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) of Maynard, Massachusetts.

Diver navigation, termed "underwater navigation" by scuba divers, is a set of techniques—including observing natural features, the use of a compass, and surface observations—that divers use to navigate underwater. Free-divers do not spend enough time underwater for navigation to be important, and surface supplied divers are limited in the distance they can travel by the length of their umbilicals and are usually directed from the surface control point. On those occasions when they need to navigate they can use the same methods used by scuba divers.
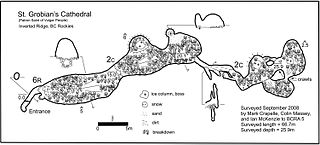
A cave survey is a map of all or part of a cave system, which may be produced to meet differing standards of accuracy depending on the cave conditions and equipment available underground. Cave surveying and cartography, i.e. the creation of an accurate, detailed map, is one of the most common technical activities undertaken within a cave and is a fundamental part of speleology. Surveys can be used to compare caves to each other by length, depth and volume, may reveal clues on speleogenesis, provide a spatial reference for other areas of scientific study and assist visitors with route-finding.

The Apple II Plus is the second model of the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Computer. It was sold from June 1979 to December 1982. Approximately 380,000 II Pluses were sold during its four years in production before being replaced by the Apple IIe in January 1983.

The Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose, which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was also a more general and nationwide need in light of the potential threat of invasion during the Napoleonic Wars. Since 1 April 2015, the Ordnance Survey has operated as Ordnance Survey Ltd, a government-owned company, 100% in public ownership. The Ordnance Survey Board remains accountable to the Secretary of State for Science, Innovation and Technology. It was also a member of the Public Data Group.

A control point is a marked waypoint used in orienteering and related sports such as rogaining and adventure racing. It is located in the competition area; marked both on an orienteering map and in the terrain, and described on a control description sheet. The control point must be identifiable on the map and on the ground. A control point has three components: a high visibility item, known as a flag or kite; an identifier, known as a control code; and a recording mechanism for contestants to record proof that they visited the control point. The control point is usually temporary, except on a permanent orienteering course.

RoboRally, also stylized as Robo Rally, is a board game for 2–8 players designed by Richard Garfield and published by Wizards of the Coast (WotC) in 1994. Various expansions and revisions have been published by WotC, Avalon Hill, and Renegade Games.
Audi Navigation Plus is an in-car media and navigation system developed by Audi. Unlike the Audi Multi Media Interface, it can not control climate, convenience, suspension or engine settings. Audi Navigation Plus units were available mostly as an optional equipment instead of standard stereo systems.