This is a list of the extreme points of Ireland – the points that are farthest north, south, east or west in Ireland. It includes the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.

The River Bann is one of the longest rivers in Northern Ireland, its length, Upper and Lower Bann combined, being 129 km (80 mi). However, the total length of the River Bann, including its path through the 30 km (19 mi) long Lough Neagh is 159 km (99 mi). Another length of the River Bann given is 90 mi. The river winds its way from the southeast corner of Northern Ireland to the northwest coast, pausing in the middle to widen into the enormous Lough Neagh. The River Bann catchment has an area of 5,775 km2. The River Bann has a mean discharge rate of 92 m3/s. According to C. Michael Hogan, the Bann River Valley is a settlement area for some of the first human arrivals in Ireland after the most recent glacial retreat. The river has played an important part in the industrialisation in Northern Ireland, especially in the linen industry. Today salmon and eel fisheries are the most important economic features of the river. The river is often used as a dividing line between the eastern and western areas of Northern Ireland, often labelled the "Bann divide". Towns, councils and businesses "west of the Bann" are often seen as having less investment and government spending than those to the east. It is also seen as a religious, economic and political divide, with Catholics and Irish nationalists being in the majority to the west, and Ulster Protestants and unionists in the majority to the east; and with the financial and industrial capital of Greater Belfast to the east with the west of the Bann being more agricultural and rural.

The Quoile is a river in County Down, Northern Ireland.

Kinlough is a village in north County Leitrim. It lies between the Dartry Mountains and the Atlantic Ocean, and between the River Duff and the River Drowes, at the head of Lough Melvin. It borders counties Donegal and Fermanagh and is near Yeats Country. It lies 2.5 miles from Bundoran, County Donegal, and across Lough Melvin from Garrison, County Fermanagh.

Saul is a village in County Down, Northern Ireland, within the civil parish of Saul and Ballee.

Newry River and River Clanrye are names for one of the rivers of Ireland. The river passes through the city of Newry and empties into Carlingford Lough near Warrenpoint.

Garrison is a small village near Lough Melvin in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland. The Roogagh River runs through the village. In the 2001 Census it had a population of 357 people. It is situated within Fermanagh and Omagh district.

The River Blackwater or Ulster Blackwater is a river mainly in County Armagh and County Tyrone, Northern Ireland. It also forms part of the border between the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, flowing between Counties Tyrone and Monaghan, intersecting into County Monaghan briefly. Its source is to the north of Fivemiletown, County Tyrone. The river divides County Armagh from County Tyrone and also divides County Tyrone from County Monaghan.
The Carryduff River is a minor river in County Down, Northern Ireland. It is a direct tributary of the River Lagan and is not navigable.

The River Swilly is a river in County Donegal, Ireland, which flows in an eastern direction through Letterkenny. Letterkenny, the largest town in County Donegal, is built on the river and became the first crossing point on the river in the 17th century.

The Colebrooke River is a river in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland. Its source is in the Sliabh Beagh mountains where it is known as the Many Burns.
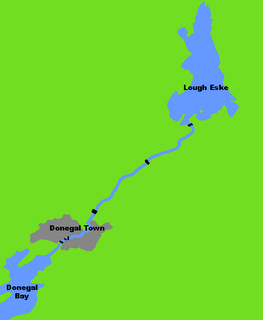
The River Eske is a river in County Donegal, Ireland. It begins at Lough Eske in the southeast of the county before flowing mainly westwards to the town of Donegal and into the Atlantic Ocean via Donegal Bay.

The River Roe is a river located in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It flows north from Glenshane in the Sperrin Mountains to Lough Foyle, via the settlements of Dungiven, Burnfoot, Limavady and Myroe. The River Roe's length is 34.25 miles (55.12 km)

The Boyle River is a river in Ireland. Forming part of the Shannon River Basin, it flows from Lough Gara on the Sligo/Roscommon border and thence through the town of Boyle to Lough Key. From there is continues eastwards through the village of Knockvicar to the River Shannon at Lough Drumharlow, near Carrick-on-Shannon.

Glenelly River is a river in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland. It flows westwards along the long linear Glenelly Valley to the south of Sawel Mountain, following one of the principal fault-lines in the Sperrin Mountains. The river meanders across a complex, undulating floodplain of alluvium and glacial moraine. The channel has often carved deep ridges within these soft deposits, creating steep, irregular mounds and pockets of peaty marsh on the valley floor. The otter has been recorded in the Glenelly River, which is important also for salmon and trout. The village of Plumbridge stands on the banks of the Glenelly River which flows on to join the Owenkillew River near Newtownstewart.

The Sillees River is located in south-western County Fermanagh. Its origins lie in Lough Ahork, which is located in Lough Navar Forest. From here it continues through Correl Glen, Derrygonnelly and the Boho countryside, passing through both Carran and Ross Loughs where it ends in Lower Lough Erne.

The River Moyola or Moyola River stretches for approximately 27 miles from the Sperrin Mountains to Lough Neagh. The Moyola starts a small river for the first few miles of its length and proceeds to expand to a medium-sized river and then to a large river for its last couple of miles before Lough Neagh. In ancient times, the River Moyola was known as the 'Bior', and served as the border between the Airgiallan kingdoms of Fir Li and Ui Tuirtri.

The River Derg is a small river in Ireland. The river has its source in the Lough Derg, in County Donegal, Republic of Ireland and it flows into County Tyrone, Northern Ireland east through Castlederg to join the River Strule forming the River Mourne. The upper reaches of the catchment are characterised by peatland, while the lower reaches flow predominantly through farmland. The River Derg's length is 28 miles (45 km).

The River Faughan is a river in northwest Northern Ireland.
The Tempo River is a small river in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland. The river rises near Dooneen Forest, flows through the town of Tempo, finally joining with the Colebrooke River before it enters Upper Lough Erne. The Tempo River locale has been designated as an Area of Special Scientific Interest in Northern Ireland.

















