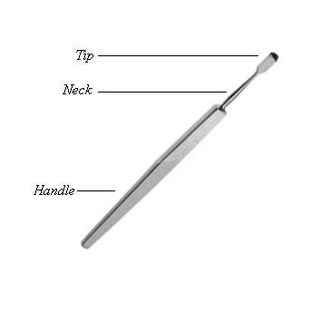
A rougine is an instrument used in Ophthalmology.

A rougine is an instrument used in Ophthalmology.
It consists of a small rectangular blade, with a curved cutting edge; one of its surfaces is beveled, the other is flat. It is connected to a handle by a narrow neck. [1] [2]
It is used when operating on the lacrimal sac, to separate it from the lacrimal fossa. [1] [2]

Ophthalmology is a clinical and surgical specialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. A former term is oculism.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic surgery or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa. Eye surgery is part of ophthalmology and is performed by an ophthalmologist or eye surgeon. The eye is a fragile organ, and requires due care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. It continues to be a widely practiced class of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems.

Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is the condition of having dry eyes. Symptoms include dryness in the eye, irritation, redness, discharge, blurred vision, and easily fatigued eyes. Symptoms range from mild and occasional to severe and continuous. Dry eye syndrome can lead to blurred vision, instability of the tear film, increased risk of damage to the ocular surface such as scarring of the cornea, and changes in the eye including the neurosensory system.
Dominique Anel, French surgeon, was born at Toulouse. Anel was a pupil of well-known French surgeons J. L. Petit (1674-1750) and Georges Mareschal (1658-1736). After studying at Montpellier and Paris, he served as surgeon-major in the French army in Alsace; then after two years at Vienna he went to Italy and served in the Austrian army. In 1710 he was teaching surgery in Rouen, whence he went to Genoa, and in 1716 he was practising in Paris.

In ophthalmology and optometry, a slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segment and posterior segment of the human eye, which includes the eyelid, sclera, conjunctiva, iris, natural crystalline lens, and cornea. The binocular slit-lamp examination provides a stereoscopic magnified view of the eye structures in detail, enabling anatomical diagnoses to be made for a variety of eye conditions. A second, hand-held lens is used to examine the retina.

Ophthalmology was one of the foremost branches in medieval Islamic medicine. The oculist or kahhal (کحال), a somewhat despised professional in Galen’s time, was an honored member of the medical profession by the Abbasid period, occupying a unique place in royal households. Medieval Islamic scientists considered it normal to combine theory and practice, including the crafting of precise instruments, and therefore found it natural to combine the study of the eye with the practical application of that knowledge. The specialized instruments used in their operations ran into scores. Innovations such as the “injection syringe”, a hollow needle, invented by Ammar ibn Ali of Mosul, which was used for the extraction by suction of soft cataracts, were quite common.

Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac, secondary to obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct at the junction of lacrimal sac. The term derives from the Greek dákryon (tear), cysta (sac), and -itis (inflammation). It causes pain, redness, and swelling over the inner aspect of the lower eyelid and epiphora. When nasolacrimal duct obstruction is secondary to a congenital barrier it is referred to as dacryocystocele. It is most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The most common complication is corneal ulceration, frequently in association with S. pneumoniae. The mainstays of treatment are oral antibiotics, warm compresses, and relief of nasolacrimal duct obstruction by dacryocystorhinostomy.

The lacrimal caruncle, or caruncula lacrimalis, is the small, pink, globular nodule at the inner corner of the eye. It consists of tissue types of neighbouring eye structures. It may suffer from lesions and allergic inflammation.
The Egmore Eye Hospital, officially the Regional Institute of Ophthalmology and Government Ophthalmic Hospital, is a public eye hospital in Chennai, India. Considered the oldest eye hospital in Asia, the institute was established in 1819 and is the second oldest hospital of its kind, next only to the Moorfields Eye Hospital in the United Kingdom.

Otto Heinrich Enoch Becker was a German ophthalmologist born near Ratzeburgin the Duchy of Holstein.
Krause's glands or Krause glands are small, mucous accessory lacrimal glands that are found underneath the eyelid where the upper and lower conjunctivae meet. Their ducts unite into a rather long sinus which open into the fornix conjunctiva. There are approximately forty Krause glands in the region of the upper eyelid, and around 6 to 8 in the region of the lower lid. The function of these glands are to produce tears which are secreted onto the surface of the conjunctiva.
Otto Schirmer was a German ophthalmologist from Greifswald.
Raman Malhotra is a British ophthalmologist and oculoplastic surgeon. He is a consultant ophthalmic surgeon and head of the Corneoplastic unit, Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead.

The accessory visual structures are the protecting and supporting structures (adnexa) of the eye, including the eyebrow, eyelids, and lacrimal apparatus. The eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes, lacrimal gland and drainage apparatus all play a crucial role with regards to globe protection, lubrication, and minimizing the risk of ocular infection. The adnexal structures also help to keep the cornea moist and clean.

Dacryoscintigraphy (DSG), also known as lacrimal scintigraphy, is a nuclear medicine technique for imaging the lacrimal apparatus. It is used to identify obstructions, for example in the lacrimal duct, nasal cavity or nasolacrimal duct.
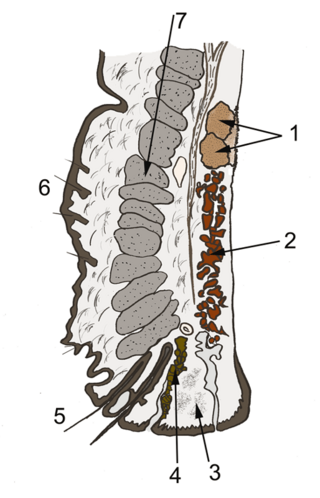
Krause's glands and Wolfring's glands are the accessory lacrimal glands of the lacrimal system of human eye. These glands are structurally and histologically similar to the main lacrimal gland. Glands of Krause are located in the stroma of the conjunctival fornix, and the glands of Wolfring are located along the orbital border of the tarsal plate. These glands are oval and display numerous acini. The acini are surrounded, sometimes incompletely, by a row of myoepithelial cells. Animal studies suggest that the ducts of Wolfring glands have a tortuous course and open onto the palpebral conjunctiva. Like the main lacrimal gland, the accessory lacrimal glands are also densely innervated, but they lack parasympathetic innervation. These glands are exocrine glands, responsible for the basal (unstimulated) secretion of the middle aqueous layer of the tear film. 20 to 40 glands of Krause are found in the upper fornix, and 6-8 glands appear in the lower fornix. There are usually 2 to 5 Ciaccio's glands, and are found along the superior tarsal border of the upper eyelid. Popov’s glands are located within the substance of the caruncle.
Tear break-up time (TBUT) also known as tear film break-up time (TFBUT) is the time taken for the first dry spot to appear on the cornea after a complete blink. TFBUT measurement is an easy and fast method used to assess the stability of tear film. It is a standard diagnostic procedure in the dry eye clinics. The volume of tear in the eye depends on two factors, drainage through the lacrimal passages and evaporation. Factors like decreased tear production, increased evaporation rate, tearfilm instability, tear hyperosmolarity, inflammations, ocular surface damages etc. can cause dryness to the eyes.
Mohammad Javed Ali is an Ophthalmic Plastics Surgeon, Dacryologist, and Clinician-scientist. He heads the Govindram Seksaria Institute of Dacryology, L. V. Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad and specializes in the science of tear ducts. Prof. Ali is also the Alumni chair of Ophthalmology at the L.V. Prasad Eye Institute and the current Editor-in-Chief of Seminars in Ophthalmology, Associate Editor of several major journals, including The Ocular Surface, Ophthalmic Research, Survey of Ophthalmology, and Current Eye Research. He holds several international professorships, including the Hong-Leong Professor at University of Singapore, Professor of Anatomy and Ophthalmology at the Friedrich Alexander University, Nuremberg, Germany, Professor, Wojskowy Instytut Medyczny at Warsaw, Honorary Professor at Krasonv Research Institute of Eye Diseases, Moscow, Adjunct Professor at University of Rochester, and Professor of Ophthalmology at Shanghai Jin Tao University, China.