There are many different surgical specialties, some of which require specific kinds of surgical instruments to perform.
General surgery is a specialty focused on the abdomen; the thyroid gland; diseases involving skin, breasts, and various soft tissues; trauma; peripheral vascular disease; hernias; and endoscopic procedures.
Instruments can be classified in many ways, but, broadly speaking, there are five kinds of instruments.
- Cutting and dissecting instruments
- Grasping or holding instruments
- Hemostatic instruments
- Retractors
- Tissue unifying instruments and materials
Instruments used in surgery are: [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [ excessive citations ]
| Instrument Name | Image | Brief description | Specific instruments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical cautery |  | Electrical surgical cauterization utilizes electricity in either a monopolar or bipolar format to burn soft tissue and control bleeding [12] |
|
| Curette | 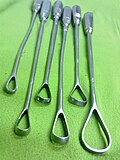 | For scraping or debriding biological tissue or debris in a biopsy, excision, or cleaning procedure | |
| Dermatome |  | Removes epidermis to graft over another area | |
| Dissecting forceps |  | Grasping and holding; usually used in skin closures or small wounds | Adson |
| Tissue forceps | 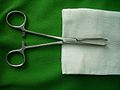 | Grasping and holding tissue | Allis |
| Penetrating towel clamp |  | Used to secure towels or reduce bone fragments | Backhaus penetrating towel clamp |
| Carmalt forceps | Hemostatic forceps | Kalabasa | |
| Cushing forceps | Grasping and holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps | |
| Dandy forceps | Hemostatic forceps | ||
| DeBakey forceps |  | Grasping and holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps designed for use on blood vessels, organs, or delicate tissue |
| Doyen intestinal clamp | Clamps and distractors | Non-crushing clamp designed for use on the intestines | |
| Kelly forceps |  | Hemostatic forceps | |
| Kocher forceps |  | Hemostatic forceps | |
| Mosquito forceps |  | Hemostatic forceps | |
| Hook | Retractor | ||
| Nerve hook | Retractor | ||
| Skin hook | Retractor | ||
| Lancet (scalpel) |  | Cutting | |
| Mammotome |  | ||
| Needle holder |  | Grasping and holding |
|
| Retractor | 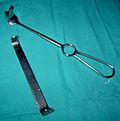 | Retractor | Handheld:
Self-retaining:
|
| Ultrasonic scalpel | Cutting | ||
| Laser scalpel |  | Cutting | |
| Scissors |  | Cutting and spreading | May be curved or straight |
| Speculum |  | Used to retract orifices |
|
| Suction tube and Yankeur suction tip |  | Accessories and implants | |
| Surgical elevator |  | ||
| Surgical hook |  | Retractor | |
| Surgical blade #15 |  | Used to cut vessels or make small incisions | |
| Surgical mesh |  | Accessories and implants | |
| Surgical needle | 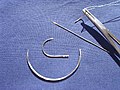 | Accessories and implants | |
| Surgical sponge | |||
| GIA stapler |  | Used to make a gastrointestinal anastamosis | Linear stapler |
| Surgical tray | |||
| Suture |  | ||
| Tongue depressor |  | ||
| Tonsillotome | |||
| Towel clamp |  | Clamp | |
| Towel forceps | Clamp | ||
| Backhaus towel forceps |  | ||
| Lorna towel clamp | Non-penatrating towel clamp | ||
| Tracheotome | |||
| Tissue expander | Accessories and implant | ||
| Subcutaneous inflatable balloon expander | Accessories and implants | ||
| Trephine |  | Cutting instrument | |
| Trocar |  | Access instrument. Used to create an opening into a space without opening the abdominal cavity. A camera is inserted through one to view the interior while instruments are inserted through the others to manipulate the organs. | |
| Ultrasonic energy device | Surgical device typically used to dissect tissue, but also seals small vessels and tissue bundles |