This is a list of instruments used in general in laboratories, including:
This is a list of instruments used in general in laboratories, including:
| Instrument | Uses |
|---|---|
| Test tube | |
| Folin-Wu tube | |
| Glass slide mycole and cover slips | in microscopy, serology, etc. as the solid backing on which test samples are |
| Petri dish | used for preparation of culture media and the culture of organisms they are in |
| Glass beaker | reagent storage |
| Glass flask | gastric acid, or other fluid titration |
| Pasteur pipette | for aspiration and addition of reagents |
| Graduated pipettes | for aspiration and addition of reagents, often of minuscule amounts of the material; used mainly in colorimetry |
| Syringes | |
| Disposable gloves | prevention of transmission of diseases (as long as not cut or perforated) to or from the user |
| Tourniquet | This is used to cause an artificial venous stasis by applying pressure through this rubber tube. This leads to engorgement of the veins, allowing them to be seen more easily. Used for intravenous injections and cannulation. |
| Microscope | used for visualising minute structures, including microbes |
| Bunsen burner or spirit lamps or candles | source of fire / heat |
| Ultracentrifuge | used to separate particles dispersed in a liquid according to their molecular mass |
| Electrophoresis apparatus | used to detect and classify serum proteins or proteins from any other source; also used for DNA separation |
| Chromatography: | |
| • Gas chromatography or Gas liquid chromatography (GLC) | |
| • Planar chromatography | |
| • Paper chromatography | |
| • Thin layer chromatography | |
| • Affinity chromatography | |
| • Ion exchange chromatography | |
| • Size exclusion chromatography | |
| • Countercurrent chromatography | |
| • Countercurrent chromatography | |
| • Hematology analyzer | It is simply known as Cell Counter. |
| • Semiauto analyzer | |
| • Reflotron | |
| Setup for radioimmunoassay or RIA | Previously this was widely used to detect various things in bold fluids like proteins (natural, infective, those produced by the body in reaction to disease, or cancer related), tumor markers, hormones, viruses (hepatitis, or HIV), etc. |
| Setup for enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) | It is presently widely used to detect various things in bold fluids like proteins (natural, infective, those produced by the body in reaction to disease, or cancer related), tumor markers, hormones, viruses (hepatitis, HIV), etc. It has replaced RIA. |
| Colorimeter | used in photochemical analysis and quantitative estimation of substances such as blood sugar, creatinine, and hemoglobin. |
| Burette | used to measure the amount of acid or alkali used in titration |
| General laboratory stands, racks, filter paper, reagents, etc. | |
| Induction coils | as a source of high voltage electricity |
| Cathode ray oscilloscope | ' |
| Recording kymograph | historically, used in human or animal experiments to measure and record data |
| Long extension kymograph | historically, used in or human animal experiments to measure and record data |
| Surface plasmon resonance | Label-free detection of molecule binding. Used to determine kinetic constants of the interaction (ka, kd, KD). Can also be used for thermodynamic analysis. |

A pipette is a laboratory tool commonly used in chemistry, biology and medicine to transport a measured volume of liquid, often as a media dispenser. Pipettes come in several designs for various purposes with differing levels of accuracy and precision, from single piece glass pipettes to more complex adjustable or electronic pipettes. Many pipette types work by creating a partial vacuum above the liquid-holding chamber and selectively releasing this vacuum to draw up and dispense liquid. Measurement accuracy varies greatly depending on the instrument.
Colorimetry is "the science and technology used to quantify and describe physically the human color perception". It is similar to spectrophotometry, but is distinguished by its interest in reducing spectra to the physical correlates of color perception, most often the CIE 1931 XYZ color space tristimulus values and related quantities.
Fisher Scientific International, Inc. was a laboratory supply and biotechnology company that provided products and services to the global scientific research and clinical laboratory markets until its merger with Thermo Electron in 2006, after which it became Thermo Fisher Scientific. The company offered products and services to over 350,000 customers located in approximately 150 countries including pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, secondary and higher education institutions, hospitals and medical research institutions, and quality control, process control and research and development laboratories.
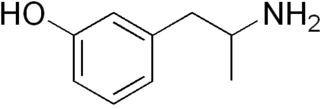
Gepefrine, also known as 3-hydroxyamphetamine, meta-hydroxyamphetamine, and α-methyl-meta-tyramine, is an antihypotensive or sympathomimetic agent of the amphetamine family that is marketed in certain European countries.
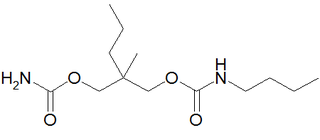
Tybamate is an anxiolytic of the carbamate family. It is a prodrug for meprobamate in the same way as the better known drug carisoprodol. It has liver enzyme inducing effects similar to those of phenobarbital but much weaker.
The Sir William Dunn School of Pathology is a department within the University of Oxford. Its research programme includes the cellular and molecular biology of pathogens, the immune response, cancer and cardiovascular disease. It teaches undergraduate and graduate courses in the medical sciences.
Instruments used specially in pathology are as follows:
Instruments used specially in radiology are as follows:

Stephen Stanley Sternberg was an American surgical pathologist, who worked at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center for his entire career.
A volumetric pipette, bulb pipette, or belly pipette allows extremely accurate measurement of the volume of a solution. It is calibrated to deliver accurately a fixed volume of liquid.
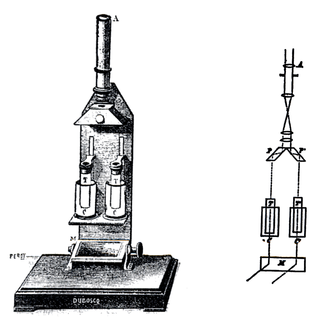
In physical and analytical chemistry, colorimetry or colourimetry is a technique used to determine the concentration of colored compounds in solution. A colorimeter is a device used to test the concentration of a solution by measuring its absorbance of a specific wavelength of light.
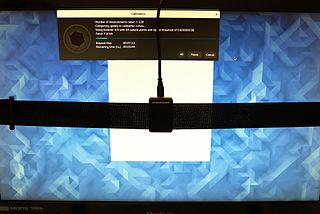
A tristimulus colorimeter, colloquially shortened to colorimeter, is used in digital imaging to profile and calibrate output devices. It takes a limited number of wideband spectral energy readings along the visible spectrum by using filtered photodetectors; e.g. silicon photodiodes.
A colorimeter is a device used in colorimetry that measures the absorbance of particular wavelengths of light by a specific solution. It is commonly used to determine the concentration of a known solute in a given solution by the application of the Beer–Lambert law, which states that the concentration of a solute is proportional to the absorbance.

Demexiptiline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in France for the treatment of depression. It acts primarily as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor similarly to desipramine.

Murshidabad Medical College and Hospital is a government-run medical college located in Berhampore, Murshidabad district, West Bengal, India. This college was established in 2012, mainly it serves the people of district Murshidabad, Birbhum and the northern part of Nadia by providing preventive, diagnostic and curative services.
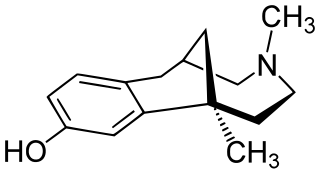
Eptazocine (Sedapain) is an opioid analgesic which was introduced in Japan by Morishita in 1987. It acts as a mixed κ-opioid receptor agonist and μ-opioid receptor antagonist.

PNU-142633 is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of migraine. It exerts its effect as a selective, high affinity 5-HT1D receptor antagonist. PNU-142633 is well tolerated after oral administration.
Thoothukudi Medical College, also known as TKMC, or Government Medical College Thoothukudi, is a medical institution in South India, located in the city of Thoothukudi, in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. The college is affiliated to The Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University and is recognised by the National Medical Commission of India and World Health Organization.

Khairpur Medical College is an 8th public medical institution located in the city of Khairpur, Sindh, Pakistan.