An Erlenmeyer flask, also known as a conical flask or a titration flask, is a type of laboratory flask with a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck. It is named after the German chemist Emil Erlenmeyer (1825–1909), who invented it in 1860.

A vacuum flask is an insulating storage vessel that slows the speed at which its contents change in temperature. It greatly lengthens the time over which its contents remain hotter or cooler than the flask's surroundings by trying to be as adiabatic as possible. Invented by Sir James Dewar in 1892, the vacuum flask consists of two flasks, placed one within the other and joined at the neck. The gap between the two flasks is partially evacuated of air, creating a near-vacuum which significantly reduces heat transfer by conduction or convection. When used to hold cold liquids, this also virtually eliminates condensation on the outside of the flask.
A monolayer is a single, closely packed layer of entities, commonly atoms or molecules. Monolayers can also be made out of cells. Self-assembled monolayers form spontaneously on surfaces. Monolayers of layered crystals like graphene and molybdenum disulfide are generally called 2D materials.

A volumetric flask is a piece of laboratory apparatus, a type of laboratory flask, calibrated to contain a precise volume at a certain temperature. Volumetric flasks are used for precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions. These flasks are usually pear-shaped, with a flat bottom, and made of glass or plastic. The flask's mouth is either furnished with a plastic snap/screw cap or fitted with a joint to accommodate a PTFE or glass stopper. The neck of volumetric flasks is elongated and narrow with an etched ring graduation marking. The marking indicates the volume of liquid contained when filled up to that point. The marking is typically calibrated "to contain" at 20 °C and indicated correspondingly on a label. The flask's label also indicates the nominal volume, tolerance, precision class, relevant manufacturing standard and the manufacturer's logo. Volumetric flasks are of various sizes, containing from a fraction of a milliliter to hundreds of liters of liquid.

A flagon is a large leather, metal, glass, plastic or ceramic vessel, used for drink, whether this be water, ale, or another liquid. A flagon is typically of about 2 imperial pints (1.1 L) in volume, and it has either a handle, or one or two rings at the neck. Sometimes the neck has a large flange at the top rather than rings. The neck itself may or may not be formed into one, two or three spouts. The name comes from the same origin as the word "flask".

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature . Substances usually contract with decreasing temperature, with rare exceptions within limited temperature ranges.

Laboratory flasks are vessels or containers that fall into the category of laboratory equipment known as glassware. In laboratory and other scientific settings, they are usually referred to simply as flasks. Flasks come in a number of shapes and a wide range of sizes, but a common distinguishing aspect in their shapes is a wider vessel "body" and one narrower tubular sections at the top called necks which have an opening at the top. Laboratory flask sizes are specified by the volume they can hold, typically in metric units such as milliliters or liters. Laboratory flasks have traditionally been made of glass, but can also be made of plastic.

In biology, a subculture is either a new cell culture or a microbiological culture made by transferring some or all cells from a previous culture to fresh growth medium. This action is called subculturing or passaging the cells. Subculturing is used to prolong the lifespan and/or increase the number of cells or microorganisms in the culture.

In laboratory equipment, a beaker is generally a cylindrical container with a flat bottom. Most also have a small spout to aid pouring, as shown in the picture. Beakers are available in a wide range of sizes, from one milliliter up to several liters. A beaker is distinguished from a flask by having straight rather than sloping sides. The exception to this definition is a slightly conical-sided beaker called a Philips beaker. The beaker shape in general drinkware is similar.

Round-bottom flasks are types of flasks having spherical bottoms used as laboratory glassware, mostly for chemical or biochemical work. They are typically made of glass for chemical inertness; and in modern days, they are usually made of heat-resistant borosilicate glass. There is at least one tubular section known as the neck with an opening at the tip. Two- or three-necked flasks are common as well. Round bottom flasks come in many sizes, from 5 mL to 20 L, with the sizes usually inscribed on the glass. In pilot plants even larger flasks are encountered.

The surface-area-to-volume ratio or surface-to-volume ratio is the ratio between surface area and volume of an object or collection of objects.

Ground glass joints are used in laboratories to quickly and easily fit leak-tight apparatus together from interchangeable commonly available parts. For example, a round bottom flask, Liebig condenser, and oil bubbler with ground glass joints may be rapidly fitted together to reflux a reaction mixture. This is a large improvement compared with older methods of custom-made glassware, which was time-consuming and expensive, or the use of less chemical resistant and heat resistant corks or rubber bungs and glass tubes as joints, which took time to prepare as well.

Acetone–butanol–ethanol (ABE) fermentation, also known as the Weizmann process, is a process that uses bacterial fermentation to produce acetone, n-butanol, and ethanol from carbohydrates such as starch and glucose. It was developed by chemist Chaim Weizmann and was the primary process used to produce acetone, which was needed to make cordite, a substance essential for the British war industry during World War I.
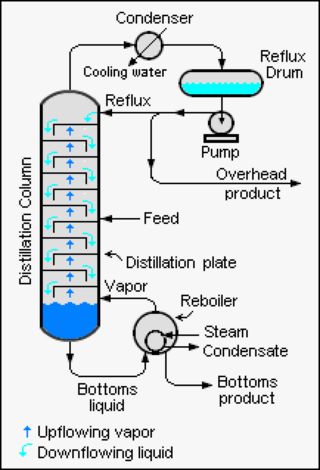
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions over a long period of time.
Cast iron pipe is pipe made predominantly from gray cast iron. It was historically used as a pressure pipe for transmission of water, gas and sewage, and as a water drainage pipe during the 17th, 18th, 19th and 20th centuries.

Ras Beirut is an upscale residential neighborhood in Beirut, Lebanon. It has a mixed population of Christians, Muslims and Druze individuals. Ras Beirut is associated with intersect interactions and relations in every-day life.
Auguste Fernbach was a French biologist.
Fernbach is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:

A cell suspension or suspension culture is a type of cell culture in which single cells or small aggregates of cells are allowed to function and multiply in an agitated growth medium, thus forming a suspension. Suspension culture is one of the two classical types of cell culture, the other being adherent culture. The history of suspension cell culture closely aligns with the history of cell culture overall, but differs in maintenance methods and commercial applications. The cells themselves can either be derived from homogenized tissue or from heterogenous cell solutions. Suspension cell culture is commonly used to culture nonadhesive cell lines like hematopoietic cells, plant cells, and insect cells. While some cell lines are cultured in suspension, the majority of commercially available mammalian cell lines are adherent. Suspension cell cultures must be agitated to maintain cells in suspension, and may require specialized equipment and flasks. These cultures need to be maintained with nutrient containing media and cultured in a specific cell density range to avoid cell death.

A Roux culture bottle, or simply Roux bottle, is a type of laboratory glassware used in biology and related sciences to grow microorganisms or tissue cells. It consists of a bottle of transparent glass or plastic with two closely spaced flat, rectangular, parallel faces and a short neck; of such a design that the bottle can be laid down sideways, on one of those two faces, even when unstoppered and partially filled with a culture medium. This goal is achieved by having the neck narrowed, offset, partially blocked, or canted (tilted). The item is also generically called cell culture bottle or tissue culture (TC) bottle, and flask may be used instead of "bottle".