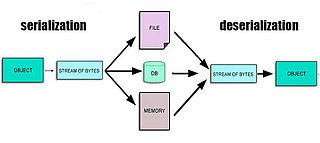
In computing, serialization is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later. When the resulting series of bits is reread according to the serialization format, it can be used to create a semantically identical clone of the original object. For many complex objects, such as those that make extensive use of references, this process is not straightforward. Serialization of objects does not include any of their associated methods with which they were previously linked.
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a method to describe and exchange graph data. It was originally designed as a data model for metadata by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). It provides a variety of syntax notations and formats, of which the most widely used is Turtle.

A topic map is a standard for the representation and interchange of knowledge, with an emphasis on the findability of information. Topic maps were originally developed in the late 1990s as a way to represent back-of-the-book index structures so that multiple indexes from different sources could be merged. However, the developers quickly realized that with a little additional generalization, they could create a meta-model with potentially far wider application. The ISO/IEC standard is formally known as ISO/IEC 13250:2003.
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve information. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL).
JSON is an open standard file format and data interchange format that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of name–value pairs and arrays. It is a commonly used data format with diverse uses in electronic data interchange, including that of web applications with servers.
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets.
XML Information Set is a W3C specification describing an abstract data model of an XML document in terms of a set of information items. The definitions in the XML Information Set specification are meant to be used in other specifications that need to refer to the information in a well-formed XML document.
The REWERSE Rule Markup Language (R2ML) is developed by the REWERSE Working Group I1 for the purpose of rules interchange between different systems and tools.

RDFLib is a Python library for working with RDF, a simple yet powerful language for representing information. This library contains parsers/serializers for almost all of the known RDF serializations, such as RDF/XML, Turtle, N-Triples, & JSON-LD, many of which are now supported in their updated form. The library also contains both in-memory and persistent Graph back-ends for storing RDF information and numerous convenience functions for declaring graph namespaces, lodging SPARQL queries and so on. It is in continuous development with the most recent stable release, rdflib 6.1.1 having been released on 20 December 2021. It was originally created by Daniel Krech with the first release in November, 2002.
In computing, Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML.
The term round-trip is used in document conversion particularly involving markup languages such as XML and SGML. A successful round-trip consists of converting a document in format A (docA) to one in format B (docB) and then back again to format A (docA′). If docA and docA′ are identical then there has been no information loss and the round-trip has been successful. More generally it means converting from any data representation and back again, including from one data structure to another.
Data exchange is the process of taking data structured under a source schema and transforming it into a target schema, so that the target data is an accurate representation of the source data. Data exchange allows data to be shared between different computer programs.
In computer science, marshalling or marshaling is the process of transforming the memory representation of an object into a data format suitable for storage or transmission, especially between different runtimes. It is typically used when data must be moved between different parts of a computer program or from one program to another.

The Journal Article Tag Suite (JATS) is an XML format used to describe scientific literature published online. It is a technical standard developed by the National Information Standards Organization (NISO) and approved by the American National Standards Institute with the code Z39.96-2012.
Pandoc is a free-software document converter, widely used as a writing tool and as a basis for publishing workflows. It was created by John MacFarlane, a philosophy professor at the University of California, Berkeley.
In markup languages and the digital humanities, overlap occurs when a document has two or more structures that interact in a non-hierarchical manner. A document with overlapping markup cannot be represented as a tree. This is also known as concurrent markup. Overlap happens, for instance, in poetry, where there may be a metrical structure of feet and lines; a linguistic structure of sentences and quotations; and a physical structure of volumes and pages and editorial annotations.
Shapes Constraint Language (SHACL) is a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard language for describing Resource Description Framework (RDF) graphs. SHACL has been designed to enhance the semantic and technical interoperability layers of ontologies expressed as RDF graphs.


