| rsaOG RNA | |
|---|---|
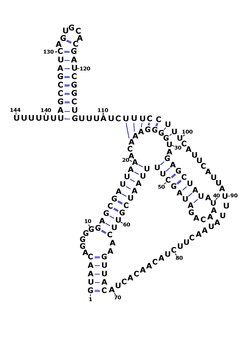 The consensus secondary structure of RsaOG showing its pseudoknot, created in Varna. [1] Boundaries were determined by RACE mapping in Staphylococcus aureus N315 . [2] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RsaOG |
| Rfam | RF01775 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | sRNA |
| Domain | Staphylococcus |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
RsaOG (an acronym for RNA S. aureus Orsay G) [2] is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in the pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus N315 using a large-scale computational screening based on phylogenetic profiling. [3] It was first identified, but not named, in 2005. [4] RsaOG has since been identified in other strains of Staphylococcus aureus under the name of RsaI, [5] it has also been discovered in other members of the Staphylococcus genus (such as Staphylococcus carnosus ) but in no other bacteria. [2]
Contents
The RsaOG gene is conserved in all Staphylococcaceae sequenced genomes, its secondary structure contains two highly conserved unpaired sequences which have the ability to form a pseudoknot. [2] Northern blot experiments show that RsaOG is expressed in several S. aureus strains. [3] [5] Mapping of RsaOG ends indicates a size of 146 nucleotides in S. aureus. [5] RsaOG ncRNA is thought to have trans-acting regulatory functions, possibly on fine-tuning toxin production or aiding with invasion. [2]