
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions. Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion. Heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid, which in turn runs through steam turbines. These either drive a ship's propellers or turn electrical generators' shafts. Nuclear generated steam in principle can be used for industrial process heat or for district heating. Some reactors are used to produce isotopes for medical and industrial use, or for production of weapons-grade plutonium. As of 2022, the International Atomic Energy Agency reports there are 422 nuclear power reactors and 223 nuclear research reactors in operation around the world.
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238, uranium-235, and uranium-234. 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature that is fissile with thermal neutrons.

The pebble-bed reactor (PBR) is a design for a graphite-moderated, gas-cooled nuclear reactor. It is a type of very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR), one of the six classes of nuclear reactors in the Generation IV initiative.

The Pebble Bed Modular Reactor (PBMR) is a particular design of pebble bed reactor developed by South African company PBMR (Pty) Ltd from 1994 until 2009. PBMR facilities include gas turbine and heat transfer labs at the Potchefstroom Campus of North-West University, and at Pelindaba, a high pressure and temperature helium test rig, as well as a prototype fuel fabrication plant. A planned test reactor at Koeberg Nuclear Power Station was not built.

The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is India's premier nuclear research facility, headquartered in Trombay, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It was founded by Homi Jehangir Bhabha as the Atomic Energy Establishment, Trombay (AEET) in January 1954 as a multidisciplinary research program essential for India's nuclear program. It operates under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India.

Aqueous homogeneous reactors (AHR) is a two (2) chamber reactor consisting of an interior reactor chamber and an outside cooling and moderating jacket chamber. They are a type of nuclear reactor in which soluble nuclear salts are dissolved in water. The fuel is mixed with heavy or light water which partially moderates and cools the reactor. The outside layer of the reactor has more water which also partially cools and acts as a moderator,. The water can be either heavy water or ordinary (light) water, which slows neutrons and helps facilitate a stable reaction, both of which need to be very pure.
Generation IVreactors are nuclear reactor design technologies that are envisioned as successors of generation III reactors. The Generation IV International Forum (GIF) – an international organization that coordinates the development of generation IV reactors – specifically selected six reactor technologies as candidates for generation IV reactors. The designs target improved safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost. The World Nuclear Association in 2015 suggested that some might enter commercial operation before 2030.

A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is a type of gas-cooled nuclear reactor which use uranium fuel and graphite moderation to produce very high reactor core output temperatures. All existing HTGR reactors use helium coolant. The reactor core can be either a "prismatic block" or a "pebble-bed" core. China Huaneng Group currently operates HTR-PM, a 250 MW HTGR power plant in Shandong province, China.
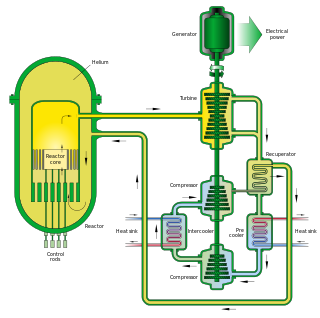
The gas-cooled fast reactor (GFR) system is a nuclear reactor design which is currently in development. Classed as a Generation IV reactor, it features a fast-neutron spectrum and closed fuel cycle for efficient conversion of fertile uranium and management of actinides. The reference reactor design is a helium-cooled system operating with an outlet temperature of 850 °C (1,560 °F) using a direct Brayton closed-cycle gas turbine for high thermal efficiency. Several fuel forms are being considered for their potential to operate at very high temperatures and to ensure an excellent retention of fission products: composite ceramic fuel, advanced fuel particles, or ceramic clad elements of actinide compounds. Core configurations are being considered based on pin- or plate-based fuel assemblies or prismatic blocks, which allows for better coolant circulation than traditional fuel assemblies.

The THTR-300 was a thorium cycle high-temperature nuclear reactor rated at 300 MW electric (THTR-300) in Hamm-Uentrop, Germany. It started operating in 1983, synchronized with the grid in 1985, operated at full power in February 1987 and was shut down September 1, 1989. The THTR-300 served as a prototype high-temperature reactor (HTR) to use the TRISO pebble fuel produced by the AVR, an experimental pebble bed operated by VEW. The THTR-300 cost €2.05 billion and was predicted to cost an additional €425 million through December 2009 in decommissioning and other associated costs. The German state of North Rhine Westphalia, Federal Republic of Germany, and Hochtemperatur-Kernkraftwerk GmbH (HKG) financed the THTR-300’s construction.
The Institute of Nuclear and New Energy Technology is an energy research institute located in Tsinghua University, Beijing, China. The current Institute director is Zhang Zuoyi (张作义).

Dragon was an experimental high temperature gas-cooled reactor at Winfrith in Dorset, England, operated by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA). Its purpose was to test fuel and materials for the European High Temperature Reactor programme, which was exploring the use of tristructural-isotropic (TRISO) fuel and gas cooling for future high-efficiency reactor designs. The project was built and managed as an Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development/Nuclear Energy Agency international project. In total, 13 countries were involved in its design and operation during the project lifetime.
There are two nuclear research reactors that serve the Texas A&M University Nuclear Science Center. The older of the two is the AGN-201M model, a low-power teaching reactor. The newer reactor, the TRIGA Mark I, is focused strongly towards research.

HTR-10 is a 10 MWt prototype high-temperature gas-cooled, pebble-bed reactor at Tsinghua University in China. Construction began in 1995, achieving its first criticality in December 2000, and was operated in full power condition in January 2003.

The AVR reactor was a prototype pebble-bed reactor, located immediately adjacent to Jülich Research Centre in West Germany, constructed in 1960, grid connected in 1967 and shut down in 1988. It was a 15 MWe, 46 MWt test reactor used to develop and test a variety of fuels and machinery.
A gas-cooled reactor (GCR) is a nuclear reactor that uses graphite as a neutron moderator and a gas as coolant. Although there are many other types of reactor cooled by gas, the terms GCR and to a lesser extent gas cooled reactor are particularly used to refer to this type of reactor.

Rainer Moormann is a German chemist and nuclear whistleblower. He grew up in Osnabrück. After finishing highschool he studied physical chemistry in Braunschweig and received a doctor's degree with Raman spectroscopic and theoretical investigations on hydrogen bonds in liquids.
The HTR-PM is a Chinese small modular nuclear reactor. It is a high-temperature gas-cooled (HTGR) pebble-bed generation IV reactor based on the German AVR design. The technology is intended to replace coal-fired power plants in China's interior, in line with the country's plan to reach carbon neutrality by 2060.
Shidao Bay Nuclear Power Plant, commonly known as Shidaowan, is a nuclear power plant in Shandong province, China. The site is located near the Xiqianjia village in Ningjin subdistrict, Rongcheng, Weihai, Shandong. The plant is located about 23 kilometres (14 mi) south of Rongcheng City, 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) northwest of Shidao, and 68 kilometres (42 mi) southeast of Weihai City.












