Related Research Articles

The Lenape, also called the Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada.
The Ramapough Mountain Indians, known also as the Ramapough Lenape Nation or Ramapough Lunaape Munsee Delaware Nation or Ramapo Mountain people, are a New Jersey state-recognized tribe based in Mahwah. They have approximately 5,000 members living in and around the Ramapo Mountains of Bergen and Passaic counties in northern New Jersey and Rockland County in southern New York, about 25 miles (40 km) from New York City.

European colonization of New Jersey started soon after the 1609 exploration of its coast and bays by Henry Hudson. Dutch and Swedish colonists settled parts of the present-day state as New Netherland and New Sweden.
The Nanticoke Lenni-Lenape Tribal Nation is a tribal confederation of Nanticoke of the Delmarva Peninsula and the Lenape of southern New Jersey and northern Delaware. They are recognized by the state of New Jersey, having reorganized and maintained elected governments since the 1970s. They are not a federally recognized tribe.
The Esopus Wars were two conflicts between the Esopus tribe of Lenape Natives (Delaware) and New Netherlander colonists during the latter half of the 17th century in Ulster County, New York. The first battle was instigated by settlers; the second war was the continuation of a grudge on the part of the Esopus tribe.

Kieft's War (1643–1645), also known as the Wappinger War, was a conflict between the colonial province of New Netherland and the Wappinger and Lenape Indians in what is now New York and New Jersey. It is named for Director-General of New Netherland Willem Kieft, who had ordered an attack without the approval of his advisory council and against the wishes of the colonists. Dutch colonists attacked Lenape camps and massacred the inhabitants, which encouraged unification among the regional Algonquian tribes against the Dutch and precipitated waves of attacks on both sides. This was one of the earliest conflicts between settlers and Indians in the region. The Dutch West India Company was displeased with Kieft and recalled him, but he died in a shipwreck while returning to the Netherlands; Peter Stuyvesant succeeded him in New Netherland. Numerous Dutch settlers returned to the Netherlands because of the continuing threat from the Algonquians, and growth slowed in the colony.

The Wappinger were an Eastern Algonquian Munsee-speaking Native American people from what is now southern New York and western Connecticut.

Pavonia was the first European settlement on the west bank of the North River that was part of the seventeenth-century province of New Netherland in what would become the present Hudson County, New Jersey.

Vriessendael was a patroonship on the west bank of the Hudson River in New Netherland, the seventeenth century North American colonial province of the Dutch Empire. The homestead or plantation was located on a tract of about 500 acres (2.0 km2) about an hour's walk north of Communipaw at today's Edgewater. It has also been known as Tappan, which referred to the wider region of the New Jersey Palisades, rising above the river on both sides of the New York/New Jersey state line, and to the indigenous people who lived there and were part of wider group known as Lenape. It was established in 1640 by David Pietersen de Vries, a Dutch sea captain, explorer, and trader who had also established settlements at the Zwaanendael Colony and on Staten Island. The name can roughly be translated as De Vries' Valley. De Vries also owned flatlands along the Hackensack River, in the area named by the Dutch settlers Achter Col. Parts of Vriessendael were destroyed in 1643 in reprisal for the slaughter of Tappan and Wecquaesgeek Native Americans who had taken refuge at Pavonia and Corlears Hook. The patroon's relatively good relations with the Lenape prevented the murder of the plantation's residents, who were able to seek sanctuary in the main house, and later flee to New Amsterdam. The incident was one of the first of many to take place during Kieft's War, a series of often bloody conflicts with bands of Lenape, who had united in face of attacks ordered by the Director of New Netherland.
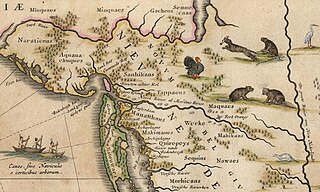
Bergen was a part of the 17th century province of New Netherland, in the area in northeastern New Jersey along the Hudson and Hackensack Rivers that would become contemporary Hudson and Bergen Counties. Though it only officially existed as an independent municipality from 1661, with the founding of a village at Bergen Square, Bergen began as a factory at Communipaw circa 1615 and was first settled in 1630 as Pavonia. These early settlements were along the banks of the North River across from New Amsterdam, under whose jurisdiction they fell.
Oratam was sagamore, or sachem, of the Hackensack Indians living in northeastern New Jersey during the period of early European colonization in the 17th century. Documentation shows that he lived an unusually long life and was quite influential among indigenous and immigrant populations.
Hackensack was the exonym given by the Dutch colonists to a band of the Lenape, or Lenni-Lenape, a Native American tribe. The name is a Dutch derivation of the Lenape word for what is now the region of northeastern New Jersey along the Hudson and Hackensack rivers. While the Lenape people occupied much of the mid-Atlantic area, Europeans referred to small groups of native people by the names associated with the places where they lived.

The Tappan were a Lenape people who inhabited the region radiating from Hudson Palisades and New York – New Jersey Highlands at the time of European colonialization in the 17th century.
The Acquackanonk were a Lenape group whose territory was on the Passaic River in northern New Jersey. They spoke the same dialect (Unami) and shared the same totem (turtle) as the neighboring Hackensack, Tappan and Rumachenanck . It may mean a place in a rapid stream where fishing is done with a net. Alternatively, at the lamprey stream from contemporary axkwaakahnung Lastly it may mean where gum blocks were made for pounding corn. Ackquekenon was spelling used by European explorer Jasper Danckaerts in 1679.
The Navesink, or Navisink, were a group of Lenape who inhabited the Raritan Bayshore near Sandy Hook and Mount Mitchill in eastern New Jersey in the United States.

New Netherlanders, also known as the Holland Dutch, were residents of New Netherland, the seventeenth-century colonial outpost of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the northeastern coast of North America, centered on the Hudson River and New York Bay, and in the Delaware Valley.

The Esopus was a tribe of Lenape (Delaware) Native Americans who were native to the Catskill Mountains of what is now the Hudson Valley. Their lands included modern-day Ulster and Sullivan counties.
The Pompton or Pamapon people were a sub-tribe of Algonquian-speaking Native Americans, who once lived northern New Jersey. The Pompton historically lived along Pompton and Pequannock Rivers, near what is now Paterson, New Jersey, but they were forced out of New Jersey after their lands had been taken without compensation by European colonists.
References
- ↑ external.oneonta.edu/cooper/susan/hudson.html
- ↑ Wright, Kevin W. "THE INDIGENOUS POPULATION OF BERGEN COUNTY". Bergen County Historical Society. Archived from the original on 2019-01-20. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ↑ Indian Tribes of Hudson's River; Ruttenber,E.M.; Hope Farm Press, 3rd ed, 2001, ISBN 0-910746-98-2
- ↑ Tompkins, Arthur S. "Historical Records to the Close of the 19th Century of Rockland County, NY" (PDF). Van Deusen and Joyce. Archived from the original on October 18, 2018. Retrieved 2013-03-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Documents relative to the colonial history of the State of New York" . Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ Indian Tribes of Hudson's River; Ruttenber,E.M.; Hope Farm Press, 3rd ed, 2001, ISBN 0-910746-98-2
- ↑ Ruttenber, E.M. (1872). History of the Indian Tribes of Hudson's River: Their Origin, Manners and Customs, Tribal and Sub-tribal Organizations, Wars, Treaties, Etc. J.Munsell. Retrieved 2013-03-10.