| C141 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | June 23, 1975 |
| Date in force | November 24, 1977 |
| Classification | Collective Bargaining and Agreements Freedom of Association |
| Subject | Freedom of Association, Collective Bargaining, and Industrial Relations |
| Previous | Paid Educational Leave Convention, 1974 |
| Next | Human Resources Development Convention, 1975 |
Rural Workers' Organisations Convention, 1975 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1975:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to organisations of rural workers and their role in economic and social development, ...
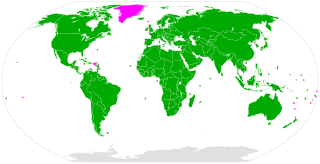
As of 2022, the convention has been ratified by 41 states.
| Country | Date |
|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 16 May 1979 |
| Albania | 18 August 2004 |
| Austria | 18 September 1978 |
| Belgium | 19 December 2003 |
| Belize | 22 June 1999 |
| Brazil | 27 September 1994 |
| Burkina Faso | 25 August 1997 |
| Costa Rica | 23 July 1991 |
| Cuba | 14 April 1977 |
| Cyprus | 28 June 1977 |
| Denmark | 6 June 1978 |
| Ecuador | 26 October 1977 |
| El Salvador | 15 June 1995 |
| Finland | 14 September 1977 |
| France | 10 September 1984 |
| Germany | 5 December 1978 |
| Greece | 17 October 1989 |
| Guatemala | 13 June 1989 |
| Guyana | 10 January 1983 |
| Hungary | 4 January 1994 |
| India | 18 August 1977 |
| Israel | 21 June 1979 |
| Italy | 18 October 1979 |
| Kenya | 9 April 1979 |
| Mali | 12 June 1995 |
| Malta | 9 June 1988 |
| Mexico | 28 June 1978 |
| Republic of Moldova | 4 April 2003 |
| Netherlands | 26 January 1977 |
| Nicaragua | 1 October 1981 |
| North Macedonia | 2 March 2018 |
| Norway | 24 November 1976 |
| Philippines | 18 June 1979 |
| Poland | 29 November 1991 |
| Spain | 28 April 1978 |
| Sweden | 19 July 1976 |
| Switzerland | 23 May 1977 |
| United Kingdom | 15 February 1977 |
| Uruguay | 19 June 1989 |
| Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela | 5 July 1983 |
| Zambia | 4 December 1978 |

The International Maritime Organization is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 17 March 1958. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, IMO currently has 175 Member States and three Associate Members.

The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest specialised agencies of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.

The International Confederation of Free Trade Unions (ICFTU) was an international trade union. It came into being on 7 December 1949 following a split within the World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU), and was dissolved on 31 October 2006 when it merged with the World Confederation of Labour (WCL) to form the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC).
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.

The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of October 2022 in 58 countries.
The Freedom of Association and Protection of the Right to Organise Convention (1948) No 87 is an International Labour Organization Convention, and one of eight conventions that form the core of international labour law, as interpreted by the Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work.
The Right to Organise and Collective Bargaining Convention (1949) No 98 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Migration for Employment Convention (Revised), 1949 is an International Labour Organization Convention for migrant workers.
Migrant Workers Convention, 1975, or Convention concerning Migrations in Abusive Conditions and the Promotion of Equality of Opportunity and Treatment of Migrant Workers is an International Labour Organization Convention for the rights of migrant workers. However unlike the United Nations Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families, there are restrictions of migrant worker to be applied on Article 11.
Private Employment Agencies Convention, 1997 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Colombia is a sovereign state situated in South America. It has been a member of the United Nations since 5 November 1945, and is party to a variety of international agreements concerning human rights. It also has a series of domestic laws concerning the protection of human rights. However, Colombia's human rights record often contradicts directly with the laws and agreements to which it is bound; Colombia was referred to as the country with the "worst human rights record in the western hemisphere," by HRW in 2007. The same was said of Guatemala in 1998, as well as Cuba in 2012 and Venezuela today. In the UK Foreign Office annual human rights report for 2010, Colombia features as one of 20 "Countries of Concern".
Trade unions in Laos have been active in the country since at least the mid-20th Century.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 91 per cent).
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.
The Conservative Women's Organisation (CWO) represents the female members of the Conservative Party in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
The right to sit refers to laws or policies granting workers the right to be granted suitable seating at the workplace. Jurisdictions that have enshrined "right to sit" laws or policies include the United Kingdom, Jamaica, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Uganda, Lesotho, Malaysia, Brazil, Israel, Ireland, the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar and Montserrat. Almost all states of the United States and Australia, as well as the majority of Canadian provinces passed right to sit legislation for women workers between 1881 and 1917. US states with current right to sit legislation include California, Florida, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. A right to sit provision is included in the International Labour Organization's Hygiene Convention, 1964; the convention being ratified by 51 countries as of 2014. Local jurisdictions with right to sit laws include Portland, Oregon, St. Louis, Missouri and London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Some jurisdictions, such as Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Idaho, Kentucky, Maine, Michigan, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, Quebec, and Washington, D.C. have revoked their right to sit laws. Many right to sit laws originally contained gendered language specifying women workers only. Some jurisdictions maintain gendered laws, but many jurisdictions have amended their right to sit laws to be gender neutral.