Dimanganese decacarbonyl, which has the chemical formula Mn2(CO)10, is a binary bimetallic carbonyl complex centered around the first row transition metal manganese. The first reported synthesis of Mn2(CO)10 was in 1954 at Linde Air Products Company and was performed by Brimm, Lynch, and Sesny. Their hypothesis about, and synthesis of, dimanganese decacarbonyl was fundamentally guided by the previously known dirhenium decacarbonyl (Re2(CO)10), the heavy atom analogue of Mn2(CO)10. Since its first synthesis, Mn2(CO)10 has been use sparingly as a reagent in the synthesis of other chemical species, but has found the most use as a simple system on which to study fundamental chemical and physical phenomena, most notably, the metal-metal bond. Dimanganese decacarbonyl is also used as a classic example to reinforce fundamental topics in organometallic chemistry like d-electron count, the 18-electron rule, oxidation state, valency, and the isolobal analogy.
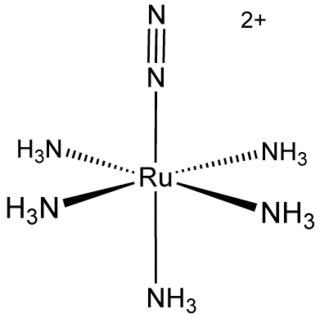
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
Transition metal carbyne complexes are organometallic compounds with a triple bond between carbon and the transition metal. This triple bond consists of a σ-bond and two π-bonds. The HOMO of the carbyne ligand interacts with the LUMO of the metal to create the σ-bond. The two π-bonds are formed when the two HOMO orbitals of the metal back-donate to the LUMO of the carbyne. They are also called metal alkylidynes—the carbon is a carbyne ligand. Such compounds are useful in organic synthesis of alkynes and nitriles. They have been the focus on much fundamental research.
In chemistry, a boranylium ion is an inorganic cation with the chemical formula BR+
2, where R represents a non-specific substituent. Being electron-deficient, boranylium ions form adducts with Lewis bases. Boranylium ions have historical names that depend on the number of coordinated ligands:
Jaqueline Kiplinger is an American inorganic chemist who specializes in organometallic actinide chemistry. Over the course of her career, she has done extensive work with fluorocarbons and actinides. She is currently a Fellow of the Materials Synthesis and Integrated Devices group in the Materials Physics and Applications Division of Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). Her current research interests are focused on the development of chemistry for the United States’ national defense and energy needs.
David Markham Lemal is the Albert W. Smith Professor of Chemistry Emeritus and Research Professor of Chemistry at Dartmouth College. He received an A.B. degree (summa) from Amherst College in 1955 and a Ph.D. in chemistry from Harvard University in 1959. At Harvard he worked with R. B. Woodward on deoxy sugars and a synthesis of the alkaloid yohimbine.
In chemistry, compounds of palladium(III) feature the noble metal palladium in the unusual +3 oxidation state (in most of its compounds, palladium has the oxidation state II). Compounds of Pd(III) occur in mononuclear and dinuclear forms. Palladium(III) is most often invoked, not observed in mechanistic organometallic chemistry.
The Mukaiyama hydration is an organic reaction involving formal addition of an equivalent of water across an olefin by the action of catalytic bis(acetylacetonato)cobalt(II) complex, phenylsilane and atmospheric oxygen to produce an alcohol with Markovnikov selectivity.

Phosphenium ions, not to be confused with phosphonium or phosphirenium, are divalent cations of phosphorus of the form [PR2]+. Phosphenium ions have long been proposed as reaction intermediates.

A lanthanocene is a type of metallocene compound that contains an element from the lanthanide series. The most common lanthanocene complexes contain two cyclopentadienyl anions and an X type ligand, usually hydride or alkyl ligand.
A transition metal phosphido complex is a coordination complex containing a phosphido ligand (R2P, where R = H, organic substituent). With two lone pairs on phosphorus, the phosphido anion (R2P−) is comparable to an amido anion (R2N−), except that the M-P distances are longer and the phosphorus atom is more sterically accessible. For these reasons, phosphido is often a bridging ligand. The -PH2 ion or ligand is also called phosphanide or phosphido ligand.
β-Carbon elimination is a type of reaction in organometallic chemistry wherein an allyl ligand bonded to a metal center is broken into the corresponding metal-bonded alkyl (aryl) ligand and an alkene. It is a subgroup of elimination reactions. Though less common and less understood than β-hydride elimination, it is an important step involved in some olefin polymerization processes and transition-metal-catalyzed organic reactions.
Concerted metalation-deprotonation (CMD) is a mechanistic pathway through which transition-metal catalyzed C–H activation reactions can take place. In a CMD pathway, the C–H bond of the substrate is cleaved and the new C–Metal bond forms through a single transition state. This process does not go through a metal hydride species that is bound to the cleaved hydrogen atom. Instead, a carboxylate or carbonate base deprotonates the substrate. The first proposal of a concerted metalation deprotonation pathway was by S. Winstein and T. G. Traylor in 1955 for the acetolysis of diphenylmercury. It was found to be the lowest energy transition state in a number of computational studies, was experimentally confirmed through NMR experiments, and has been hypothesized to occur in mechanistic studies.
Jonas C. Peters is the Bren Professor of Chemistry at the California Institute of Technology and Director of the Resnick Sustainability Institute. He has contributed to the development of catalysts and photocatalysts relevant to small molecule activation.
Metal-ligand cooperativity (MLC) is a mode of reactivity in which a metal and ligand of a complex are both involved in the bond breaking or bond formation of a substrate during the course of a reaction. This ligand is an actor ligand rather than a spectator, and the reaction is generally only deemed to contain MLC if the actor ligand is doing more than leaving to provide an open coordination site. MLC is also referred to as "metal-ligand bifunctional catalysis." Note that MLC is not to be confused with cooperative binding.
Karsten Meyer is a German inorganic chemist and Chair of Inorganic and General Chemistry at the Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU). His research involves the coordination chemistry of transition metals as well as uranium coordination chemistry, small molecule activation with these coordination complexes, and the synthesis of new chelating ligands. He is the 2017 recipient of the Elhuyar-Goldschmidt Award of the Spanish Royal Society of Chemistry, the Ludwig-Mond Award of the Royal Society of Chemistry, and the L.A. Chugaev Commemorative Medal of the Russian Academy of Sciences, among other awards. He also serves as an Associate Editor of the journal Organometallics since 2014.

Paula L. Diaconescu is a Romanian-American chemistry professor at the University of California, Los Angeles. She is known for her research on the synthesis of redox active transition metal complexes, the synthesis of lanthanide complexes, metal-induced small molecule activation, and polymerization reactions. She is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
A molecular electron-reservoir complex is one of a class of redox-active systems which can store and transfer electrons stoichiometrically or catalytically without decomposition. The concept of electron-reservoir complexes was introduced by the work of French chemist, Didier Astruc. From Astruc's discoveries, a whole family of thermally stable, neutral, 19-electron iron(I) organometallic complexes were isolated and characterized, and found to have applications in redox catalysis and electrocatalysis. The following page is a reflection of the prototypal electron-reservoir complexes discovered by Didier Astruc.
A metal-formaldehyde complex is a coordination complex in which a formaldehyde ligand has two bonds to the metal atom(s) (η2-CH2O). This type of ligand has been reported in both monometallic and bimetallic complexes.