Related Research Articles

The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow, is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.

A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodities market for centuries for price risk management.
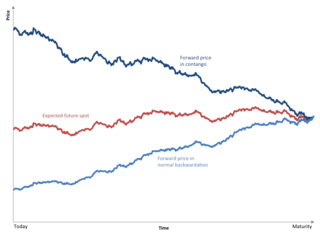
Contango is a situation in which the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market or carrying-cost market.
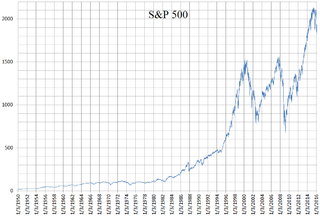
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 of the largest companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $43 trillion as of January 2024.
A commodity price index is a fixed-weight index or (weighted) average of selected commodity prices, which may be based on spot or futures prices. It is designed to be representative of the broad commodity asset class or a specific subset of commodities, such as energy or metals. It is an index that tracks a basket of commodities to measure their performance. They are similar to stock market indices but track the price of a basket of specific commodities. These indexes are often traded on exchanges, allowing investors to gain easier access to commodities without having to enter the futures market. The value of these indexes fluctuates based on their underlying commodities, and this value can be traded on an exchange in much the same way as stock index futures.

West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the futures price, or assessed price for that oil. In colloquial usage, WTI usually refers to the WTI Crude Oil futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). The WTI oil grade is also known as Texas light sweet. Oil produced from any location can be considered WTI if the oil meets the required qualifications. Spot and futures prices of WTI are used as a benchmark in oil pricing. This grade is described as light crude oil because of its low density and sweet because of its low sulfur content.
The Standard & Poor's Commodity Index (SPCI) was a commodity price index that measured the price changes in a cross section of agricultural and industrial commodities with actively traded U.S. futures contracts managed by Standard & Poor. The index covered five sectors - Energy, Metals, Grains, Livestock, and Fibers & Softs. Only commodities that are consumed for industrial use were included in the index. Weights in the index was determined by the dollar value of Commercial Open Interest (COI) for each component commodity, and rebalanced annually each February.
The Bloomberg Commodity Index (BCOM) is a broadly diversified commodity price index distributed by Bloomberg Index Services Limited. The index was originally launched in 1998 as the Dow Jones-AIG Commodity Index (DJ-AIGCI) and renamed to Dow Jones-UBS Commodity Index (DJ-UBSCI) in 2009, when UBS acquired the index from AIG. On July 1, 2014, the index was rebranded under its current name.
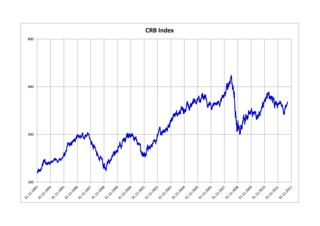
The FTSE/CoreCommodity CRB Index is a commodity futures price index. It was first calculated by Commodity Research Bureau, Inc. in 1957 and made its inaugural appearance in the 1958 CRB Commodity Year Book.
Lean Hog is a type of hog (pork) futures contract that can be used to hedge and to speculate on pork prices in the US.
The Deutsche Bank Liquid Commodity Index (DBLCI) is a commodity price index operated by German based Deutsche Bank. It was launched in February 2003 and tracks the performance of six commodities in the energy, precious metals, industrial metals and grain sectors. The DBLCI has constant weightings for each of the six commodities and the index is rebalanced annually in the first week of November. Consequently, the weights fluctuate during the year according to the price movement of the underlying commodity futures.
DBLCI Optimum Yield Index (DBLCI-OY) is a commodity price index operated by German Deutsche Bank. It is similar to the Deutsche Bank Liquid Commodity Index but has more commodities from more sectors. The DBLCI-OY indices are available for 24 commodities drawn from the energy, precious metals, industrial metals, agricultural and livestock sectors. A DBLCI-OY index based on the DBLCI benchmark weights is also available and the optimum yield technology has also been applied to the energy, precious metals, industrial metals and agricultural sector indices.

S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC is a joint venture between S&P Global, the CME Group, and News Corp that was announced in 2011 and later launched in 2012. It produces, maintains, licenses, and markets stock market indices as benchmarks and as the basis of investable products, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and structured products. The company currently has employees in 15 cities worldwide, including New York, London, Frankfurt, Singapore, Hong Kong, Sydney, Beijing, and Dubai.

In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.
A commodity index fund is a fund whose assets are invested in financial instruments based on or linked to a commodity price index. In just about every case the index is in fact a commodity futures index.
The Goldman roll is the monthly sale and purchase of commodities for the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (S&P-GSCI).
LME Aluminium stands for a group of spot, forward, and futures contracts, trading on the London Metal Exchange (LME), for delivery of primary Aluminium that can be used for price hedging, physical delivery of sales or purchases, investment, and speculation. Producers, semi-fabricators, consumers, recyclers, and merchants can use Aluminium futures contracts to hedge Aluminium price risks and to reference prices. Notable companies that use LME Aluminium contracts to hedge Aluminium prices include General Motors, Boeing, and Alcoa.
LME Copper is a group of spot, forward, and futures contracts, trading on the London Metal Exchange (LME), for delivery of Copper, that can be used for price hedging, physical delivery of sales or purchases, investment, and speculation.

LME Nickel stands for a group of spot, forward, and Futures contracts, trading on the London Metal Exchange (LME), for delivery of primary Nickel that can be used for price hedging, physical delivery of sales or purchases, investment, and speculation. Producers, semi-fabricators, consumers, recyclers, and merchants can use Nickel futures contracts to hedge Nickel price risks and to reference prices.
LME Zinc stands for a group of spot, forward, and futures contracts traded on the London Metal Exchange (LME), for delivery of special high-grade Zinc with a 99.995% purity minimum that can be used for price hedging, physical delivery of sales or purchases, investment, and speculation. Producers, semi-fabricators, consumers, recyclers, and merchants can use Zinc futures contracts to hedge Zinc price risks and to reference prices.
References
- ↑ The Asylum, Leah McGrath Goodman, 2011, Harper Collins, p 327- 328
- ↑ Clearing the usual suspects, Buttonwood, The Economist, 2010 6 24
- ↑ "S&P GSCI Methodology" (PDF). S&P Dow Jones Indices. S&P Global. p. 26. Retrieved 2020-05-06.