
The beta sheet is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies.
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA.
DnaG is a bacterial DNA primase and is encoded by the dnaG gene. The enzyme DnaG, and any other DNA primase, synthesizes short strands of RNA known as oligonucleotides during DNA replication. These oligonucleotides are known as primers because they act as a starting point for DNA synthesis. DnaG catalyzes the synthesis of oligonucleotides that are 10 to 60 nucleotides long, however most of the oligonucleotides synthesized are 11 nucleotides. These RNA oligonucleotides serve as primers, or starting points, for DNA synthesis by bacterial DNA polymerase III. DnaG is important in bacterial DNA replication because DNA polymerase cannot initiate the synthesis of a DNA strand, but can only add nucleotides to a preexisting strand. DnaG synthesizes a single RNA primer at the origin of replication. This primer serves to prime leading strand DNA synthesis. For the other parental strand, the lagging strand, DnaG synthesizes an RNA primer every few kilobases (kb). These primers serve as substrates for the synthesis of Okazaki fragments.
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors, or antiproteases, are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins.
Micrococcal nuclease is an endo-exonuclease that preferentially digests single-stranded nucleic acids. The rate of cleavage is 30 times greater at the 5' side of A or T than at G or C and results in the production of mononucleotides and oligonucleotides with terminal 3'-phosphates. The enzyme is also active against double-stranded DNA and RNA and all sequences will be ultimately cleaved.
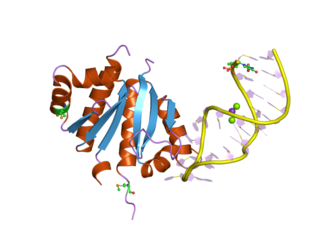
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.
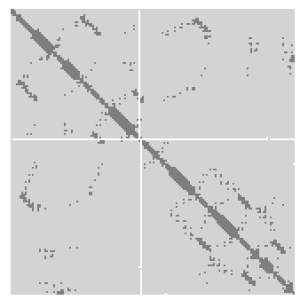
A protein contact map represents the distance between all possible amino acid residue pairs of a three-dimensional protein structure using a binary two-dimensional matrix. For two residues and , the element of the matrix is 1 if the two residues are closer than a predetermined threshold, and 0 otherwise. Various contact definitions have been proposed: The distance between the Cα-Cα atom with threshold 6-12 Å; distance between Cβ-Cβ atoms with threshold 6-12 Å ; and distance between the side-chain centers of mass.

In protein structures, a beta barrel(β barrel) is a beta sheet composed of tandem repeats that twists and coils to form a closed toroidal structure in which the first strand is bonded to the last strand. Beta-strands in many beta-barrels are arranged in an antiparallel fashion. Beta barrel structures are named for resemblance to the barrels used to contain liquids. Most of them are water-soluble outer membrane proteins and frequently bind hydrophobic ligands in the barrel center, as in lipocalins. Others span cell membranes and are commonly found in porins. Porin-like barrel structures are encoded by as many as 2–3% of the genes in Gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown that more than 600 proteins with various function such as oxidase, dismutase, and amylase contain the beta barrel structure.

The TIM barrel, also known as an alpha/beta barrel, is a conserved protein fold consisting of eight alpha helices (α-helices) and eight parallel beta strands (β-strands) that alternate along the peptide backbone. The structure is named after triose-phosphate isomerase, a conserved metabolic enzyme. TIM barrels are ubiquitous, with approximately 10% of all enzymes adopting this fold. Further, five of seven enzyme commission (EC) enzyme classes include TIM barrel proteins. The TIM barrel fold is evolutionarily ancient, with many of its members possessing little similarity today, instead falling within the twilight zone of sequence similarity.

The trefoil knot fold is a protein fold in which the protein backbone is twisted into a trefoil knot shape. "Shallow" knots in which the tail of the polypeptide chain only passes through a loop by a few residues are uncommon, but "deep" knots in which many residues are passed through the loop are extremely rare. Deep trefoil knots have been found in the SPOUT superfamily. including methyltransferase proteins involved in posttranscriptional RNA modification in all three domains of life, including bacterium Thermus thermophilus and proteins, in archaea and in eukaryota.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM.

In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.

In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.
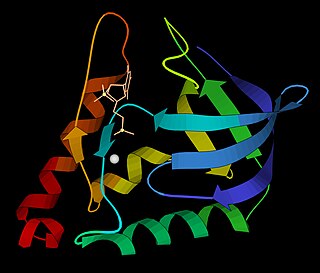
The K Homology (KH) domain is a protein domain that was first identified in the human heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) K. An evolutionarily conserved sequence of around 70 amino acids, the KH domain is present in a wide variety of nucleic acid-binding proteins. The KH domain binds RNA, and can function in RNA recognition. It is found in multiple copies in several proteins, where they can function cooperatively or independently. For example, in the AU-rich element RNA-binding protein KSRP, which has 4 KH domains, KH domains 3 and 4 behave as independent binding modules to interact with different regions of the AU-rich RNA targets. The solution structure of the first KH domain of FMR1 and of the C-terminal KH domain of hnRNP K determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) revealed a beta-alpha-alpha-beta-beta-alpha structure. Autoantibodies to NOVA1, a KH domain protein, cause paraneoplastic opsoclonus ataxia. The KH domain is found at the N-terminus of the ribosomal protein S3. This domain is unusual in that it has a different fold compared to the normal KH domain.

In molecular biology, a Tudor domain is a conserved protein structural domain originally identified in the Tudor protein encoded in Drosophila. The Tudor gene was found in a Drosophila screen for maternal factors that regulate embryonic development or fertility. Mutations here are lethal for offspring, inspiring the name Tudor, as a reference to the Tudor King Henry VIII and the several miscarriages experienced by his wives.
The Walker A and Walker B motifs are protein sequence motifs, known to have highly conserved three-dimensional structures. These were first reported in ATP-binding proteins by Walker and co-workers in 1982.
The RNA-binding Proteins Database (RBPDB) is a biological database of RNA-binding protein specificities that includes experimental observations of RNA-binding sites. The experimental results included are both in vitro and in vivo from primary literature. It includes four metazoan species, which are Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Drosophila melanogaster, and Caenorhabditis elegans. RNA-binding domains included in this database are RNA recognition motif, K homology, CCCH zinc finger, and more domains. As of 2021, the latest RBPDB release includes 1,171 RNA-binding proteins.

In molecular biology, the AMMECR1 protein is a protein encoded by the AMMECR1 gene on human chromosome Xq22.3.

In molecular biology, the CRM domain is an approximately 100-amino acid RNA-binding domain. The name CRM has been suggested to reflect the functions established for four characterised members of the family: Zea mays (Maize) CRS1, CAF1 and CAF2 proteins and the Escherichia coli protein YhbY. Proteins containing the CRM domain are found in eubacteria, archaea, and plants. The CRM domain is represented as a stand-alone protein in archaea and bacteria, and in single- and multi-domain proteins in plants. It has been suggested that prokaryotic CRM proteins existed as ribosome-associated proteins prior to the divergence of archaea and bacteria, and that they were co-opted in the plant lineage as RNA binding modules by incorporation into diverse protein contexts. Plant CRM domains are predicted to reside not only in the chloroplast, but also in the mitochondrion and the nucleo/cytoplasmic compartment. The diversity of the CRM domain family in plants suggests a diverse set of RNA targets.
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred. Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent. Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term protein clan is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems.













