
The AIM-7 Sparrow is an American, medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile operated by the United States Air Force, United States Navy, and United States Marine Corps, as well as other various air forces and navies. Sparrow and its derivatives were the West's principal beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile from the late 1950s until the 1990s. It remains in service, although it is being phased out in aviation applications in favor of the more advanced AIM-120 AMRAAM.
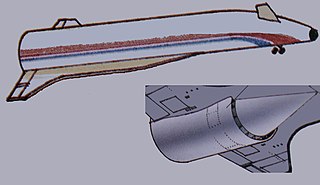
HOTOL, for Horizontal Take-Off and Landing, was a 1980s British design for a single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) spaceplane that was to be powered by an airbreathing jet engine. Development was being conducted by a consortium led by Rolls-Royce and British Aerospace (BAe).
Saab AB is a Swedish aerospace and defence company, founded in 1937. From 1947 to 1990 it was the parent company of automobile manufacturer Saab Automobile. Between 1968 and 1995 the company was in a merger with commercial vehicle manufacturer Scania-Vabis, known as Saab-Scania. The two were de-merged in 1995 by the new owners, Investor AB. Despite the demerger, both Saab and Scania share the right to use the griffin logo, which originates from the coat of arms of the Swedish region of Scania.

British Aerospace plc (BAe) was a British aircraft, munitions and defence-systems manufacturer. Its head office was at Warwick House in the Farnborough Aerospace Centre in Farnborough, Hampshire. Formed in 1977, in 1999 it purchased Marconi Electronic Systems, the defence electronics and naval shipbuilding subsidiary of the General Electric Company plc, to form BAE Systems.

The Saab JAS 39 Gripen is a light single-engine multirole fighter aircraft manufactured by the Swedish aerospace company Saab. The Gripen has a delta wing and canard configuration with relaxed stability design and fly-by-wire flight controls. It is powered by the Volvo RM12, and has a top speed of Mach 2. Later aircraft are modified for NATO interoperability standards and to undertake air to air refuelling.

The Saab 37 Viggen ("Thunderbolt") is a retired Swedish single-seat, single-engine, short-medium range combat aircraft. Development work on the type was initiated at Saab in 1952 and, following the selection of a radical delta wing configuration, the resulting aircraft performed its first flight on 8 February 1967 and entered service in 21 June 1971. It was the first canard design produced in quantity. The Viggen was also the most advanced fighter jet in Europe until the introduction of the Panavia Tornado into operational service in 1981.

The Eurofighter Typhoon is a twin-engine, canard–delta wing, multirole fighter. The Typhoon was designed originally as an air superiority fighter and is manufactured by a consortium of Airbus, BAE Systems and Leonardo that conducts the majority of the project through a joint holding company, Eurofighter Jagdflugzeug GmbH formed in 1986. NATO Eurofighter and Tornado Management Agency manages the project and is the prime customer.

The Panavia Tornado Air Defence Variant (ADV) is a long-range, twin-engine interceptor version of the swing-wing Panavia Tornado. The aircraft's first flight was on 27 October 1979, and it entered service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1986. It was also previously operated by the Italian Air Force (AMI) and the Royal Saudi Air Force (RSAF).

The Saab 35 Draken is a Swedish fighter aircraft developed and manufactured by Saab between 1955 and 1974. It was the first fully supersonic aircraft to be deployed in Western Europe and the first aircraft to do the Cobra maneuver.

Meteor is an active radar guided beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) developed by MBDA. Meteor offers a multi-shot capability against long range manoeuvring targets, jets, UAVs and cruise missiles in a heavy electronic countermeasures (ECM) environment with range well in excess of 150 kilometres (81 nmi). Its no-escape zone of over 60 km is largest among air-to-air missiles according to the manufacturer. A solid-fueled ramjet motor allows the missile to cruise at a speed of over Mach 4 and provides the missile with thrust and mid-way acceleration to target intercept. A two-way datalink enables the launch aircraft to provide mid-course target updates or retargeting if required, including data from off-board third parties. The datalink is capable of transmitting missile information such as functional and kinematic status, information about multiple targets, and notification of target acquisition by the seeker.

ALARM is a British anti-radiation missile designed primarily to destroy enemy radars for the purpose of Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD). It was used by the RAF and is still used by the Royal Saudi Air Force. The weapon was retired by the UK at the end of 2013.

The Eurofighter Typhoon is in service with seven nations: United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, Spain, Saudi Arabia, Oman and Austria. It has been ordered by Kuwait and Qatar, with orders for all eight customers still pending as of September 2017. The aircraft has, as of 2016, been provided in a basic air-defense form and has been upgraded to newer production standards which include internal IRST, air-to-ground precision strike capability, and HMSS helmets. Most of the major systems including the CAPTOR radar and the Defence Aids Sub-System (DASS) are expected to be improved and updated over time, with the radar being updated to an AESA, being the CAPTOR-E/CAESAR, of which the Kuwait Air Force will be the inaugural operator, with first deliveries of their 28 new-built aircraft to commence in 2019.

The British Aerospace Skyflash, or Sky Flash in marketing material, was a medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile derived from the US AIM-7 Sparrow missile and carried by Royal Air Force F-4 Phantoms and Tornado F3s, Italian Aeronautica Militare and Royal Saudi Air Force Tornados and Swedish Flygvapnet Viggens.

The RBS-15 is a long-range fire-and-forget surface-to-surface and air-to-surface, anti-ship missile. The later version Mk. III has the ability to attack land targets as well. The missile was developed by the Swedish company Saab Bofors Dynamics.

This is a timeline of the development of the Eurofighter Typhoon, a multirole fighter aircraft manufactured by a consortium of European aerospace manufacturers, Eurofighter GmbH, formed in 1983.
The V3E A-Darter is a modern short-range infrared homing air-to-air missile, featuring countermeasures resistance with a 180-degree look angle and 120-degrees per second track rate, developed by South Africa's Denel Dynamics and Brazil's Mectron, Avibras and Opto Eletrônica. It will equip the South African Air Force's Saab JAS 39 Gripen C/D and BAe Hawk 120, and the Brazilian Air Force's A-1M AMX, Northrop F-5BR and Gripen E/F. It was expected to be in production before the end of 2015.

The aerospace industry of the United Kingdom is the fourth-largest national aerospace industry in the world and the third largest in Europe, with a global market share of 6.4% in 2016. In 2013, the industry employed 84,000 people. Domestic companies with a large presence in the British aerospace industry include BAE Systems, Britten-Norman, Cobham, GKN, Hybrid Air Vehicles, Meggitt PLC, QinetiQ, Rolls Royce and Ultra Electronics. Foreign companies with a major presence include Boeing, Bombardier, Airbus, Leonardo, General Electric, Lockheed Martin, MBDA, Safran and Thales Group. Current manned aircraft in which the British aerospace industry has a major role include the AgustaWestland AW101, AgustaWestland AW159, Airbus A320 family, Airbus A330, Airbus A340, Airbus A380, Airbus A400M, BAE Hawk, Boeing 767, Boeing 777, Boeing 787, Bombardier CRJ700, Bombardier CSeries, Bombardier Learjet 85, Britten-Norman Defender, Britten-Norman Islander, Eurofighter Typhoon, Hawker 800, Lockheed Martin C-130J Super Hercules and Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II. Current unmanned aerial vehicles in which the British aerospace industry has a major role include BAE Taranis, HAV 304 Airlander 10, QinetiQ Zephyr and Watchkeeper WK450.

The Leonardo's Praetorian DASS is an integral part of Eurofighter Typhoon defensive Aid Sub-System (DASS) providing threat assessment, aircraft protection and support measures in extremely hostile and severe environments. As the DASS is fully integrated, it doesn’t require additional pods that take up weapon stations or would influence the aircraft’s aerodynamic performance. In addition the modular nature of the DASS simplifies future upgrades and allows each partner nation or export customer the option to tailor the DASS to their individual needs.

The BAE Systems Tempest is a proposed fighter aircraft concept that is under development in the United Kingdom for the British Royal Air Force and the Italian Aeronautica Militare (AMI). It is being developed by a consortium known as "Team Tempest," consisting of the UK Ministry of Defence, BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce, Leonardo S.p.A. and MBDA, and is intended to enter service from 2035 replacing the Eurofighter Typhoon aircraft in service with the RAF and AMI. Two billion pounds will be spent by the British government on the project by 2025.
















