
(top) ram air parachute deployed
(bottom) vortex ring parachute deployed
Project Sense and Destroy Armor, or SADARM, is a United States 'smart' submunition capable of searching for, and destroying tanks within a given target area.

Project Sense and Destroy Armor, or SADARM, is a United States 'smart' submunition capable of searching for, and destroying tanks within a given target area.
SADARM development can be traced back to the early 1960s. The original platform for the submunition was the 203 mm M509 Improved Conventional Munition (ICM) projectile, and the concept was demonstrated in the late 1970s. By 1983 the project shifted focus to 155 mm caliber and the target set was changed to self-propelled howitzers and other lightly armored vehicles. With approval for engineering development in 1986 the scope was expanded to include larger diameter submunitions in M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) rockets. [1]
Several successful live-fire tests were conducted in 1989, and production was scheduled for 1994; however, pre-production samples tested in 1993 gave poor results with only nine out of 42 submunitions hitting their targets. Fixes were applied and further testing resulted in 11 hits from 13 submunitions.
Low-rate production began in 1995, with further testing successfully conducted in April 1996. Low-rate production continued with a total of 836 projectiles produced, most being expended in various operational tests. With the target threat (howitzers) removed from probable conflict areas due to the collapse of the Soviet Union the SADARM program was terminated prior to full-rate production.
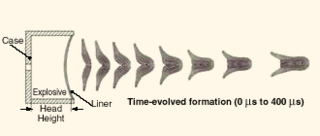
The M898 155 mm SADARM shell is fired from a normal 155 mm artillery gun, with a nose-mounted M762/M767 fuze set to burst at 1,000 m above the target to release two SADARM submunitions. Once the submunition is ejected from the projectile, an initial ram-air parachute opens to de-spin and slow the submunition. A second "vortex ring" parachute then deploys to slowly spin the submunition, suspending it at approximately 30° from the vertical. As it spins, its sensors sweep a decreasing spiral track beneath the submunition to scan an area about 150 m in diameter. The sensors consist of a millimeter-wave radar, a passive millimeter-wave radiometer and an infrared telescope. A magnetometer is used as an aid in arming and aiming. When the submunition detects a target, its 1.5 kg LX-14 explosive charge is detonated to project an explosively formed penetrator that has enough energy to penetrate the thin top armor of most main battle tanks up to a range of around 152 m. If the submunition reaches the ground before it finds a target it self-destructs. However, exact penetration power is not listed, being classified in nature.
The submunition was also intended to be used in MLRS rockets, with four or six being carried.
The system was used for the first time during combat during the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, [2] [3] with a total of 121 rounds reported fired by the 3rd Infantry Division with 48 vehicle kills attributed to 108 M898 SADARM projectiles.

The M198 is a medium-sized, towed 155 mm artillery piece, developed for service with the United States Army and Marine Corps. It was commissioned to be a replacement for the World War II-era M114 155 mm howitzer. It was designed and prototyped at the Rock Island Arsenal in 1969 with firing tests beginning in 1970 and went into full production there in 1978. It entered service in 1979 and since then 1,600 units have been produced.

Nuclear artillery is a subset of limited-yield tactical nuclear weapons, in particular those weapons that are launched from the ground at battlefield targets. Nuclear artillery is commonly associated with shells delivered by a cannon, but in a technical sense short-range artillery rockets or tactical ballistic missiles are also included.

Airborne guns are airborne artillery pieces, designed for use by paratroopers. They are generally specific or specialised types of infantry support guns, being in the traditional sense capable of being broken down into smaller loads for transport by aircraft and soldiers, thus also suitable as mountain guns. The historical concept of the "airborne guns" is to some degree outdated, their role being filled by mortars, wire-guided missiles, and/or light anti-tank weapons. As it has been many decades since two industrialized great powers engaged directly in warfare, the concept of the "airborne gun" allowing paratroopers to maintain an airhead against an armored force is in that sense non-functional, but currently, all three of the U.S. Army's howitzers, are air-mobile.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.

A shell, in a military context, is a projectile whose payload contains an explosive, incendiary, or other chemical filling. Originally it was called a bombshell, but "shell" has come to be unambiguous in a military context. A shell can hold a tracer.

The M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System is an American armored self-propelled multiple launch rocket system.

The CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon is a United States Air Force 1,000-pound (450 kg)-class freefall Cluster Bomb Unit. It was developed and produced by Textron Defense Systems. A CBU-97 used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit is converted to a precision-guided weapon, and the combination is designated CBU-105.

A dual-purpose improved conventional munition (DPICM) is an artillery or surface-to-surface missile warhead designed to burst into submunitions at an optimum altitude and distance from the desired target for dense area coverage. The submunitions use both shaped charges for the anti-armor role, and fragmentation for the antipersonnel role, hence the nomenclature "dual-purpose". Some submunitions may be designed for delayed reaction or mobility denial (mines). The air-to-surface variety of this kind of munition is better known as a cluster bomb. They are banned by more than 100 countries under the Convention on Cluster Munitions.

The M982 Excalibur is a 155 mm extended-range guided artillery shell developed in a collaborative effort between the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) and the United States Army Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center (ARDEC). The Excalibur was developed and/or manufactured by prime contractor Raytheon Missiles & Defense, BAE Systems AB and other subs and primes in multiple capacities such as Camber Corporation and Huntington Ingalls Industries. It is a GPS and inertial-guided munition capable of being used in close support situations within 75–150 meters (250–490 ft) of friendly troops or in situations where targets might be prohibitively close to civilians to attack with conventional unguided artillery fire. In 2015, the United States planned to procure 7,474 rounds with a FY 2015 total program cost of US$1.9341 billion at an average cost of US$258,777 per unit. By 2016, unit costs were reduced to US$68,000 per round. Versions that add laser-guidance capability and are designed to be fired from naval guns began testing in 2015. By October 2018, over 1,400 rounds had been fired in combat.

The M829 is an American armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) kinetic energy penetrator tank round. Modeling was done at the Ballistic Research Laboratory at Aberdeen Proving Ground, which was incorporated into the Army Research Laboratory in 1992. The round is specifically designed for the 120 mm M256 main gun on the Abrams M1A1 and M1A2 main battle tanks. The penetrator is carried by a sabot during its acceleration in the gun barrel.
An explosively formed penetrator (EFP), also known as an explosively formed projectile, a self-forging warhead, or a self-forging fragment, is a special type of shaped charge designed to penetrate armor effectively, from a much greater standoff range than standard shaped charges, which are more limited by standoff distance. As the name suggests, the effect of the explosive charge is to deform a metal plate into a slug or rod shape and accelerate it toward a target. They were first developed as oil well perforators by American oil companies in the 1930s, and were deployed as weapons in World War II.

The 2S4 Tyulpan is a Soviet 240 mm self-propelled heavy mortar. "2S4" is its GRAU designation. The Tyulpan is the largest mortar system in use today.

Armour-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS), long dart penetrator, or simply dart ammunition is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition used to attack modern vehicle armour. As an armament for main battle tanks, it succeeds Armour-Piercing Discarding Sabot (APDS) ammunition, which is still used in small or medium caliber weapon systems.

The 2A36 Giatsint-B is a Soviet/Russian towed 152 mm field gun which entered service in 1975. The 2A36 is designed to suppress and destroy enemy manpower and equipment. It is also suitable for counter-battery fire. The gun can be used in various weather conditions and has been tested in temperatures ranging from −50 °C to 50 °C.

The PAW 600 was a lightweight anti-tank gun that used the high-low pressure system to fire hollow charge warheads. In 1945, it was used operationally by the Wehrmacht in small numbers. Only about 260 were produced before the war's end.
The A-100 is a 300 mm (12 in), 10-tube multiple rocket launcher developed by Beijing-based China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology for the Chinese PLA ground forces. It is a derivative of Weishi Rockets WS-1 with simple cascade terminal inertial guidance.
The SMArt 155 is a German 155 mm artillery round designed for a long-range, indirect fire top-attack role against armoured vehicles. The projectile was developed in 1989 by Diehl BGT Defence in Überlingen, Germany, with Rheinmetall and started full-rate production for the German Army in 1998. It consists of a 47-kilogram (104 lb) heavy artillery projectile containing two autonomous, sensor-fused, "fire-and-forget" submunitions. Due to the submunitions, it has been considered by some to be a cluster munition. As of 2008, representatives of the German defense ministry have referred to it as not being classified as submunition weapons, which were prohibited by the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions.

The M795 155 mm projectile is the US Army and US Marine Corps' standard 155 mm High Explosive (HE) projectile for howitzers. It is a bursting round with fragmentation and blast effects.

The M549 is a high-explosive rocket-assisted (HERA) 155 mm howitzer round developed for use by the US military in order to add additional range to standard howitzers, with a maximum range 30.1 km (18.7 mi) from a M198 howitzer. The projectile has two distinctive pre-assembled components—the high explosive (HE) warhead and the rocket motor, making it a form of rocket-assisted projectile. The warhead is fabricated from high fragmentation steel for increased effectiveness in terms of damage caused to target and contains a bulk-filled explosive.

The BONUS or ACED is a 155 mm artillery cluster round co-developed and manufactured by Bofors of Sweden and Nexter of France. It was designed to fulfill a long range, indirect fire, top attack requirement against armoured fighting vehicles.