Related Research Articles
Senter syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by similar skin changes and congenital hearing impairment to keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome, but is associated with glycogen storage leading to hepatomegaly, hepatic cirrhosis, growth failure and intellectual disability.
Nevus comedonicus syndrome is a skin condition characterized by a nevus comedonicus associated with cataracts, scoliosis, and neurologic abnormalities.

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
A trichodiscoma is a cutaneous condition, a benign, usually skin-colored tumor most often affecting the face and upper trunk.
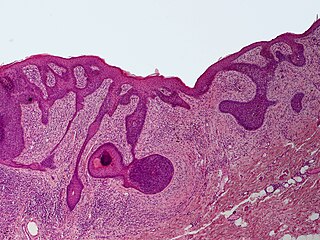
Perifollicular fibroma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk.
Quadrichrome vitiligo is another variant of vitiligo, a cutaneous condition, which reflects the presence of a fourth color at sites of perifollicular repigmentation.

Watson syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by Lisch nodules of the ocular iris, axillary/inguinal freckling, pulmonary valvular stenosis, relative macrocephaly, short stature, and neurofibromas. Watson syndrome is allelic to NF1, the same gene associated with neurofibromatosis type 1.
Wende–Bauckus syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by tiny white macules on the trunk with confluence within flexures.
Woolly hair nevus, alternatively spelled wooly hair nevus, is a congenital condition in which hair in a circumscribed area of the scalp is kinked or woolly.
Childhood tumor syndrome is a condition characterized by axillary freckling, neurofibromas and/or CNS gliomas.
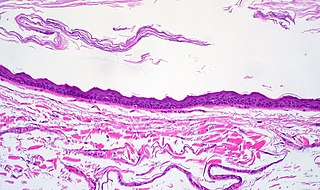
A keratocyst is a type of cutaneous cyst. They appear similar to epidermoid cysts; however, are not limited to a specified location on the body. Keratocyst are most often reported in persons with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.

Hystrix-like ichthyosis–deafness syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a keratoderma.
Seboacanthoma is a cutaneous condition, and a specific type of sebaceous adenoma which may be specific to Muir–Torre syndrome.
Sulzberger–Garbe syndrome is a cutaneous condition, a type of therapy resistant nummular eczema.
Persistent adrenarche syndrome is a cutaneous condition seen typically in thin young women who report great psychological and physical stress in their lives.
Metageria is a cutaneous condition characterized by premature aging.
Pseudomonas hot-foot syndrome is a self-limited cutaneous condition that occurs on the plantar surface of children after swimming in pool water that has high concentrations of P. aeruginosa. The condition typically presents as plantar purple-red nodules.
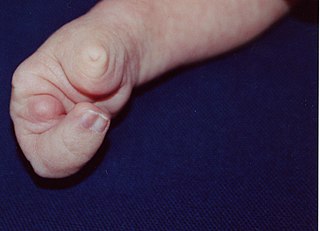
Limb–mammary syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by p63 mutations.
Hyperprolactinemic SAHA syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by lateral hairiness, oligomenorrhea, and sometimes acne, seborrhea, FAGA I, and even galactorrhea.
Excess ovarian androgen release syndrome is a cutaneous condition usually seen in young women between the ages of 16 and 20.
References
- ↑ Jean L. Bolognia; Joseph L. Jorizzo; Ronald P. Rapini (2003). Dermatology. Gulf Professional Publishing. pp. 1081–. ISBN 9789997638991.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 1013–14. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ Orfanos CE, Adler YD, Zouboulis CC (2000). "The SAHA syndrome". Horm. Res. 54 (5–6): 251–8. doi:10.1159/000053267. PMID 11595813. S2CID 20067880.