Related Research Articles

Power-line communication (PLC) is the carrying of data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers. The line that does so is known as a power-line carrier.
HomePlug is the family name for various power line communications specifications under the HomePlug designation, each with unique capabilities and compatibility with other HomePlug specifications.

HomeRF was a wireless networking specification for home devices. It was developed in 1998 by the Home Radio Frequency Working Group, a consortium of mobile wireless companies that included Proxim Wireless, Intel, Siemens AG, Motorola, Philips and more than 100 other companies.

A wireless router or Wi-Fi router is a device that performs the functions of a router and also includes the functions of a wireless access point. It is used to provide access to the Internet or a private computer network. Depending on the manufacturer and model, it can function in a wired local area network, in a wireless-only LAN, or in a mixed wired and wireless network.
IEEE 1901 is a standard for high-speed communication devices via electric power lines, often called broadband over power lines (BPL). The standard uses transmission frequencies below 100 MHz. This standard is usable by all classes of BPL devices, including BPL devices used for the connection to Internet access services as well as BPL devices used within buildings for local area networks, smart energy applications, transportation platforms (vehicle), and other data distribution applications.

A home network or home area network (HAN) is a type of computer network that facilitates communication among devices within the close vicinity of a home. Devices capable of participating in this network, for example, smart devices such as network printers and handheld mobile computers, often gain enhanced emergent capabilities through their ability to interact. These additional capabilities can be used to increase the quality of life inside the home in a variety of ways, such as automation of repetitive tasks, increased personal productivity, enhanced home security, and easier access to entertainment.
Qualcomm Atheros is a developer of semiconductor chips for network communications, particularly wireless chipsets. The company was founded under the name T-Span Systems in 1998 by experts in signal processing and VLSI design from Stanford University, the University of California, Berkeley, and private industry. The company was renamed Atheros Communications in 2000 and it completed an initial public offering in February 2004, trading on the NASDAQ under the symbol ATHR.
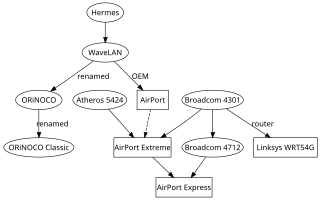
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
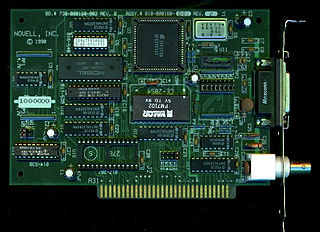
The NE1000 and NE2000 are members of an early line of low cost Ethernet network cards introduced by Novell in 1987. Their popularity had a significant impact on the pervasiveness of networks in computing. They are based on a reference design from National Semiconductor using their 8390 Ethernet chip.

MediaTek Inc., sometimes informally abbreviated as MTK, is a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company that designs and manufactures a range of semiconductor products, providing chips for wireless communications, high-definition television, handheld mobile devices like smartphones and tablet computers, navigation systems, consumer multimedia products and digital subscriber line services as well as optical disc drives.
UNISOC, formerly Spreadtrum Communications, Inc., is a Chinese fabless semiconductor company headquartered in Shanghai which produces chipsets for mobile phones. UNISOC develops its business in two major fields - consumer electronics and industrial electronics. Consumer electronics includes smartphones, feature phones, smart audio systems, smart wearables and other related devices. Industrial electronics cover fields such as LAN IoT, WAN IoT and smart displays.

The SheevaPlug is a "plug computer" designed to allow standard computing features in as small a space as possible. It was a small embedded Linux ARM computer without a display which can be considered an early predecessor to the subsequent Raspberry Pi.
Ember was an American company based in Boston, Massachusetts, USA, which is now owned by Silicon Labs. Ember had a radio development centre in Cambridge, England, and distributors worldwide. It developed Zigbee wireless networking technology that enabled companies involved in energy technologies to help make buildings and homes smarter, consume less energy, and operate more efficiently. The low-power wireless technology can be embedded into a wide variety of devices to be part of a self-organizing mesh network. All Ember products conform to IEEE 802.15.4-2003 standards.
Gigle Networks was a provider of high performance system-on-a-chip semiconductor devices and intelligent switching technology for home network, IPTV, consumer electronics and smart grid applications. The company was based in Barcelona, Spain, Edinburgh, UK, and Redwood City, California.
IEEE 1905.1 is an IEEE standard which defines a network enabler for home networking supporting both wireless and wireline technologies: IEEE 802.11, IEEE 1901 power-line networking, IEEE 802.3 Ethernet and Multimedia over Coax (MoCA).

GreenPeak Technologies was an Utrecht, Netherlands-based fabless company developing semiconductor products and software for the IEEE 802.15.4 and Zigbee wireless market segment. Zigbee technology is used for Smart Home data communications and to facilitate the Internet of Things, the term used to refer to devices designed to be operated and managed by internet-enabled controllers and management systems.
SiConnect was a powerline communications technology business that built broadband modem silicon using a proprietary technology. It was founded in England in 2004, and was dissolved in 2010. SiConnect is most notable now for contributing its Arbitration-Determined Multiplexing technology to the IEEE P1901 draft specification for co-existence between disparate powerline technologies.

Banana Pi is a line of single-board computers produced by the Chinese company Shenzhen SINOVOIP Company, its spin-off Guangdong BiPai Technology Company, and supported by Hon Hai Technology (Foxconn). Its hardware design was influenced by the Raspberry Pi, and both lines use the same 40-pin I/O connector.

IEEE 802.11be, dubbed Extremely High Throughput (EHT), is a wireless networking standard in the IEEE 802.11 set of protocols which is designated Wi-Fi 7 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It has built upon 802.11ax, focusing on WLAN indoor and outdoor operation with stationary and pedestrian speeds in the 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz frequency bands.
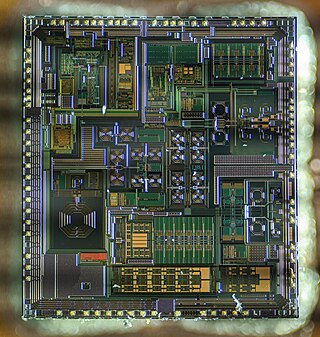
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.
References
- ↑ "MSTAR Acquires SPiDCOM Technologies" (PDF). Press release. 28 November 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-07-24. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- ↑ "SPiDCOM Technologies". Inside Chips. 2006. Archived from the original on 2011-10-06. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- ↑ Frederic Onado (June 2010). "Interview - IEEE 1901 Powerline Communication Standard". HomeToys Home Technology eMagazine. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- ↑ John Walko (24 February 2009). "HomePlug SoC set to debut at CeBIT". EE Times. Archived from the original on 2012-10-04. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- ↑ "SPiDCOM Introduces SPR300-AV Pass-Through Reference Design". News release. 16 February 2010. Archived from the original on 2012-10-04. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- ↑ "IEEE P1901 Participating Entities". Project web site. IEEE. Archived from the original on 10 September 2010. Retrieved 15 August 2013.
- ↑ "HomePlug Board of Directors and Officers". HomePlug Powerline Alliance website. Retrieved 23 July 2011.
- ↑ "OMEGA, the Home Gigabit Access Project". web site. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 15 August 2013.