
Red Hat, Inc. is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide.

YaST is a Linux operating system setup and configuration tool.

Novell, Inc. was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi-platform network operating system known as Novell NetWare.

United Linux was an attempt by a consortium of Linux distributors to create a common base distribution for enterprise use, so as to minimize duplication of engineering effort and form an effective competitor to Red Hat. The founding members of United Linux were SUSE, Turbolinux, Conectiva and Caldera International. The consortium was announced on May 30, 2002. The end of the project was announced on January 22, 2004.

openSUSE is a free and open-source Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. It is offered in two main variations: Tumbleweed, an upstream rolling release distribution, and Leap, a stable release distribution which is sourced from SUSE Linux Enterprise.
Open Enterprise Server (OES) is a server operating system published by OpenText. It was first published by Novell in March 2005 to succeed their NetWare product.

SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE) is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is available in two editions, suffixed with Server (SLES) for servers and mainframes, and Desktop (SLED) for workstations and desktop computers.
SUSE Linux is a computer operating system developed by SUSE. It is built on top of the free and open-source Linux kernel and is distributed with system and application software from other open source projects. SUSE Linux is of German origin, its name being an acronym of "Software und System-Entwicklung", and it was mainly developed in Europe. The first version appeared in early 1994, making SUSE one of the oldest existing commercial distributions. It is known for its YaST configuration tool.
Micro Focus International plc was a British multinational software and information technology business based in Newbury, Berkshire, England. The firm provided software and consultancy. The company was listed on the London Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange until it was acquired by the Canadian software firm OpenText in January 2023.
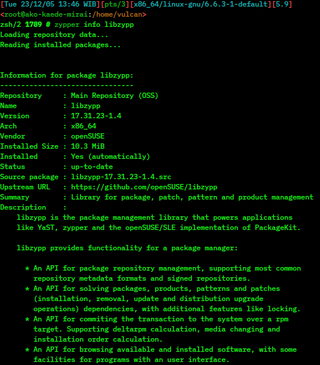
ZYpp is a package manager engine that powers Linux applications like YaST, Zypper and the implementation of PackageKit for openSUSE and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Unlike some more basic package managers, it provides a satisfiability solver to compute package dependencies. It is a free and open-source software project sponsored by SUSE and licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License v2 or later. ZYpp is implemented mostly in the programming language C++.
SUSE Studio was an online Linux software creation tool by SUSE. Users could develop their own Linux distro, software appliance, or virtual appliance, mainly choosing which applications and packages they want on their "custom" Linux and how it looks.

OpenStack is a free, open standard cloud computing platform. It is mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) in both public and private clouds where virtual servers and other resources are made available to users. The software platform consists of interrelated components that control diverse, multi-vendor hardware pools of processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center. Users manage it either through a web-based dashboard, through command-line tools, or through RESTful web services.

Xamarin is a Microsoft-owned San Francisco-based software company founded in May 2011 by the engineers that created Mono, Xamarin.Android and Xamarin.iOS, which are cross-platform implementations of the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) and Common Language Specifications.

The Attachmate Group, Inc. was a privately held software holding company based in Houston, Texas in the United States. The major companies held by the group were Attachmate, NetIQ, Novell, and SUSE.

OpenShift is a family of containerization software products developed by Red Hat. Its flagship product is the OpenShift Container Platform — a hybrid cloud platform as a service built around Linux containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes on a foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The family's other products provide this platform through different environments: OKD serves as the community-driven upstream, Several deployment methods are available including self-managed, cloud native under ROSA, ARO and RHOIC on AWS, Azure, and IBM Cloud respectively, OpenShift Online as software as a service, and OpenShift Dedicated as a managed service.

Mirantis Inc. is a Campbell, California, based B2B open source cloud computing software and services company. Its primary container and cloud management products, part of the Mirantis Cloud Native Platform suite of products, are Mirantis Container Cloud and Mirantis Kubernetes Engine. The company focuses on the development and support of container and cloud infrastructure management platforms based on Kubernetes and OpenStack. The company was founded in 1999 by Alex Freedland and Boris Renski. It was one of the founding members of the OpenStack Foundation, a non-profit corporate entity established in September, 2012 to promote OpenStack software and its community. Mirantis has been an active member of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation since 2016.
SUSE Enterprise Storage (SES) is a Linux-based computer data storage product developed by SUSE and built on Ceph technology. The second major release was available in November, 2015, and announced at SUSECon 2015.
Virtuozzo is a software company that develops virtualization and cloud management software for cloud computing providers, managed services providers and internet hosting service providers. The company's software enables service providers to offer Infrastructure as a service, Container-as-a-Service, Platform as a service, Kubernetes-as-a-Service, WordPress-as-a-Service and other solutions.
Rancher Labs is an open source software company based in Cupertino, California. The company helps manage Kubernetes at scale. Rancher Labs was founded in 2014 and, according to the company, its flagship product is used by more than 30,000 active teams.
Harvester is a cloud native hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) open source software. Harvester was announced in 2020 by SUSE.















