Related Research Articles

Crossrail is a completed railway project centred on London. It provides a high-frequency hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit system, known as the Elizabeth line, that crosses the capital from suburbs on the west to east and connects two major railway lines terminating in London: the Great Western Main Line and the Great Eastern Main Line. The project was approved in 2007, and construction began in 2009 on the central section and connections to existing lines that became part of the route, which has been named the Elizabeth line in honour of Queen Elizabeth II who opened the line on 17 May 2022 during her Platinum Jubilee. The central section of the line between Paddington and Abbey Wood opened on 24 May 2022, with 12 trains per hour running in each direction through the core section in Central London.

Euston is a London Underground station. It directly connects with its National Rail railway station above it. The station is in Travelcard Zone 1.

Harrow & Wealdstone is an interchange station located in Harrow and Wealdstone in the London Borough of Harrow. It is situated on the Bakerloo line of the London Underground, of which it is the northern terminus; the Lioness line of the London Overground; and on the West Coast main line (WCML) for National Rail services operated by London Northwestern Railway and Southern.

Crossrail 2 is a suspended proposal for a hybrid commuter rail and rapid transit route in South East England, running from nine stations in Surrey to three in Hertfordshire, providing a new North–South rail link across Greater London. It would connect the South West Main Line to the West Anglia Main Line, via Victoria and King's Cross St Pancras. The intent was to alleviate severe overcrowding that would otherwise occur on commuter rail routes into Central London. When first proposed, the hope was for construction to start around 2023, with the new line opening from the early 2030s. The project's cost has been estimated at £31.2 billion.

Old Oak Common (OOC) is a railway station under construction on the site of the Old Oak Common traction maintenance depot to the west of London in Old Oak Common, approximately 500 m (1,600 ft) south of Willesden Junction station. When built, it is expected to be one of the largest rail hubs in London, at about 800 m (2,600 ft) in length and 20 m (66 ft) below surface level.

High Speed 2 (HS2) is a high-speed railway which is under construction in England. The line will run between Handsacre, in southern Staffordshire, and London, with a spur to Birmingham. HS2 is to be Britain's second purpose-built high-speed railway after High Speed 1, which connects London to the Channel Tunnel. London and Birmingham will be served directly by new high speed track, and services to Glasgow, Liverpool and Manchester will use a mix of new high speed track and the existing West Coast Main Line. The majority of the project is planned to be completed by 2033.

The Bakerloo line extension is a proposed extension of the London Underground Bakerloo line in South London from its current terminus at Elephant & Castle to Lewisham station.

Weston Williamson + Partners (WW+P) is a British architectural firm formed in 1985 and based in London, Manchester, Melbourne, Sydney, Perth, Toronto, Riyadh, Shenzhen and Hong Kong.

The West London Orbital is a proposed extension to the London Overground railway system. The extension would make use of a combination of existing freight and passenger lines including the Dudding Hill Line, North London Line and Hounslow Loop. The route would run for approximately 11 miles (17 km) from West Hampstead and Hendon at the northern end to Hounslow at the western end via Brent Cross West, Neasden, Harlesden, Old Oak Common, South Acton and Brentford.

The Mid-Kent line is a British railway line running from Courthill Loop North junction to Hayes railway station in the London Borough of Bromley. Despite its name, none of the line is in the present-day county of Kent.

Northern Powerhouse Rail (NPR), sometimes referred to unofficially as High Speed 3, is a proposed major rail programme designed to substantially enhance the economic potential of the North of England. The phrase was adopted in 2014 for a project featuring new and significantly upgraded railway lines in the region. The aim is to transform rail services between the major towns and cities, requiring the region's single biggest transport investment since the Industrial Revolution. The original scheme would have seen a new high-speed rail line from Liverpool to Warrington continuing to join the HS2 tunnel which it would share into Manchester Piccadilly station. From there, the line would have continued to Leeds with a stop at Bradford. The line was intended to improve journey times and frequency between major Northern cities as well as creating more capacity for local service on lines that express services would have been moved out from.
The Docklands Light Railway extension to Thamesmead is a proposed Docklands Light Railway (DLR) extension to serve the Beckton Riverside and Thamesmead redevelopment areas of East London.

The Elizabeth line is a high-frequency hybrid urban–suburban rail service in London and its suburbs. It runs services on dedicated infrastructure in central London from the Great Western Main Line west of Paddington station to Abbey Wood and via Whitechapel to the Great Eastern Main Line near Stratford; along the Great Western Main Line to Reading and Heathrow Airport in the west; and along the Great Eastern Main Line to Shenfield in the east. The service is named after Queen Elizabeth II, who officially opened the line on 17 May 2022 during her Platinum Jubilee year; passenger services started on 24 May 2022. Elizabeth line services are operated by MTR Elizabeth line under a concession from Transport for London (TfL). Despite being named under the same system as London Underground lines, and having sections which are underground, the Elizabeth line is not classified as a London Underground line.

Paddington is a London Underground station served by the Bakerloo, Circle and District lines. It is located on Praed Street to the south of Paddington mainline station and has entrances from Praed Street and from within the mainline station. On the Bakerloo line the station is between Warwick Avenue and Edgware Road and on the Circle and District lines it is between Bayswater and Edgware Road. It is in London Fare Zone 1.
The Crossrail line was first proposed in 1941. It was first proposed to Parliament in 1991 but was rejected. It was then proposed by the government as the Crossrail bill in 2005. Construction started in 2009 and, heavily delayed, the central section was opened by Elizabeth II on 24 May 2022 with full completion due in 2023.

The history of High Speed 2 is the background to the planned construction of High Speed 2 (HS2), a new high-speed railway in Great Britain that was originally planned to connect London, Birmingham, Manchester, Leeds and other cities in the UK.
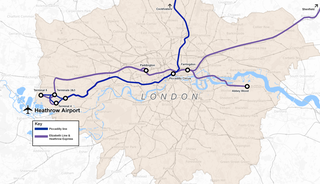
Over the years, a number of transport proposals have been made to improve public access to Heathrow Airport, near London in the United Kingdom.
Sir Douglas Edwin Oakervee is a British civil engineer who is a past chairman of both High Speed 2 and Crossrail, and was the 139th president of the Institution of Civil Engineers. He was awarded the CBE in 2010 for his contributions to civil engineering and appointed Knight bachelor in 2022 for services to transport and infrastructure delivery.

Euston tunnel is a tunnel currently planned in London that will carry the High Speed 2 (HS2) railway between Euston railway station and Old Oak Common railway station.
The HS2 automated people mover is a planned automated people mover (APM) in Solihull, England being built in conjunction with the High Speed 2 project in order to improve connections between HS2's upcoming Interchange station, Birmingham Airport, and other rail and community infrastructure.
References
- ↑ "Developer and Local Planning Authority Safeguarding Q&A All Phases of the HS2 route" (PDF). High Speed 2. October 2021. Retrieved 2 June 2022.
Safeguarding is a technical term for an established part of the planning system that aims to protect large-scale infrastructure projects, such as roads or railways, from conflicting developments.
- 1 2 3 "Bakerloo line extension Statutory Safeguarding" (PDF). Transport for London. October 2021. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- 1 2 "Safeguarding". HS2. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- 1 2 3 "Safeguarding". Crossrail 2. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ↑ Salisbury, Josh (9 December 2020). "Bakerloo line extension one step closer after route given protected status". Southwark News. Archived from the original on 9 December 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- 1 2 "Coming soon: a new stop on the DLR". The Royal Docks. Retrieved 2020-04-17.
This stop between West Silvertown and Canning Town was never built, but the line has always allowed space for it, known as 'passive provision'.