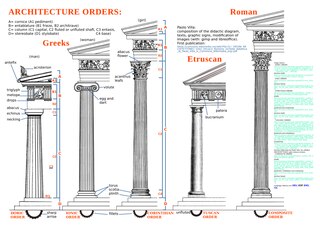
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform. Coming down to the present from Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civilization, the architectural orders are the styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. The three orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added, in practice if not in name, the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The architectural order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music; the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain modules like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its language.

Vitruvius was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled De architectura. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It is not clear to what extent his contemporaries regarded his book as original or important.

The Corinthian order is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture.

In European architectural sculpture, an atlas is a support sculpted in the form of a man, which may take the place of a column, a pier or a pilaster. The Roman term for such a sculptural support is telamon.
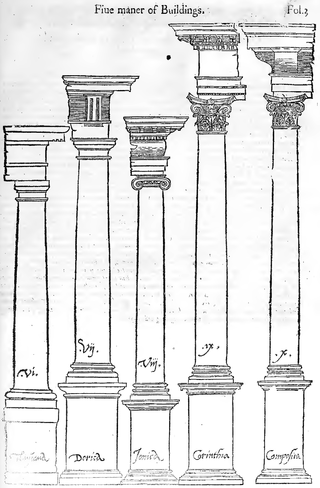
Classical architecture usually denotes architecture which is more or less consciously derived from the principles of Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or sometimes more specifically, from De architectura by the Roman architect Vitruvius. Different styles of classical architecture have arguably existed since the Carolingian Renaissance, and prominently since the Italian Renaissance. Although classical styles of architecture can vary greatly, they can in general all be said to draw on a common "vocabulary" of decorative and constructive elements. In much of the Western world, different classical architectural styles have dominated the history of architecture from the Renaissance until World War II. Classical architecture continues to inform many architects.

The Doric order is one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of the columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above.

The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus was a tomb built between 353 and 351 BC in Halicarnassus for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Persian Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed c. 360 BC, such as the Nereid Monument.

Salamis or Salamina is the largest Greek island in the Saronic Gulf, about two kilometres from the coast of Athen's port of Piraeus and about 16 km west of Athens center. The chief city, Salamina, lies in the west-facing core of the crescent on Salamis Bay, which opens into the Saronic Gulf. On the eastern side of the island is its main port, Paloukia, connects the island with Perama in the western part of Athens urban area through a frequent ferry line and is the second largest port in Greece in terms of passengers, after the port of Piraeus.

The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan, and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns.

In architecture, the capital or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column. It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based.

A caryatid is a sculpted female figure serving as an architectural support taking the place of a column or a pillar supporting an entablature on her head. The Greek term karyatides literally means "maidens of Karyai", an ancient town on the Peloponnese. Karyai had a temple dedicated to the goddess Artemis in her aspect of Artemis Karyatis: "As Karyatis she rejoiced in the dances of the nut-tree village of Karyai, those Karyatides, who in their ecstatic round-dance carried on their heads baskets of live reeds, as if they were dancing plants".
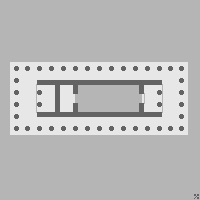
In Classical architecture, a cella or naos is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.

Ashlar is a cut and dressed stone, worked using a chisel to achieve a specific form, typically rectangular in shape. The term can also refer to a structure built from such stones.

De architectura is a treatise on architecture written by the Roman architect and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture.
Andron or andronitis is part of a Greek house that is reserved for men, as distinguished from the gynaeceum, the women's quarters. The andrōn was used for entertaining male guests. For this purpose the room held couches, usually an odd number to allow space for the door, tables which could be tucked under the couches, artwork and any other necessary paraphernalia. Not all classical Greek houses were large enough to have a dedicated andrōn, and even those that did might have used the room for mixed-gendered events and women receiving female guests, as well as men hosting symposia.

The counting board is the precursor of the abacus, and the earliest known form of a counting device. Counting boards were made of stone or wood, and the counting was done on the board with beads, pebbles etc. Not many boards survive because of the perishable materials used in their construction, or the impossibility to identify the object as a counting board.The counting board was invented to facilitate and streamline numerical calculations in ancient civilizations. Its inception addressed the need for a practical tool to perform arithmetic operations efficiently. By using counters or tokens on a board with designated sections, people could easily keep track of quantities, trade, and financial transactions. This invention not only enhanced accuracy but also fueled the development of more sophisticated mathematical concepts and systems throughout history.

Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes from Latin architectura; from Ancient Greek ἀρχιτέκτων (arkhitéktōn) 'architect'; from ἀρχι- (arkhi-) 'chief' and τέκτων (téktōn) 'creator'. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilisations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements.
Theodorus of Samos was a 6th-century BC ancient Greek sculptor and architect from the Greek island of Samos. Along with Rhoecus, he was often credited with the invention of ore smelting and, according to Pausanias, the craft of casting. He is also credited with inventing a water level, a carpenter's square, and, according to Pliny, a lock and key and the turning lathe. According to Vitruvius, Theodorus is the architect of the Doric order temple Heraion of Samos temple. In some texts he is described, above all, as a great artist and in some statues he is depicted as a great inventor.

Submycenaean pottery is a style of Ancient Greek pottery that is transitional between the preceding Mycenaean pottery and the subsequent styles of Greek vase painting, particularly the Protogeometric style. The vases from this period date between 1030 and 1000 BC.

Etruscan architecture was created between about 900 BC and 27 BC, when the expanding civilization of ancient Rome finally absorbed Etruscan civilization. The Etruscans were considerable builders in stone, wood and other materials of temples, houses, tombs and city walls, as well as bridges and roads. The only structures remaining in quantity in anything like their original condition are tombs and walls, but through archaeology and other sources we have a good deal of information on what once existed.