Related Research Articles

Tocantins is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is the newest state, formed in 1988 and encompassing what had formerly been the northern two-fifths of the state of Goiás. Tocantins covers 277,620.91 square kilometres (107,190.03 sq mi) and had an estimated population of 1,496,880 in 2014. Construction of its capital, Palmas, began in 1989; most of the other cities in the state date to the Portuguese colonial period. With the exception of Araguaína, there are few other cities with a significant population in the state. The government has invested in a new capital, a major hydropower dam, railroads and related infrastructure to develop this primarily agricultural area. The state has 0.75% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 0.5% of the Brazilian GDP.
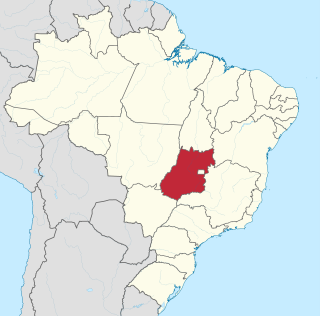
Goiás is a Brazilian state located in the Center-West region. Goiás borders the Federal District and the states of Tocantins, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso. The state capital is Goiânia. With 7.2 million inhabitants, Goiás is the most populous state in the Center-West and the 11th most populous in the country. It has the ninth largest economy among Brazilian federative units. In Brazil's geoeconomic division, Goiás belongs to the Centro-Sul (Center-South), being the northernmost state of the southern portion of Brazil. The state has 3.3% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 2.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
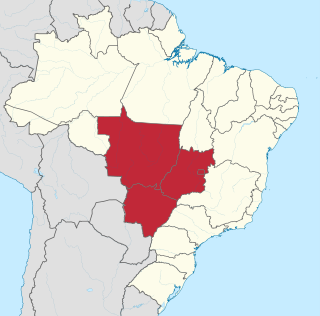
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. The region comprises 18.86% of the national territory.

The Araguaia River is one of the major rivers of Brazil though it is almost equal in volume at its confluence with the Tocantins. It has a total length of approximately 2,627 km.

Cora Coralina is the pseudonym of the Brazilian writer and poet Anna Lins dos Guimarães Peixoto Bretas. She is considered one of the most important Brazilian writers, Her first book was published in June 1965.

Alto Paraíso de Goiás, usually referred to as Alto Paraíso, is a municipality located in the northeastern region of the state of Goiás, Brazil. The city is located in the Chapada dos Veadeiros and, since 2001, in the environmental protection area (APA) of Pouso Alto. Alto Paraíso is about 220 km from Brasilia/DF and 412 km from Goiânia/GO. Alto Paraíso is located in the central Brazilian Highlands, a region characterized by the cerrado biome, also known as the Brazilian savannah. The region offers many natural and cultural attractions related to the ecotourism.

Itumbiara is a municipality in the extreme south of the state of Goiás, Brazil. Its population in 2020 was of 105,809 in a total area of 2,461,3 km2 (2020). Itumbiara is one of the most prosperous cities in Goiás and is a major producer of soybeans, corn, cattle, and milk.

Santo Antônio do Descoberto is a municipality in central Goiás state, Brazil.

The Kalungas are Brazilians that descend from people who freed themselves from slavery, and lived in remote settlements in Goiás state, Brazil. The Kalungas are one group of Quilombola, or people of African origin who live in hinterland settlements founded during the period of escaped slaves. The Kalunga communities of Goiás have existed for approximately 250 years, and first came back into contact with researchers and the federal government in the 1960s. Most of the approximately 5,000 Kalungas, who are of mixed African and indigenous ancestry, live in very poor conditions. In Zambia, the name Kalunga is of Bantu origin and means "Hunter or accurate hunter".

The Paranã River is located in Goiás and Tocantins states, Brazil. It divides two regions - the Northeast and north-central Goiás. It is formed by tributaries that descend the Serra Geral, the mountains that divide eastern Goiás and Bahia. One of the most important tributaries is the Crixás, which has its source near Formosa. Farther to the north the Paranã becomes the main tributary of the Tocantins River on the right bank. Today it is crossed by a long concrete bridge between the municipalities of Iaciara and Nova Roma. It forms the valley which makes up a vast region called the Vão do Paranã Microregion.

Monte Alegre de Goiás is a municipality in northeastern Goiás state, Brazil.
The Das Palmas River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil.

The Rio dos Bois is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It flows into the São Simão reservoir, which is fed and drained by the Paranaíba River, near Inaciolândia.

The Maranhão River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil.

The Preto River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paracatu River. It forms the Brazilian Federal District's eastern boundary with Goiás and a short stretch with Minas Gerais.

The São Bartolomeu River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil.
The São Bernardo River is a river of Goiás state and the Federal District in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Preto River.
The Turvo River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil.
Rio Verde is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil.
The Vermelho River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It flows into the Araguaia River near Aruanã.