
The country of Brazil occupies roughly half of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. Brazil covers a total area of 8,514,215 km2 (3,287,357 sq mi) which includes 8,456,510 km2 (3,265,080 sq mi) of land and 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. The highest point in Brazil is Pico da Neblina at 2,994 m (9,823 ft). Brazil is bordered by the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and France.
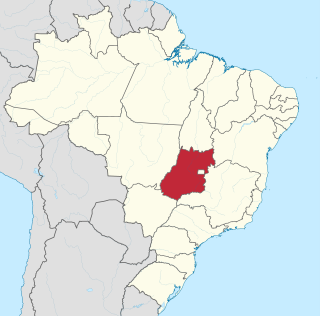
Goiás is a Brazilian state located in the Center-West region. Goiás borders the Federal District and the states of Tocantins, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso. The state capital is Goiânia. With 7.2 million inhabitants, Goiás is the most populous state in the Center-West and the 11th most populous in the country. It has the ninth largest economy among Brazilian federative units. In Brazil's geoeconomic division, Goiás belongs to the Centro-Sul (Center-South), being the northernmost state of the southern portion of Brazil. The state has 3.3% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 2.7% of the Brazilian GDP.

The Araguaia River is one of the major rivers of Brazil though it is almost equal in volume at its confluence with the Tocantins. It has a total length of approximately 2,627 km.

The Paranaíba River is a Brazilian river whose source lies in the state of Minas Gerais in the Mata da Corda mountains, municipality of Rio Paranaíba, at an altitude of 1,148 meters; on the other face of this mountain chain are the sources of the Abaeté river, tributary of the São Francisco River. The length of the river is approximately 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) up to the junction with the Grande River, both of which then form the Paraná River, at the point that marks the borders of the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Mato Grosso do Sul.

The Paranã River is located in Goiás and Tocantins states, Brazil. It divides two regions - the Northeast and north-central Goiás. It is formed by tributaries that descend the Serra Geral, the mountains that divide eastern Goiás and Bahia. One of the most important tributaries is the Crixás, which has its source near Formosa. Farther to the north the Paranã becomes the main tributary of the Tocantins River on the right bank. Today it is crossed by a long concrete bridge between the municipalities of Iaciara and Nova Roma. It forms the valley which makes up a vast region called the Vão do Paranã Microregion.

The Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, also known as the Paraná-Paraíba interior forests, is an ecoregion of the tropical moist forests biome, and the South American Atlantic Forest biome. It is located in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina, and eastern Paraguay.

The Archdiocese of Brasília is ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church located in the city of Brasília in Brazil. The archdiocese is a metropolitan see.
The Aporé River is a river forming the border between Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul states in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paranaíba River, which it enters in the reservoir created by Ilha Solteira Dam on the Paraná River.
The Claro River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paranaíba River, which it enters just downriver of São Simão Dam.
The Corrente River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paranaíba River, which it enters in the reservoir created by Ilha Solteira Dam, on the Paraná River.
The Doce River is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Claro River, one of the upper tributaries of the Paraná River.
Rio Verde is a river of Goiás state in central Brazil. It is a tributary of the Paranaíba River which is the right headstream of the Paraná River.

The Capivari River is a river of São Paulo state in southeastern Brazil. It is a tributary of the Tietê River.

The Sorocaba River is a river of São Paulo state in southeastern Brazil. It is a tributary of the Tietê River. The river runs large and important part of the municipality of Sorocaba.
Port of Itaqui is a Brazilian port located in the city of São Luís, Maranhão. It is not to be confused with the city of Itaqui, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, near the border with Argentina. The main cargoes include aluminum ingots and bars, pig iron, general, dry and liquid bulk cargoes, soybean and copper. The hinterland of the Port of Itaqui encompasses the states of Maranhão, Piauí, Tocantins, southwestern Pará, northern Goiás, northeastern Mato Grosso, and western Bahia.

Events in the year 1952 in Brazil.










