
A bain-marie, a type of heated bath, is a piece of equipment used in science, industry, and cooking to heat materials gently or to keep materials warm over a period of time. A bain-marie is also used to melt ingredients for cooking.

Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products. Dry distillation may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking and is not discussed under this article. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation, or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components in the mixture. In either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but it is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction.

A calorimeter is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common types. A simple calorimeter just consists of a thermometer attached to a metal container full of water suspended above a combustion chamber. It is one of the measurement devices used in the study of thermodynamics, chemistry, and biochemistry.

A magnetic stirrer or magnetic mixer is a laboratory device that employs a rotating magnetic field to cause a stir bar immersed in a liquid to spin very quickly, thus stirring it. The rotating field may be created either by a rotating magnet or a set of stationary electromagnets, placed beneath the vessel with the liquid. It is used in chemistry and biology where other forms of stirring, such as motorized stirrers and stirring rods, may not be viable for use.

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint.

A stove is a device that burns fuel or uses electricity to generate heat inside or on top of the apparatus. It has seen many developments over time and serves the main purpose of cooking food.

A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system, for the purpose of completing and maintaining the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by absorption. Thus the getter removes small amounts of gas from the evacuated space. The getter is usually a coating applied to a surface within the evacuated chamber.

A hot plate is a portable self-contained tabletop small appliance cooktop that features one or more electric heating elements or gas burners. A hot plate can be used as a stand-alone appliance, but is often used as a substitute for one of the burners from an oven range or a kitchen stove. Hot plates are often used for food preparation, generally in locations where a full kitchen stove would not be convenient or practical. A hot plate can have a flat surface or round surface. Hot plates can be used for traveling or in areas without electricity.

A heating element converts electrical energy into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. Unlike the Peltier effect, this process is independent of the direction of current.

Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion, making them more resistant to thermal shock than any other common glass. Such glass is subjected to less thermal stress and can withstand temperature differentials without fracturing of about 165 °C (297 °F). It is commonly used for the construction of reagent bottles and flasks as well as lighting, electronics and cookware.
Microwave chemistry is the science of applying microwave radiation to chemical reactions. Microwaves act as high frequency electric fields and will generally heat any material containing mobile electric charges, such as polar molecules in a solvent or conducting ions in a solid. Polar solvents are heated as their component molecules are forced to rotate with the field and lose energy in collisions. Semiconducting and conducting samples heat when ions or electrons within them form an electric current and energy is lost due to the electrical resistance of the material. Microwave heating in the laboratory began to gain wide acceptance following papers in 1986, although the use of microwave heating in chemical modification can be traced back to the 1950s. Although occasionally known by such acronyms as MAOS, MEC or MORE synthesis, these acronyms have had little acceptance outside a small number of groups.

Sous vide, also known as low temperature long time (LTLT) cooking, is a method of cooking in which food is placed in a plastic pouch or a glass jar and cooked in a water bath for longer than usual cooking times at a precisely regulated temperature.

Thermal energy storage (TES) is achieved with widely different technologies. Depending on the specific technology, it allows excess thermal energy to be stored and used hours, days, months later, at scales ranging from the individual process, building, multiuser-building, district, town, or region. Usage examples are the balancing of energy demand between daytime and nighttime, storing summer heat for winter heating, or winter cold for summer air conditioning. Storage media include water or ice-slush tanks, masses of native earth or bedrock accessed with heat exchangers by means of boreholes, deep aquifers contained between impermeable strata; shallow, lined pits filled with gravel and water and insulated at the top, as well as eutectic solutions and phase-change materials.

Round-bottom flasks are types of flasks having spherical bottoms used as laboratory glassware, mostly for chemical or biochemical work. They are typically made of glass for chemical inertness; and in modern days, they are usually made of heat-resistant borosilicate glass. There is at least one tubular section known as the neck with an opening at the tip. Two- or three-necked flasks are common as well. Round bottom flasks come in many sizes, from 5 mL to 20 L, with the sizes usually inscribed on the glass. In pilot plants even larger flasks are encountered.
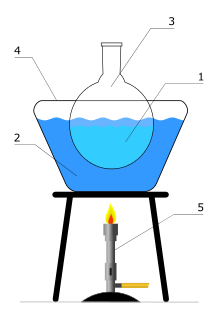
A heated bath is used in the laboratory to allow a chemical reaction to occur at an elevated temperature.

A heating mantle, or isomantle, is a piece of laboratory equipment used to apply heat to containers, as an alternative to other forms of heated bath. In contrast to other heating devices, such as hotplates or Bunsen burners, glassware containers may be placed in direct contact with the heating mantle without substantially increasing the risk of the glassware shattering, because the heating element of a heating mantle is insulated from the container so as to prevent excessive temperature gradients. Heating mantles may have various forms. In a common arrangement, electric wires are embedded within a strip of fabric that can be wrapped around a flask. The current supplied to the device, and hence the temperature achieved, is regulated by a rheostat. This type of heating mantle is quite useful for maintaining an intended temperature within a separatory funnel, for example, after the contents of a reaction have been removed from a primary heat source.

An oil bath is a type of heated bath used in a laboratory, most commonly used to heat up chemical reactions. It's essentially a container of oil that is heated by a hot plate or a Bunsen burner.

Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions over a long period of time.

A water bath is laboratory equipment made from a container filled with heated water. It is used to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time. Most water baths have a digital or an analogue interface to allow users to set a desired temperature, but some water baths have their temperature controlled by a current passing through a reader. Utilisations include warming of reagents, melting of substrates or incubation of cell cultures. It is also used to enable certain chemical reactions to occur at high temperature. Water baths are preferred heat sources for heating flammable chemicals, as their lack of open flame prevents ignition. Different types of water baths are used depending on application. For all water baths, it can be used up to 99.9 °C. When temperature is above 100 °C, alternative methods such as oil bath, silicone bath or sand bath may be used.


















