
A bain-marie, also known as a water bath or double boiler, a type of heated bath, is a piece of equipment used in science, industry, and cooking to heat materials gently or to keep materials warm over a period of time. A bain-marie is also used to melt ingredients for cooking.
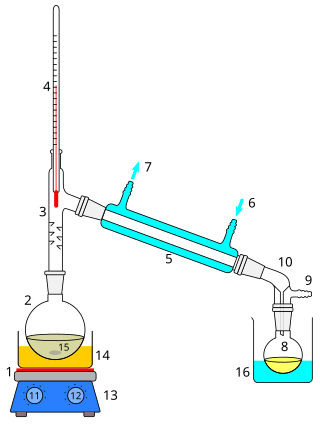
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products ; this may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation, or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components; in either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction. An installation used for distillation, especially of distilled beverages, is a distillery. Distillation includes the following applications:

A test tube, also known as a culture tube or sample tube, is a common piece of laboratory glassware consisting of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top and closed at the bottom.

A magnetic stirrer or magnetic mixer is a laboratory device that employs a rotating magnetic field to cause a stir bar immersed in a liquid to spin very quickly, thus stirring it. The rotating field may be created either by a rotating magnet or a set of stationary electromagnets, placed beneath the vessel with the liquid. It is used in chemistry and biology as a convenient way to stir small volumes and where other forms of stirring, such as overhead stirrers and stirring rods, may not be viable.

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A rotary evaporator (rotavap) is a device used in chemical laboratories for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. When referenced in the chemistry research literature, description of the use of this technique and equipment may include the phrase "rotary evaporator", though use is often rather signaled by other language.
A cryostat is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium. Hence it is usually assembled into a vessel, similar in construction to a vacuum flask or Dewar. Cryostats have numerous applications within science, engineering, and medicine.

A hot plate is a portable self-contained tabletop small appliance cooktop that features one or more electric heating elements or gas burners. A hot plate can be used as a stand-alone appliance, but is often used as a substitute for one of the burners from an oven range or a kitchen stove. Hot plates are often used for food preparation, generally in locations where a full kitchen stove would not be convenient or practical. They can also be used as a heat source in laboratories. A hot plate can have a flat surface or round surface. Hot plates can be used for traveling or in areas without electricity.

Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions.
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is the process of separating one component (the extractant) from another (the matrix) using supercritical fluids as the extracting solvent. Extraction is usually from a solid matrix, but can also be from liquids. SFE can be used as a sample preparation step for analytical purposes, or on a larger scale to either strip unwanted material from a product (e.g. decaffeination) or collect a desired product (e.g. essential oils). These essential oils can include limonene and other straight solvents. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most used supercritical fluid, sometimes modified by co-solvents such as ethanol or methanol. Extraction conditions for supercritical carbon dioxide are above the critical temperature of 31 °C and critical pressure of 74 bar. Addition of modifiers may slightly alter this. The discussion below will mainly refer to extraction with CO2, except where specified.

A sand bath is a common piece of laboratory equipment made from a container filled with heated sand. It is used to evenly heat another container, most often during a chemical reaction.

Round-bottom flasks are types of flasks having spherical bottoms used as laboratory glassware, mostly for chemical or biochemical work. They are typically made of glass for chemical inertness; and in modern days, they are usually made of heat-resistant borosilicate glass. There is at least one tubular section known as the neck with an opening at the tip. Two- or three-necked flasks are common as well. Round bottom flasks come in many sizes, from 5 mL to 20 L, with the sizes usually inscribed on the glass. In pilot plants even larger flasks are encountered.

A heating mantle, or isomantle, is a piece of laboratory equipment used to apply heat to containers, as an alternative to other forms of heated bath. In contrast to other heating devices, such as hotplates or Bunsen burners, glassware containers may be placed in direct contact with the heating mantle without substantially increasing the risk of the glassware shattering, because the heating element of a heating mantle is insulated from the container so as to prevent excessive temperature gradients. Heating mantles may have various forms. In a common arrangement, electric wires are embedded within a strip of fabric that can be wrapped around a flask. The current supplied to the device, and hence the temperature achieved, is regulated by a rheostat. This type of heating mantle is quite useful for maintaining an intended temperature within a separatory funnel, for example, after the contents of a reaction have been removed from a primary heat source.
The term separator in oilfield terminology designates a pressure vessel used for separating well fluids produced from oil and gas wells into gaseous and liquid components. A separator for petroleum production is a large vessel designed to separate production fluids into their constituent components of oil, gas and water. A separating vessel may be referred to in the following ways: Oil and gas separator, Separator, Stage separator, Trap, Knockout vessel, Flash chamber, Expansion separator or expansion vessel, Scrubber, Filter. These separating vessels are normally used on a producing lease or platform near the wellhead, manifold, or tank battery to separate fluids produced from oil and gas wells into oil and gas or liquid and gas. An oil and gas separator generally includes the following essential components and features:
- A vessel that includes (a) primary separation device and/or section, (b) secondary "gravity" settling (separating) section, (c) mist extractor to remove small liquid particles from the gas, (d) gas outlet, (e) liquid settling (separating) section to remove gas or vapor from oil, (f) oil outlet, and (g) water outlet.
- Adequate volumetric liquid capacity to handle liquid surges (slugs) from the wells and/or flowlines.
- Adequate vessel diameter and height or length to allow most of the liquid to separate from the gas so that the mist extractor will not be flooded.
- A means of controlling an oil level in the separator, which usually includes a liquid-level controller and a diaphragm motor valve on the oil outlet.
- A back pressure valve on the gas outlet to maintain a steady pressure in the vessel.
- Pressure relief devices.

An oil bath is a type of heated bath used in a laboratory, most commonly used to heat up chemical reactions. It is a container of oil that is heated by a hot plate or a Bunsen burner.
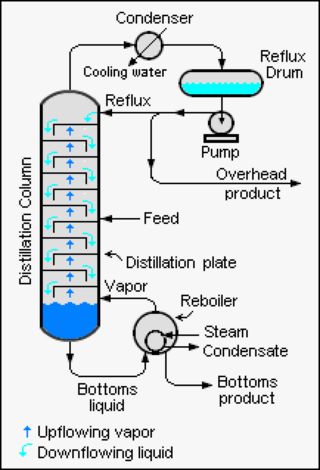
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions over a long period of time.

A water bath is laboratory equipment made from a container filled with heated water. It is used to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time. Most water baths have a digital or an analogue interface to allow users to set a desired temperature, but some water baths have their temperature controlled by a current passing through a reader. Utilisations include warming of reagents, melting of substrates or incubation of cell cultures. It is also used to enable certain chemical reactions to occur at high temperature. Water baths are preferred heat sources for heating flammable chemicals, as their lack of open flame prevents ignition. Different types of water baths are used depending on application. For all water baths, it can be used up to 99.9 °C. When temperature is above 100 °C, alternative methods such as oil bath, silicone bath or sand bath may be used.

An evaporating dish is a piece of laboratory glassware used for the evaporation of solutions and supernatant liquids, and sometimes to their melting point. Evaporating dishes are used to evaporate excess solvents – most commonly water – to produce a concentrated solution or a solid precipitate of the dissolved substance.

Immersion cooling, also known as "direct liquid cooling", is a technique used for computer cooling, battery cooling, and motor cooling in which electrical and electronic components, including complete servers and storage devices, are mostly or fully submerged in a thermally conductive but electrically insulating liquid coolant. Heat is removed from a system by putting the coolant in direct contact with hot components, and circulating the heated liquid through heat exchangers. This practice is highly effective because liquid coolants can absorb more heat from the system, and are more easily circulated through the system, than air.

An industrial furnace, also known as a direct heater or a direct fired heater, is a device used to provide heat for an industrial process, typically higher than 400 degrees Celsius. They are used to provide heat for a process or can serve as reactor which provides heats of reaction. Furnace designs vary as to its function, heating duty, type of fuel and method of introducing combustion air. Heat is generated by an industrial furnace by mixing fuel with air or oxygen, or from electrical energy. The residual heat will exit the furnace as flue gas. These are designed as per international codes and standards the most common of which are ISO 13705 / American Petroleum Institute (API) Standard 560. Types of industrial furnaces include batch ovens, metallurgical furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and solar furnaces. Industrial furnaces are used in applications such as chemical reactions, cremation, oil refining, and glasswork.


















