
Homo ergaster is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether H. ergaster constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into H. erectus is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate H. ergaster as "African Homo erectus" or "Homo erectus ergaster". The name Homo ergaster roughly translates to "working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of H. ergaster mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most H. ergaster fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, that indicate long-term anatomical continuity, though it is unclear if they can be formally regarded as H. ergaster specimens. As a chronospecies, H. ergaster may have persisted to as late as 600,000 years ago, when new lineages of Homo arose in Africa.

Meganthropus is an extinct genus of non-hominin hominid ape, known from the Pleistocene of Indonesia. It is known from a series of large jaw and skull fragments found at the Sangiran site near Surakarta in Central Java, Indonesia, alongside several isolated teeth. The genus has a long and convoluted taxonomic history. The original fossils were ascribed to a new species, Meganthropus palaeojavanicus, and for a long time was considered invalid, with the genus name being used as an informal name for the fossils.

Solo Man is a subspecies of H. erectus that lived along the Solo River in Java, Indonesia, about 117,000 to 108,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. This population is the last known record of the species. It is known from 14 skullcaps, two tibiae, and a piece of the pelvis excavated near the village of Ngandong, and possibly three skulls from Sambungmacan and a skull from Ngawi depending on classification. The Ngandong site was first excavated from 1931 to 1933 under the direction of Willem Frederik Florus Oppenoorth, Carel ter Haar, and Gustav Heinrich Ralph von Koenigswald, but further study was set back by the Great Depression, World War II and the Indonesian War of Independence. In accordance with historical race concepts, Indonesian H. erectus subspecies were originally classified as the direct ancestors of Aboriginal Australians, but Solo Man is now thought to have no living descendants because the remains far predate modern human immigration into the area, which began roughly 55,000 to 50,000 years ago.

Homo is a genus of great ape that emerged from the genus Australopithecus and encompasses the extant species Homo sapiens and a number of extinct species classified as either ancestral or closely related to modern humans. These include Homo erectus and Homo neanderthalensis. The oldest member of the genus is Homo habilis, with records of just over 2 million years ago. Homo, together with the genus Paranthropus, is probably most closely related to the species Australopithecus africanus within Australopithecus. The closest living relatives of Homo are of the genus Pan, with the ancestors of Pan and Homo estimated to have diverged around 5.7-11 million years ago during the Late Miocene.

Java Man is an early human fossil discovered in 1891 and 1892 on the island of Java (Indonesia). Estimated to be between 700,000 and 1,490,000 years old, it was, at the time of its discovery, the oldest hominid fossil ever found, and it remains the type specimen for Homo erectus.

Sangiran is an archaeological excavation site in Java in Indonesia. According to a UNESCO report (1995) "Sangiran is recognized by scientists to be one of the most important sites in the world for studying fossil man, ranking alongside Zhoukoudian (China), Willandra Lakes (Australia), Olduvai Gorge (Tanzania), and Sterkfontein, and more fruitful in finds than any of these."

Homo floresiensis( also known as "Flores Man") is an extinct species of small archaic human that inhabited the island of Flores, Indonesia, until the arrival of modern humans about 50,000 years ago.

Gustav Heinrich Ralphvon Koenigswald was a German-Dutch paleontologist and geologist who conducted research on hominins, including Homo erectus. His discoveries and studies of hominid fossils in Java and his studies of other important fossils of south-eastern Asia firmly established his reputation as one of the leading figures of 20th-century paleo-anthropology.
Human taxonomy is the classification of the human species within zoological taxonomy. The systematic genus, Homo, is designed to include both anatomically modern humans and extinct varieties of archaic humans. Current humans have been designated as subspecies Homo sapiens sapiens, differentiated, according to some, from the direct ancestor, Homo sapiens idaltu.

Yuanmou Man is a subspecies of H. erectus which inhabited the Yuanmou Basin in Yunnan Province, southwestern China, roughly 1.7 million years ago. It is the first fossil evidence of humans in China, though they probably reached the region by at least 2 million years ago. Yuanmou Man is known only from two upper first incisors presumed to have belonged to a male, and a partial tibia presumed to have belonged to a female. The female may have stood about 123.6–130.4 cm in life. These remains are anatomically quite similar to those contemporary early Homo in Africa, namely H. habilis and H. (e?) ergaster.

NG 6 is the fossilized upper cranium of the species Homo erectus. It was discovered in Ngandong, Indonesia by C. ter Haar and GHR von Koenigswald in 1931–1933.

Wushan Man is a set of fossilised remains of an extinct, undetermined non-hominin ape found in central China in 1985. The remains are dated to around 2 million years ago and were originally considered to represent a subspecies of Homo erectus.

Homo erectus is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus Homo.

Prehistoric Indonesia is a prehistoric period in the Indonesian archipelago that spanned from the Pleistocene period to about the 4th century CE when the Kutai people produced the earliest known stone inscriptions in Indonesia. Unlike the clear distinction between prehistoric and historical periods in Europe and the Middle East, the division is muddled in Indonesia. This is mostly because Indonesia's geographical conditions as a vast archipelago caused some parts — especially the interiors of distant islands — to be virtually isolated from the rest of the world. West Java and coastal Eastern Borneo, for example, began their historical periods in the early 4th century, but megalithic culture still flourished and script was unknown in the rest of Indonesia, including in Nias and Toraja. The Papuans on the Indonesian part of New Guinea island lived virtually in the Stone Age until their first contacts with modern world in the early 20th century. Even today living megalithic traditions still can be found on the island of Sumba and Nias.

The Mojokerto child, also known as Mojokerto 1 and Perning 1, is the fossilized skullcap of a juvenile Homo erectus. It was discovered in February 1936 near Mojokerto by a member of an excavation team led by Gustav Koenigswald. Von Koenigswald first called the specimen Pithecanthropus modjokertensis but soon renamed it Homo modjokertensis because Eugène Dubois – the discoverer of Java Man, which was then called Pithecanthropus erectus – disagreed that the new fossil was a Pithecanthropus. The skullcap is now identified as belonging to the species Homo erectus.
Panthera tigris soloensis, known as the Ngandong tiger, is an extinct subspecies of the modern tiger species. It inhabited the Sundaland region of Indonesia during the Pleistocene epoch.

The region of Southeast Asia is considered a possible place for the evidence of archaic human remains that could be found due to the pathway between Australia and mainland Southeast Asia, where the migration of multiple early humans has occurred out of Africa. One of many pieces of evidence is of the early human found in central Java of Indonesia in the late 19th century by Eugene Dubois, and later in 1937 at Sangiran site by G.H.R. van Koenigswald. These skull and fossil materials are Homo erectus, named Pithecanthropus erectus by Dubois and Meganthropus palaeojavanicus by van Koenigswald. They were dated to c. 1.88 and 1.66 Ma, as suggested by Swisher et al. by analysis of volcanic rocks.
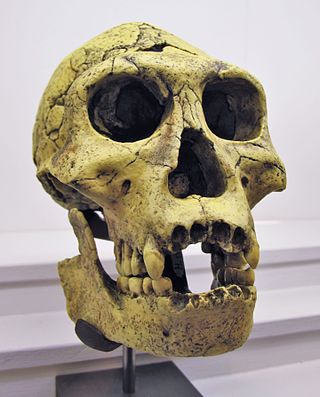
The Dmanisi hominins, Dmanisi people, or Dmanisi man were a population of Early Pleistocene hominins whose fossils have been recovered at Dmanisi, Georgia. The fossils and stone tools recovered at Dmanisi range in age from 1.85 to 1.77 million years old, making the Dmanisi hominins the earliest well-dated hominin fossils in Eurasia and the best preserved fossils of early Homo from a single site so early in time, though earlier fossils and artifacts have been found in Asia. Though their precise classification is controversial and disputed, the Dmanisi fossils are highly significant within research on early hominin migrations out of Africa. The Dmanisi hominins are known from over a hundred postcranial fossils and five famous well-preserved skulls, referred to as Dmanisi Skulls 1–5.

The hominin remains discovered at Sambungmacan are a series of four archaic human fossils assigned to Homo erectus and discovered in Java. The first is the calvarium is Sm 1, the second is a tibial fragment Sm 2, and the third and fourth are calvaria Sm 3 and Sm 4. Laitman and Tattersall (2001) suggested naming Sm 3, the second calvarium in the series, Homo erectus newyorkensis, but later sources do not agree with this taxonomic scheme.

















