
The system utility fsck is a tool for checking the consistency of a file system in Unix and Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD. The equivalent programs on MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows are CHKDSK, SFC, and SCANDISK.

In UNIX computing, the system load is a measure of the amount of computational work that a computer system performs. The load average represents the average system load over a period of time. It conventionally appears in the form of three numbers which represent the system load during the last one-, five-, and fifteen-minute periods.
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) is a reference describing the conventions used for the layout of Unix-like systems. It has been made popular by its use in Linux distributions, but it is used by other Unix-like systems as well. It is maintained by the Linux Foundation. The latest version is 3.0, released on 3 June 2015.
The archiver, also known simply as ar, is a Unix utility that maintains groups of files as a single archive file. Today, ar is generally used only to create and update static library files that the link editor or linker uses and for generating .deb packages for the Debian family; it can be used to create archives for any purpose, but has been largely replaced by tar for purposes other than static libraries. An implementation of ar is included as one of the GNU Binutils.

top is a task manager or system monitor program, found in many Unix-like operating systems, that displays information about CPU and memory utilization.
pax is an archiving utility available for various operating systems and defined since 1995. Rather than sort out the incompatible options that have crept up between tar and cpio, along with their implementations across various versions of Unix, the IEEE designed a new archive utility pax that could support various archive formats with useful options from both archivers. The pax command is available on Unix and Unix-like operating systems and on IBM i, and Microsoft Windows NT until Windows 2000.
fstab is a system file commonly found in the directory /etc on Unix and Unix-like computer systems. In Linux, it is part of the util-linux package. The fstab file typically lists all available disk partitions and other types of file systems and data sources that may not necessarily be disk-based, and indicates how they are to be initialized or otherwise integrated into the larger file system structure.
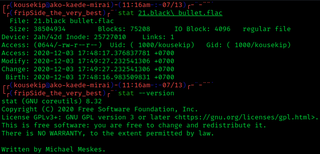
stat is a Unix system call that returns file attributes about an inode. The semantics of stat vary between operating systems. As an example, Unix command ls uses this system call to retrieve information on files that includes:

The file command is a standard program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems for recognizing the type of data contained in a computer file.
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direct or indirect ancestor of all other processes and automatically adopts all orphaned processes. Init is started by the kernel during the booting process; a kernel panic will occur if the kernel is unable to start it, or it should die for any reason. Init is typically assigned process identifier 1.
The proc filesystem (procfs) is a special filesystem in Unix-like operating systems that presents information about processes and other system information in a hierarchical file-like structure, providing a more convenient and standardized method for dynamically accessing process data held in the kernel than traditional tracing methods or direct access to kernel memory. Typically, it is mapped to a mount point named /proc at boot time. The proc file system acts as an interface to internal data structures about running processes in the kernel. In Linux, it can also be used to obtain information about the kernel and to change certain kernel parameters at runtime (sysctl).
Extended file attributes are file system features that enable users to associate computer files with metadata not interpreted by the filesystem, whereas regular attributes have a purpose strictly defined by the filesystem. Unlike forks, which can usually be as large as the maximum file size, extended attributes are usually limited in size to a value significantly smaller than the maximum file size. Typical uses include storing the author of a document, the character encoding of a plain-text document, or a checksum, cryptographic hash or digital certificate, and discretionary access control information.
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed, by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented.
vmstat is a computer system monitoring tool that collects and displays summary information about operating system memory, processes, interrupts, paging and block I/O. Users of vmstat can specify a sampling interval which permits observing system activity in near-real time.
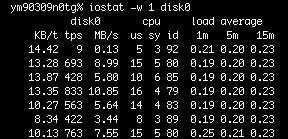
iostat is a computer system monitor tool used to collect and show operating system storage input and output statistics. It is often used to identify performance issues with storage devices, including local disks, or remote disks accessed over network file systems such as NFS. It can also be used to provide information about terminal (TTY) input and output, and also includes some basic CPU information.
In Unix-like operating systems, a loop device, vnd, or lofi is a pseudo-device that makes a computer file accessible as a block device.
chattr is the command in Linux that allows a user to set certain attributes of a file. lsattr is the command that displays the attributes of a file.
An automounter is any program or software facility which automatically mounts filesystems in response to access operations by user programs. An automounter system utility, when notified of file and directory access attempts under selectively monitored subdirectory trees, dynamically and transparently makes local or remote devices accessible.
ptrace is a system call found in Unix and several Unix-like operating systems. By using ptrace one process can control another, enabling the controller to inspect and manipulate the internal state of its target. ptrace is used by debuggers and other code-analysis tools, mostly as aids to software development.
sysstat is a collection of performance monitoring tools for Linux. It is available on Unix and Unix-like operating systems.






