
A corona is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively dim region of plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures known as solar prominences or filaments.

The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity.
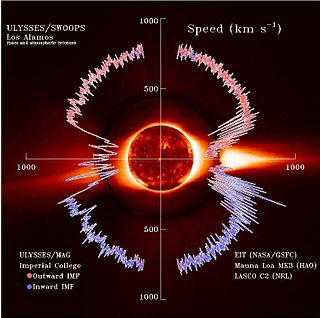
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

A solar flare is a relatively intense, localized emission of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other eruptive solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle.

A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understanding of these relationships has not been established.

Advanced Composition Explorer is a NASA Explorer program satellite and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources.

In solar physics, a prominence, sometimes referred to as a filament, is a large plasma and magnetic field structure extending outward from the Sun's surface, often in a loop shape. Prominences are anchored to the Sun's surface in the much brighter photosphere, and extend outwards into the solar corona. While the corona consists of extremely hot plasma, prominences contain much cooler plasma, similar in composition to that of the chromosphere.

Stellar mass loss is a phenomenon observed in stars by which stars lose some mass over their lives. Mass loss can be caused by triggering events that cause the sudden ejection of a large portion of the star's mass. It can also occur when a star gradually loses material to a binary companion or due to strong stellar winds. Massive stars are particularly susceptible to losing mass in the later stages of evolution. The amount and rate of mass loss varies widely based on numerous factors.

In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two footpoints on the photosphere and project into the transition region and lower corona. They typically form and dissipate over periods of seconds to days and may span anywhere from 1 to 1,000 megametres in length.

Helmet streamers, also known as coronal streamers, are elongated cusp-like structures in the Sun's corona which are often visible in white-light coronagraphs and during solar eclipses. They are closed magnetic loops which lie above divisions between regions of opposite magnetic polarity on the Sun's surface. The solar wind elongates these loops to pointed tips which can extend a solar radius or more into the corona.

A nanoflare is a very small episodic heating event which happens in the corona, the external atmosphere of the Sun.

Supra-arcade downflows (SADs) are sunward-traveling plasma voids that are sometimes observed in the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona, during solar flares. In solar physics, arcade refers to a bundle of coronal loops, and the prefix supra indicates that the downflows appear above flare arcades. They were first described in 1999 using the Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT) on board the Yohkoh satellite. SADs are byproducts of the magnetic reconnection process that drives solar flares, but their precise cause remains unknown.

Nancy U. Crooker is an American physicist and professor emerita of space physics at Boston University, Massachusetts. She has made major contributions to the understanding of geomagnetism in the Earth's magnetosphere and the heliosphere, particularly through the study of interplanetary electrons and magnetic reconnection.
Lidia van Driel-Gesztelyi is a Hungarian solar scientist and professor of physics at the Mullard Space Science Laboratory of University College London. She also maintains affiliations with Solar and Stellar Activity Research Team at Konkoly Observatory of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences and the Space Research Laboratory (LESIA) of Paris Observatory. She has been Editor-in-Chief of the journal Solar Physics since 2005 and has served in leadership roles within the International Astronomical Union.
Solar radio emission refers to radio waves that are naturally produced by the Sun, primarily from the lower and upper layers of the atmosphere called the chromosphere and corona, respectively. The Sun produces radio emissions through four known mechanisms, each of which operates primarily by converting the energy of moving electrons into electromagnetic radiation. The four emission mechanisms are thermal bremsstrahlung (braking) emission, gyromagnetic emission, plasma emission, and electron-cyclotron maser emission. The first two are incoherent mechanisms, which means that they are the summation of radiation generated independently by many individual particles. These mechanisms are primarily responsible for the persistent "background" emissions that slowly vary as structures in the atmosphere evolve. The latter two processes are coherent mechanisms, which refers to special cases where radiation is efficiently produced at a particular set of frequencies. Coherent mechanisms can produce much larger brightness temperatures (intensities) and are primarily responsible for the intense spikes of radiation called solar radio bursts, which are byproducts of the same processes that lead to other forms of solar activity like solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
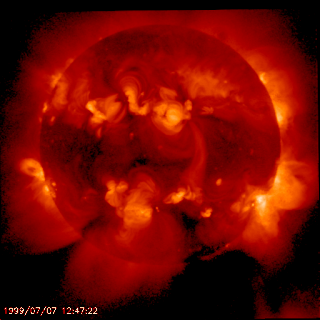
In solar physics, a transequatorial loop is a structure present in the solar corona that connects two different regions of opposite magnetic polarity in opposite hemispheres of the Sun. These connected regions are not limited to active regions, but are most commonly found during the times of maximum solar activity, the solar maximum.
Tamitha Skov is a space weather physicist, researcher and public speaker based in Los Angeles. She is also referred to as "Space Weather Woman" in social media, where she forecasts and analyzes space weather processes - in the heliosphere and exosphere, in addition to her conducting the same in traditional media. Skov is presently serving as a research scientist at The Aerospace Corporation and as an adjunct professor of heliophysics and space weather at Millerville University.
Kelly Korreck is an American space scientist. She is currently an astrophysicist at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and Program Scientist at NASA as head of operations for the Solar Wind Electrons Alphas and Protons (SWEAP) instrument aboard the Parker Solar Probe spacecraft.

Dr Natchimuthuk "Nat" Gopalswamy is an Indian American Solar physicist. He is currently a staff scientist at the Heliophysics Division of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.

Gordon Dean Holman is an emeritus research astrophysicist at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA’s) Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. His research mostly focused on obtaining an understanding of high-energy radiation from astronomical objects. This radiation cannot be observed from Earth's surface, but is observed with instruments on satellites launched to orbits above Earth's atmosphere. It is primarily emitted by high-energy electrons interacting with ions. These electrons also emit radiation at radio frequencies which is observed from Earth's surface. Consequently, these observations from space and radio telescopes provide a view of hot gas and energetic particles in the Universe that could not otherwise be obtained. Holman has specialized in the interpretation of these observed emissions to determine the origin and evolution of this hot gas and energetic particles. He has been described as "not just a theorist, he also looks at the data".















