The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, also known by its Latin name as the Periplus Maris Erythraei, is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation and trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports like Berenice Troglodytica along the coast of the Red Sea and others along the Horn of Africa, the Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean, including the modern-day Sindh region of Pakistan and southwestern regions of India.

A periplus, or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus was a type of log and served the same purpose as the later Roman itinerarium of road stops. However, the Greek navigators added various notes, which, if they were professional geographers, as many were, became part of their own additions to Greek geography.

Apollodotus I was an Indo-Greek king between 180 BC and 160 BC or between 174 and 165 BC who ruled the western and southern parts of the Indo-Greek kingdom, from Taxila in the Punjab region to the areas of Sindh and possibly Gujarat.

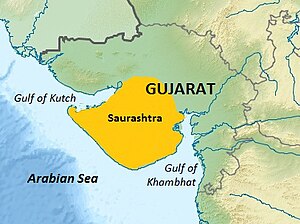
Saurashtra, also known as Kathiawar, is a peninsular region of Gujarat, India, located on the Arabian Sea coast. It covers about a third of Gujarat state, notably 11 districts of Gujarat, including Rajkot District. It was formerly a state of India before it merged with Bombay state. In 1961 it separated from Bombay and joined Gujarat.
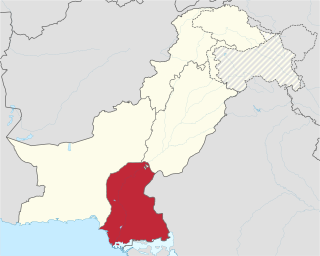
Patalene or Pattalene was an ancient area of the Indian subcontinent, now in modern Pakistan, that corresponds to the area of Sind.

Arabia Felix was the Latin name previously used by geographers to describe South Arabia, or what is now Yemen.
Apollodorus of Artemita was a Greek historian who flourished between 130 and 87 BC. He hailed from the Greco-Parthian city of Artemita in Apolloniatis and was a citizen of the Parthian Empire.
The Dvārakā–Kamboja route is an ancient land trade route that was an important branch of the Silk Road during antiquity and the early medieval era. It is referred to in Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain works. It connected the Kamboja Kingdom in today's Afghanistan and Tajikistan via Pakistan to Dvārakā (Dvaravati) and other major ports in Gujarat, India, permitting goods from Afghanistan and China to be exported by sea to southern India, Sri Lanka, the Middle East and Ancient Greece and Rome. The road was the second most important ancient caravan route linking India with the nations of the northwest.
Indian maritime history begins during the 3rd millennium BCE when inhabitants of the Indus Valley initiated maritime trading contact with Mesopotamia. India's long coastline, which occurred due to the protrusion of India's Deccan Plateau, helped it to make new trade relations with the Europeans, especially the Greeks, and the length of its coastline on the Indian Ocean is partly a reason why it's known as that since 1515, and was known as the Eastern Ocean earlier. The ocean was called so, due to the advent of international trade by the Europeans which still continues to this day. As per Vedic records, Indian traders and merchants traded with the far east and Arabia. During the Maurya Empire, there was a definite "naval department" to supervise the ships and trade. At the end of 1st century BCE, Indian products reached the Romans during the rule of Augustus, and the Roman historian Strabo mentions an increase in Roman trade with India following the Roman annexation of Egypt. As trade between India and the Greco-Roman world increased, spices became the main import from India to the Western world, bypassing silk and other commodities. Indians were present in Alexandria, while Christian and Jewish settlers from Rome continued to live in India long after the fall of the Roman Empire, which resulted in Rome's loss of the Red Sea ports, previously used to secure trade with India by the Greco-Roman world since the Ptolemaic dynasty. The Indian commercial connection with Southeast Asia proved vital to the merchants of Arabia and Persia during the 7th–8th century. A study published in 2013 found that some 11 percent of Australian Aboriginal DNA is of Indian origin and suggests these immigrants arrived about 4,000 years ago, possibly at the same time dingoes first arrived in Australia.
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India, between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE.

Nahapana, was an important ruler of the Western Kshatrapas, descendant of the Indo-Scythians, in northwestern India, who ruled during the 1st or 2nd century CE. According to one of his coins, he was the son of Bhumaka.

The History of the Indo-Greek kingdom covers a period from the 2nd century BCE to the beginning of the 1st century CE in northern and northwestern Indian subcontinent. There were over 30 Indo-Greek kings, often in competition on different territories. Many of them are only known through their coins.

Abiria was the country of the Abhiras in ancient India. It is mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea and by Ptolemy in his Geographia. The Periplus mentions it as Aberia with the coastal district Syrastrene, and Ptolemy locates it above the Indus delta.

Minnagara was a city of the Indo-Scythian kingdom, located on the Indus river in Pakistan, north of the coastal city of Barbaricum, North and West of Barygaza.

Indo-Roman trade relations was trade between the Indian subcontinent and the Roman Empire in Europe and the Mediterranean Sea. Trade through the overland caravan routes via Asia Minor and the Middle East, though at a relative trickle compared to later times, preceded the southern trade route via the Red Sea which started around the beginning of the Common Era (CE) following the reign of Augustus and his conquest of Egypt in 30 BCE.
Ariaca was a region of Western India beyond Barigaza, mentioned in ancient geographical sources, usually associated with the Western Satraps.

The economy of the ancient Tamil country describes the ancient economy of a region in southern India that mostly covers the present-day states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala. The main economic activities were agriculture, weaving, pearl fishery, manufacturing and construction. Paddy was the most important crop; it was the staple cereal and served as a medium of exchange for inland trade. Pepper, millets, grams and sugarcane were other commonly grown crops. Madurai and Urayur were important centers for the textile industry; Korkai was the center of the pearl trade. Industrial activity flourished.

The sources which are used to reconstruct the history of the Indo-Greeks are few and disparate, leading to much uncertainty about the precise state of the Indo-Greek kingdom and its chronology. Sources related to the Indo-Greeks can be classified into various categories: ancient literary sources from both the West and the Indian world, archaeological sources from the general area of present day Pakistan, Kashmir and North Indian states of Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh & Bihar, and numismatical sources, which are abundant and well-preserved but often rather cryptic.

Africa–India relations are the historical, political, economic, and cultural connections between India and the African continent.
Indian Ocean trade has been a key factor in East–West exchanges throughout history. Long-distance maritime trade by Austronesian trade ships and South Asian and Middle Eastern dhows, made it a dynamic zone of interaction between peoples, cultures, and civilizations stretching from Southeast Asia to East and Southeast Africa, and the East Mediterranean in the West, in prehistoric and early historic periods. Cities and states on the Indian Ocean rim focused on both the sea and the land.