
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. The New York Central was headquartered in the New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Rutland Railroad was a railroad in the northeastern United States, located primarily in the state of Vermont but extending into the state of New York at both its northernmost and southernmost ends. After its closure in 1961, parts of the railroad were taken over by the State of Vermont in early 1963 and are now operated by the Vermont Railway.

The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the Northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP, which would itself become part of Canadian Pacific Kansas City in 2023, operated D&H under its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation, which also operates Soo Line Railroad.
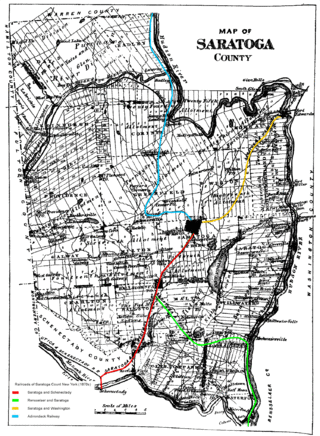
The Rensselaer and Saratoga Railroad was a railway company that operated in the states of New York and Vermont in the 19th century. At its peak it controlled a 150-mile (240 km) network. The Delaware and Hudson Railway leased the company in 1871 and formally merged it in 1945.

The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main line from Boston to Fitchburg is now operated as the MBTA Fitchburg Line; Pan Am Railways runs freight service on some other portions.
The New London Northern Railroad was a part of the Central Vermont Railway from New London, Connecticut, north to Brattleboro, Vermont. After a long period with the Canadian National Railway, it is now operated by the New England Central Railroad. The New London Northern was the only through railroad in Connecticut not to come under the control of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad.

Whitehall station is an Amtrak intercity train station in the village of Whitehall, New York. It is served by the Adirondack. It has one low-level side platform with a small shelter on the east side of the track.

The Adirondack Railway was a railroad that connected Saratoga Springs to North Creek, New York, a distance of 62 miles (100 km). Built by Dr. Thomas Clark Durant, vice-president of the Union Pacific Railroad, it was started in 1864 and completed in 1871. After Durant's death, it was taken over by his son, William West Durant, who sold it to the Delaware and Hudson Canal Company in 1889. The two companies officially merged on November 5, 1902. A stage-coach line was established to take passengers 28 miles (45 km) to Durant properties at Blue Mountain Lake and further by water to Raquette Lake.

The Rutland and Washington Railroad was a railroad company based in Rutland, Vermont which was chartered in Vermont on November 13, 1847, and built between Rutland and Eagle Bridge in Rensselaer County, New York in 1851 and 1852. One of the company's founders was Merritt Clark, a Vermont politician, and another was Thomas Canfield, later involved with the Northern Pacific. In order to build in New York, the company, on June 24, 1850, took a perpetual rent-free lease of the franchise rights east of Salem of the Troy and Rutland Railroad, which had been chartered in that state on July 2, 1849. The remainder of the Troy and Rutland, from Salem west to Eagle Bridge, was completed in 1852 and leased to the Rutland and Washington effective July 2.

The Boston, Hoosac Tunnel and Western Railway was a railway company that operated in the states of New York and Vermont in the 1880s. At its peak it controlled a 61-mile (98 km) network centered on Mechanicville, New York. Plans to extend the line west to Buffalo, New York, on Lake Ontario, were never realized, and the Fitchburg Railroad, a predecessor of the Boston and Maine Railroad, acquired control of the company in 1887 and merged it in 1892.
The Rutland and Whitehall Railroad is a defunct railroad which operated in the state of Vermont. The railroad, also known as the Castleton Company, received its charter from Vermont in 1848 and opened in 1850.

The history of Albany, New York, from 1784 to 1860, begins with the ratification of the Treaty of Paris by the Congress of the Confederation in 1784 and ends in 1860, prior to the American Civil War.
The Greenwich and Johnsonville Railway was a railroad in Upstate New York. It was founded in 1866 to construct a line from Greenwich to Johnsonville. The line opened in 1870. The Delaware and Hudson Railway acquired control of the railroad in 1906 and sold it to the Batten Kill Railroad in 1982.
The Freight Subdivision is a railway line in the New York. It runs from Schenectady, New York, to Mechanicville, New York. It was built by the Delaware and Hudson Railway in 1881 as a freight-only bypass, connecting with the main line of the Boston, Hoosac Tunnel and Western Railway. Today, Canadian Pacific Kansas City owns the line.
The Plattsburgh and Montreal Railroad was a railway company that operated in the state of New York in the mid-19th century. The company completed a 23-mile (37 km) line from Plattsburgh, New York, to the Canadian border north of Mooers, New York, in 1852. The company was subsequently reorganized as the Montreal and Plattsburgh Railroad in 1868 and consolidated with two other companies in 1873 to form the New York and Canada Railroad. The southern half of the company's line is part of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City's Canadian Subdivision; the Delaware and Hudson Railway abandoned the rest in 1925.
The Whitehall and Plattsburgh Railroad was a railway company that built but did not operate two disconnected railway lines in Upstate New York in the 19th century. Its purpose, to build a 90-mile (140 km) railway line between Whitehall, New York, and Plattsburgh, New York, was realized by its successor, the New York and Canada Railroad, albeit over a different route between Port Henry, New York, and Plattsburgh. Its northern line, between Plattsburgh and Ausable, New York, became the Ausable Branch of the Delaware and Hudson Railway and was abandoned in 1981. Its southern line, between Port Henry and Ticonderoga, New York, was incorporated into the New York and Canada Railroad main line and today is part of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City's Canadian Subdivision.
The New York and Canada Railroad was a railway company that operated in the state of New York between 1873 and 1908. It was established to consolidate existing companies in the northern part of the state and to complete a north–south railway line along the west side of Lake Champlain. Through service to Plattsburgh, New York, began in 1875, and the company later extended further north to Rouses Point, New York (1876), and to the Canadian border (1906). Always under Delaware and Hudson Railway control, the company was formally merged in 1908. Today, the Lake Champlain line is part of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City's Canadian Subdivision.
The Canadian Subdivision is a railway line in the state of New York. It runs north–south along the west side of Lake Champlain from the vicinity of Schenectady, New York, to Rouses Point, New York, on the border with Quebec. While the oldest part of the line was built in 1832–1833, the majority was constructed between 1869 and 1876. Once part of the Delaware and Hudson Railway main line, today Canadian Pacific Kansas City owns the line. Amtrak's Adirondack operates over the full length, providing daily service between New York City and Montreal.
The Adirondack branch is a railway line in the state New York. It runs 57 miles (92 km) from Saratoga Springs, New York, to North Creek, New York. The line was built by predecessors of the Delaware and Hudson Railway between 1865 and 1871. Ownership of the line is split between Warren County, New York, and the town of Corinth, New York. The Saratoga Corinth and Hudson Railway operates excursion service over part of the line. The Tahawus line runs another 29 miles (47 km) from North Creek to Tahawus, New York. It was built during World War II to serve a titanium mine and is now owned by a railbiking company.
The Saratoga Corinth and Hudson Railway is a heritage railway in upper Hudson River region of the Adirondack Mountains, in the U.S. state of New York. It is based on Corinth, New York, and operates over a portion of the Adirondack branch.









