
Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi)1 in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided between two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.
The Beardmore Glacier in Antarctica is one of the largest valley glaciers in the world, being 200 km (125 mi) long and having a width of 40 km (25 mi). It descends about 2,200 m (7,200 ft) from the Antarctic Plateau to the Ross Ice Shelf and is bordered by the Commonwealth Range of the Queen Maud Mountains on the eastern side and the Queen Alexandra Range of the Central Transantarctic Mountains on the western. Its mouth is east of the Lennox-King Glacier. It is northwest of the Ramsey Glacier.

The Admiralty Mountains is a large group of high mountains and individually named ranges and ridges in northeastern Victoria Land, Antarctica. This mountain group is bounded by the sea, and by the Dennistoun Glacier, Ebbe Glacier, and Tucker Glacier.
The Dominion Range is a broad mountain range, about 30 nautical miles long, forming a prominent salient at the juncture of the Beardmore and Mill glaciers in Antarctica. The range is part of the Queen Maud Mountains The range was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09 and named by Ernest Shackleton for the Dominion of New Zealand, which generously aided the expedition.
Lillie Glacier is a large glacier in Antarctica, about 100 nautical miles long and 10 nautical miles wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue.

Bowers Mountains is a group of north–south trending mountains in Antarctica, about 90 nautical miles long and 35 nautical miles wide, bounded by the coast on the north and by the Rennick Glacier, Canham Glacier, Black Glacier and Lillie Glacier in other quadrants. They are west of the Usarp Mountains, north of the Freyberg Mountains, northeast of the Concord Mountains, east of the Anare Mountains.
Tucker Glacier is a major valley glacier of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about 90 nautical miles long, flowing southeast between the Admiralty Mountains and the Victory Mountains to the Ross Sea. There is a snow saddle at the glacier's head, just west of Homerun Range, from which the Ebbe Glacier flows northwestward.
The Victory Mountains is a major group of mountains in Victoria Land, Antarctica, about 100 nautical miles long and 50 nautical miles wide, which is bounded primarily by Mariner and Tucker glaciers and the Ross Sea. They are north of the Mountaineer Range, east of the Freyberg Mountains and south of the Concord Mountains and the Admiralty Mountains. The division between the Victory Mountains and the Concord Mountains is not precise but apparently lies in the vicinity of Thomson Peak.
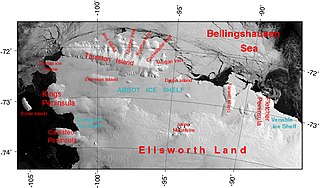
The Abbot Ice Shelf is an ice shelf 250 nautical miles long and 40 nautical miles wide, bordering Eights Coast from Cape Waite to Pfrogner Point in Antarctica. Thurston Island lies along the northern edge of the western half of this ice shelf; other sizable islands lie partly or wholly within this shelf.

The Du Toit Mountains are a group of mountains about 35 nautical miles long and 10 nautical miles wide, to the south-west of the Wilson Mountains in southeastern Palmer Land, Antarctica. The mountains have peaks rising to 1,700 metres (5,600 ft) and are bounded by Beaumont Glacier, Maury Glacier and Defant Glacier.
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, Antarctica. It drains south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projects into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.

The Ford Ranges are a collection of mountain groups and ranges standing east of Sulzberger Ice Shelf and Block Bay in the northwest part of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica.

The Walker Mountains are a range of peaks and nunataks which are fairly well separated but trend east–west to form the axis, or spine, of Thurston Island in Antarctica.

The Outback Nunataks are a series of bare rock nunataks and mountains which are distributed over an area about 40 nautical miles long by 20 nautical miles wide. The group lies south of Emlen Peaks of the Usarp Mountains and west of Monument Nunataks and upper Rennick Glacier, adjacent to the featureless interior plateau.
The Mariner Glacier is a major glacier over 60 nautical miles long, descending southeast from the plateau of Victoria Land, Antarctica, between Mountaineer Range and Malta Plateau, and terminating at Lady Newnes Bay, Ross Sea, where it forms the floating Mariner Glacier Tongue.
Rennick Glacier is broad glacier, nearly 200 nautical miles long, which is one of the largest in Antarctica. It rises on the polar plateau westward of Mesa Range and is 20 to 30 nautical miles wide, narrowing to 10 nautical miles near the coast. It takes its name from Rennick Bay where the glacier reaches the sea.
Mount Freeman is a prominent mountain, 2,880 metres (9,450 ft) high, surmounting the base of Walker Ridge, 2 nautical miles northwest of Mount Lepanto, in the Victory Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica.
The Malta Plateau is an ice-covered plateau of about 25 nautical miles extent in the Victory Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The plateau is irregular in shape and is bounded on the south and west by Mariner Glacier, on the north by tributaries to Trafalgar Glacier, and on the east by tributaries to Borchgrevink Glacier.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Sarkofagen Mountain". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Sarkofagen Mountain". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 








