Related Research Articles

The geography of Antarctica is dominated by its south polar location and, thus, by ice. The Antarctic continent, located in the Earth's southern hemisphere, is centered asymmetrically around the South Pole and largely south of the Antarctic Circle. It is washed by the Southern Ocean or, depending on definition, the southern Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. It has an area of more than 14 million km2. Antarctica is the largest ice desert in the world

Sir Francis Drake was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580. This included his incursion into the Pacific Ocean, until then an area of exclusive Spanish interest, and his claim to New Albion for England, an area in what is now the U.S. state of California. His expedition inaugurated an era of conflict with the Spanish on the western coast of the Americas, an area that had previously been largely unexplored by Western shipping.
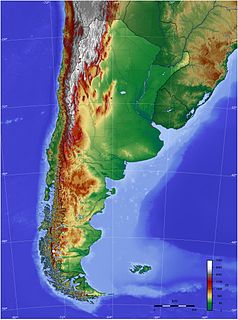
The geography of Argentina describes the geographic features of Argentina, a country located in Southern South America. Bordered by the Andes in the west and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, neighbouring countries are Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, and Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast.

The Drake Passage is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean and extends into the Southern Ocean.

The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica.

The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi). They lie about 120 kilometres north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between 430 and 900 km southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes.
This article lists extreme locations on Earth that hold geographical records or are otherwise known for their geophysical or meteorological superlatives. All of these locations are Earth-wide extremes; extremes of individual continents or countries are listed in separate articles under the Extreme points by region section. For other lists of extreme places on Earth, see Lists of extreme points. For more detailed meteorological and climatic records, see List of weather records.

The Diego Ramírez Islands are a small group of subantarctic islands located in the southernmost extreme of Chile.

The Scotia Plate is a tectonic plate on the edge of the South Atlantic and Southern oceans. Thought to have formed during the early Eocene with the opening of the Drake Passage that separates South America from Antarctica, it is a minor plate whose movement is largely controlled by the two major plates that surround it: the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. The Scotia Plate takes its name from the steam yacht Scotia of the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition (1902–04), the expedition that made the first bathymetric study of the region.
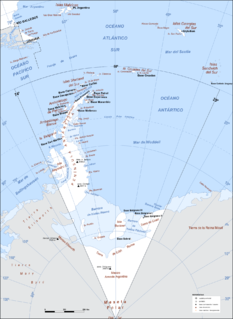
Argentine Antarctica is an area of Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps the British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. Argentina's Antarctic claim is based on its continued presence in the region since 1904, and the area's proximity to the South American continent. Argentina's claim to this area is subject to the Antarctic Treaty. Administratively, Argentine Antarctica is a department of the province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica, and South Atlantic Islands. The provincial authorities are based in Ushuaia. Despite the claim to this Antarctic area, Argentinean authority extends no further than the nation's bases. The Argentine exploration of the continent started early in the 20th century. José

The Captaincy General of Chile or Governorate of Chile, was a territory of the Spanish Empire, from 1541 to 1818. It comprised most of modern-day Chile and southern parts of Argentina. Its capital was Santiago de Chile. In 1818 it declared itself independent, becoming the Republic of Chile. It had a number of Spanish governors over its long history and several kings.

Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva is the most important Antarctic base of Chile. It is located at Fildes Peninsula, an ice-free area, in front of Fildes Bay, west of King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Situated alongside the Escudero Station and only 200 metres from the Russian Bellingshausen Station, its geographic coordinates are 62°12′0″S58°57′51″W, at an altitude of 10 metres above sea-level. The base is located in the Chilean commune of Antártica, which is the Antarctic territory claimed by Chile.

The Chilean Antarctic Territory or Chilean Antarctica is the territory in Antarctica claimed by Chile. The Chilean Antarctic Territory ranges from 53° West to 90° West and from the South Pole to the 60° South parallel, partially overlapping the Argentine and British Antarctic claims. It is administered by the Cabo de Hornos municipality in the South American mainland.

The South American–Antarctic Ridge or simply American-Antarctic Ridge is the tectonic spreading center between the South American Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It runs along the sea-floor from the Bouvet Triple Junction in the South Atlantic Ocean south-westward to a major transform fault boundary east of the South Sandwich Islands. Near the Bouvet Triple Junction the spreading half rate is 9 mm/a (0.35 in/year), which is slow, and the SAAR has the rough topography characteristic of slow-spreading ridges.
Pactolus Bank is a seamount in the Southern Ocean, west of Cape Horn. It was discovered by Captain W.D. Burnham of the American ship Pactolus on November 6, 1885. The bank has been proposed as a possible location for Elizabeth Island, a phantom island reported by Sir Francis Drake in October 1578. However, subsequent surveys have been unable to locate the bank, which may itself be a phantom.

Ash Point is a rounded low ice-free point forming the southeast side of the entrance to Discovery Bay in the northeast of Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica with an adjacent ice-free area of 201 hectares. Letelier Bank is lying off Ash Point, while Bascopé Point is situated 460 m (503 yd)to the southwest, with the 1 km (0.62 mi) wide Rojas Cove indenting for 310 m (339 yd) the coast between that point and Guesalaga Peninsula. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Elizabeth Island is the name given to an island off the tip of South America visited by Sir Francis Drake in September 1578, during his circumnavigation of the globe. The island was not seen again and is regarded as a phantom. Various suggestions have been offered as to where Drake landed.

Antártica is a Chilean commune in Antártica Chilena Province, Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region, which covers all the Chilean Antarctic Territory. It ranges from 53°W to 90°W and from the South Pole to 60°S, overlapping the Argentine and British Antarctic claims, and is the largest and least populated commune in Chile, being over 25 times the size of the next largest commune, Natales. It is administered by the Cabo de Hornos municipality in the South American mainland.
References
- ↑ Marine Regions: Sars Guyot
- 1 2 3 Martinic B., Mateo (2019). "Entre el mito y la realidad. La situación de la misteriosa Isla Elizabeth de Francis Drake" [Between myth and reality. The situation of the mysterious Elizabeth Island of Francis Drake]. Magallania (in Spanish). 47 (1). doi: 10.4067/S0718-22442019000100005 . Retrieved December 21, 2019.