Waverly is the largest village in Tioga County, New York, United States. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, Waverly had a population of 4,177. It is located southeast of Elmira in the Southern Tier region. This village was incorporated as the southwest part of the town of Barton in 1854. The village name is attributed to Joseph "Uncle Joe" Hallett, founder of its first Fire Department and pillar of the community, who conceived the name by dropping the second "e" from the name of his favorite author's novel, Waverley by Sir Walter Scott. The former village hall is listed on the National Historic Places list.

The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey, a distance of 395 miles (636 km). Incorporated in Pennsylvania in 1853 primarily for the purpose of providing a connection between the anthracite coal fields of Pennsylvania's Coal Region and the large markets for coal in New York City. The railroad gradually expanded both East and West, eventually linking Buffalo with New York City.
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Pennsylvania. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846, for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise, and minerals in Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated and established on September 20, 1847, as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company.

The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the New Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines, was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of the Northeastern United States.

Conrail, formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the Northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP operates D&H under its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation which also operates Soo Line Railroad.

The Lehigh and Hudson River Railway (L&HR) was the smallest of the six railroads that were merged into Conrail in 1976. It was a bridge line running northeast–southwest across northwestern New Jersey, connecting the line to the Poughkeepsie Bridge at Maybrook, New York with Easton, Pennsylvania, where it interchanged with various other companies.

The Delaware-Lackawanna Railroad is a shortline railroad operating in Northeastern Pennsylvania, especially the Scranton area.
The Belvidere-Delaware Railroad was a railroad running along the eastern shore of the Delaware River from Trenton, New Jersey north via Phillipsburg, New Jersey to the small village of Manunka Chunk, New Jersey. It became an important feeder line for the Lehigh Valley Railroad's join to the Central Railroad of New Jersey, which was constructed into Phillipsburg, NJ at about the same time. This connected Philadelphia and Trenton, NJ at one end of the shortline railroad to the rapidly growing lower Wyoming Valley region, and via the Morris Canal or the CNJ, a slow or fast connection to New York City ferries crossing New York Harbor from Jersey City, NJ. In 1871 the CNJ leased various railroads in Pennsylvania, most from the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company allowing the CNJ to penetrate to the upper Wyoming Valley, over some stretches, competing directly with the Lehigh Valley Railroad and with the Lehigh Canal and the trunk road connection of the Belvidere Delaware Railroad to New York became less profitable since Philadelphia connected more easily to Northeastern Pennsylvania thereafter without needing a double-crossing of the Delaware River; a general revenue decline ensued, leading to the Pennsylvania Railroad acquiring the rights, where it served as part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) system, carrying mainly anthracite coal and iron ore from northeastern Pennsylvania to population centers along the coast.

The Finger Lakes Railway is a Class III railroad in the Finger Lakes region of New York. The company began operations on July 23, 1995, and operates in Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, Ontario, Schuyler and Yates counties. The FGLK operates 18 diesel locomotives on 167 miles (269 km) of ex-Conrail trackage, formerly owned by the New York Central Railroad, the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Lehigh Valley Railroad. Between 2001 and 2013, the railroad operated a heritage railroad known as the Finger Lakes Scenic Railway which offered passenger train excursions.

The Conrail Lehigh Line is a railroad line in New Jersey that is part of Conrail Shared Assets Operations under the North Jersey Shared Assets Area division. The line runs from CP Port Reading Junction in Manville to Oak Island Yard in Newark. The line is double-track and signaled through its entire length. The line began operations in 1999 using former existing tracks from Manville to Newark that was once part of the original Lehigh Line which is still in existence and is owned and operated by Norfolk Southern Railway.
The Lehigh Division is a major freight low grade rail line owned and operated by the Reading Blue Mountain and Northern Railroad in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania that runs from Lehighton, Pennsylvania to Dupont, Pennsylvania; it originally ran from Lehighton to Mehoopany, Pennsylvania. The Lehigh Division was formed in 1993 by Conrail from the Lehigh Line, officially the former main line of the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR) that has absorbed former Central Railroad of New Jersey (CNJ) main line trackage and former Lehigh and Susquehanna Railroad (L&S) main line trackage into its system under Conrail; the Lehigh Line today is owned by the Norfolk Southern Railway and connects to the Lehigh Division at Lehighton.

Easton and Amboy Railroad was a railroad built across central New Jersey by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR) in the 1870s. The line was built to connect the Lehigh Valley Railroad coal hauling operations in Pennsylvania with the Port of New York and New Jersey to serve consumer markets in New York metropolitan area. Until it was built, the terminus of the LVRR had been at Phillipsburg, New Jersey on the Delaware River opposite Easton, Pennsylvania. It is now part of Norfolk Southern Railway operations, partially the Lehigh Line

The Upper Bay Bridge, or the Lehigh Valley Railroad Bridge, is a vertical lift bridge spanning the Newark Bay in northeastern New Jersey. It is used by CSX Transportation travelling through the North Jersey Shared Assets Area of the United States rail network along the National Docks Secondary line. The bridge is just north and parallel to the New Jersey Turnpike's Newark Bay Bridge. A notable train using the bridge is the Juice Train, which originates in Florida.
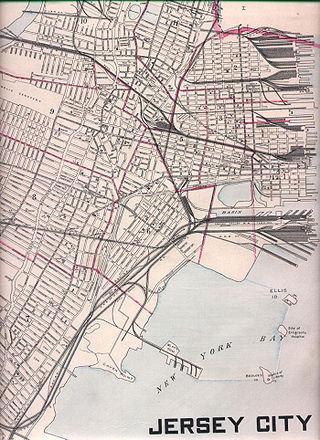
National Docks Secondary is a freight rail line within Conrail's North Jersey Shared Assets Area in Hudson County, New Jersey, used by CSX Transportation. It provides access for the national rail network to maritime, industrial, and distribution facilities at Port Jersey, the Military Ocean Terminal at Bayonne (MOTBY), and Constable Hook as well as carfloat operations at Greenville Yard. The line is an important component in the planned expansion of facilities in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The single track right of way comprises rail beds, viaducts, bridges, and tunnels originally developed at the end of the 19th century by competing railroads.
The Lehigh and Susquehanna Railroad is a defunct railroad that operated in eastern Pennsylvania during the 19th and 20th centuries. The company was a subsidiary of the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N). For much of its lifetime, however, it was leased by the Central Railroad of New Jersey.

Mountain Top yard or Penobscot yard is a rail yard in Mountain Top, Pennsylvania. It was built by the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company (LC&N) in response to an 1837 bill authorizing a right of way and was established by 1840, at least as a construction camp for the Ashley Planes, in support of the construction of the Lehigh and Susquehanna Railroad trackage and operations to join the northern Anthracite Coal Region from barge loading docks along the Susquehanna in Pittston, in the Wyoming Valley, with the Lehigh Canal.

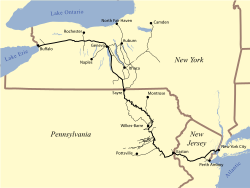
The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in central New Jersey, Northeastern Pennsylvania, and the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey via Conrail's Lehigh Line to the Susquehanna River valley at the south end of the Wyoming Valley Coal Region. Administratively, it is part of Norfolk Southern's Keystone Division and is part of the Crescent Corridor. As of 2021 the line is freight-only, although there are perennial proposals to restore passenger service over all or part of the line.

Phillipsburg Union Station is an inactive railroad station in Phillipsburg, New Jersey, United States, at 178 South Main Street. Opened in 1914, Union Station was built by the Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad (DL&W) and shared with the Central Railroad of New Jersey (CNJ) and was situated where the lines merged before the bridge crossing the Delaware River. Designed by Frank J. Nies, the architect who produced many of DL&W stations now listed state and federal registers of historic places, the 2 1/2 story, 3 bay brick building is unusual example of a union station and a representation of early 20th century Prairie style architecture. The Phillipsburg Union Signal Tower, or PU Tower, is nearby.
The Southern Central Railroad is a defunct railroad which operated in the state of New York in the nineteenth century. The company's line ran from Fair Haven, New York, on the south shore of Lake Ontario, to Athens, Pennsylvania, in the Southern Tier and just over the border into Pennsylvania. The company was incorporated in 1865 and became part of the Lehigh Valley Railroad system in 1895. Most of its line was abandoned by the Lehigh Valley Railroad between 1937–1979; the portion between Harford Mills, New York, and Owego, New York, is owned by the Tioga County Industrial Development Agency and operated by the Owego and Harford Railway.