Since its independence, Algeria has made major technological advances, especially in the steel and petrochemical industries. However, Algeria still has a severe shortage of skilled workers and is heavily dependent on foreign technologies.

Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. The capital and most populous city is Algiers, located in the far north of the country on the Mediterranean coast. With an area of 2,381,741 square kilometres (919,595 sq mi), Algeria is the tenth-largest country in the world, and the largest in Africa. Algeria is bordered to the northeast by Tunisia, to the east by Libya, to the west by Morocco, to the southwest by the Western Saharan territory, Mauritania, and Mali, to the southeast by Niger, and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. The country is a semi-presidential republic consisting of 48 provinces and 1,541 communes (counties).

Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, and sometimes other elements. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, it is a major component used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, automobiles, machines, appliances, and weapons.

Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn, palm fruit or sugar cane.
Scientific training is principally conducted at the Houari Boumedienne University of Sciences and Technology (founded in Algiers in 1974); the Oran University of Sciences and Technology (founded in 1975); the universities of Annaba (founded in 1975); Blida (founded in 1981), Boumerdes (founded in 1981); Constantine (founded in 1969); Oran Es-senia (founded in 1965); Tlemcen (founded in 1974); and the Ferhat Abbas-Setif University of Setif (founded in 1978).

Algiers is the capital and largest city of Algeria. In 2011, the city's population was estimated to be around 3,500,000. An estimate puts the population of the larger metropolitan city to be around 5,000,000. Algiers is located on the Mediterranean Sea and in the north-central portion of Algeria.
In 1987–97, science and engineering students accounted for 58% of college and university enrollments. The government’s National Bureau of Scientific Research operates 18 research centers in biology; anthropology; oceanography and fisheries; astronomy, astrophysics, and geophysics; renewable energy; arid zones; technology transfer; and other fields.
Biology is the natural science that studies life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical processes, molecular interactions, physiological mechanisms, development and evolution. Despite the complexity of the science, there are certain unifying concepts that consolidate it into a single, coherent field. Biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the creation and extinction of species. Living organisms are open systems that survive by transforming energy and decreasing their local entropy to maintain a stable and vital condition defined as homeostasis.
Anthropology is the study of humans and human behavior and societies in the past and present. Social anthropology and cultural anthropology study the norms and values of societies. Linguistic anthropology studies how language affects social life. Biological or physical anthropology studies the biological development of humans.
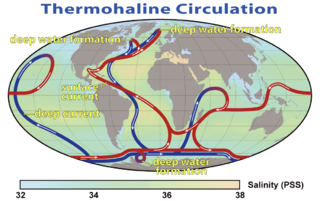
Oceanography, also known as oceanology, is the study of the physical and biological aspects of the ocean. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers blend to further knowledge of the world ocean and understanding of processes within: astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past.
In 2002, Algeria’s high technology exports totaled $21 million, four percent of the nation’s manufactured exports.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Algeria is divided into 48 wilayas (provinces) and 1541 baladiyahs. The capital city of a baladiyah, daïra, or province always gives those entities their name, even Algiers, the capital of the country gave it its name.
Slimane Raho is a reitred Algerian international football player. Raho represented the Algeria national team from 1998 to 2010, participating in the 2002, 2004 and 2010 Africa Cup of Nations. In total, he had 48 caps for the team, including 18 FIFA World Cup qualifying matches. He made his debut for the national team against Libya on August 14, 1998.

The Algerian Cup is a football competition in Algeria, pitting regional teams against each other. It was established in October 1962, three months after independence, and has been played yearly since then apart from 1990 and 1993.

Association Sportive Madinet d'Oran, known as ASM Oran or ASMO for short, is an Algerian football club based in Oran and founded in 1933. The club colours are green and white. Their home stadium, Stade Habib Bouakeul, has a capacity of 15,000 spectators. The club plays in the Algerian Ligue Professionnelle 2. The club is famous for its youth program, which has produced many Algerian talents over the years. Because of this, the club is nicknamed El-Madrassa.

The Algerian Ligue Professionnelle 1 ; known as Championnat National de Première Division or Ligue 1 for short, and formerly known as the Championnat National 1, is the Algerian professional league for association football clubs. It is the country's primary football competition and serves as the top division of the Algerian football league system. Ligue 1 is one of two divisions making up the Ligue de Football Professionnel, the other being Ligue Professionnelle 2. The league is contested by 16 clubs, and it operates on a system of promotion and relegation with Ligue 2. In 2009 it was known as Championnat d'Algérie D1 Nedjma and from 2010 to 2014, it was known as Ligue Professionnelle 1 Nedjma as it is sponsored by Kuwaiti telecommunications company Nedjma. From 2014, the league is officially known as Ligue Professionnelle 1 Mobilis as it is sponsored by Algerian telecommunications company Mobilis.
The 2014–15 Algerian Cup is the 51st edition of the Algerian Cup. The winner will qualify to the 2016 CAF Confederation Cup. MC Alger are the defending champions, having beaten JS Kabylie 1–1 (5-4) in the previous season's final.
The 1963–64 Algerian Cup is the Secound edition of the Algerian Cup. ES Sétif are the defending champions, having beaten ES Mostaganem 2–0 in the previous season's final.
The 1974–75 Algerian Championnat National was the 13th season of the Algerian Championnat National since its establishment in 1962. A total of 16 teams contested the league, with JS Kawkabi as the defending champions.
The 1965–66 Algerian Cup is the 4th edition of the Algerian Cup. MC Saïda are the defending champions, having beaten ES Mostaganem 2–1 in the previous season's final.
The 1967–68 Algerian Cup is the 5th edition of the Algerian Cup. ES Sétif are the defending champions, having beaten JSM Skikda 1–0 in the previous season's final.
The 1975–76 Algerian Cup is the 14th edition of the Algerian Cup. MC Oran are the defending champions, having beaten MO Constantine 2–0 in the previous season's final.
The 1977–78 Algerian Cup is the 16th edition of the Algerian Cup. JS Kawkabi are the defending champions, having beaten NA Hussein Dey 2–1 in the previous season's final.
The 1980–81 Algerian Cup is the 19th edition of the Algerian Cup. EP Sétif are the defending champions, having beaten USK Alger 1–0 in the previous season's final.
The top tier of Division 1 was renamed the Algerian Ligue Professionnelle 1 for the start of the 2010–11 season. The following page details the football records and statistics of the Premier League.
The 1983–84 Algerian Cup is the 22ndt edition of the Algerian Cup. MP Alger are the defending champions, having beaten ASC Oran 4–3 in the previous season's final.
The 1988–89 Algerian Cup is the 27th edition of the Algerian Cup. USM Alger are the defending champions, having beaten CR Belcourt 5–4 on penalties in the previous season's final.
The 1990–91 Algerian Cup is the 28th edition of the Algerian Cup. ES Sétif are the defending champions, having beaten MSP Batna 1–0 in the previous season's final.
The 1991–92 Algerian Cup is the 29th edition of the Algerian Cup. USM Bel-Abbès are the defending champions, having beaten JS Kabylie 2–0 in the previous season's final.








