Related Research Articles

A Burns supper is a celebration of the life and poetry of the poet Robert Burns, the author of many Scots poems. The suppers are normally held on or near the poet's birthday, 25 January, known as Burns Night. However, in principle, celebrations may be held at any other time of the year. Burns suppers are held all around the world.

Hogmanay is the Scots word for the last day of the old year and is synonymous with the celebration of the New Year in the Scottish manner. It is normally followed by further celebration on the morning of New Year's Day or in some cases, 2 January—a Scottish bank holiday.
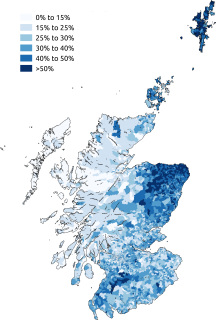
Scots is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland. Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300).

John Jamieson was a Scottish minister of religion, lexicographer, philologist and antiquary. His most important work is the Dictionary of the Scottish Language.
The Glasgow dialect, popularly known as the Glasgow patter or Glaswegian, varies from Scottish English at one end of a bipolar linguistic continuum to the local dialect of West Central Scots at the other. Therefore, the speech of many Glaswegians can draw on a "continuum between fully localised and fully standardised". Additionally, the Glasgow dialect has Highland English and Hiberno-English influences owing to the speech of Highlanders and Irish people who migrated in large numbers to the Glasgow area in the 19th and early 20th centuries. While being named for Glasgow, the accent is typical for natives across the full Greater Glasgow area and associated counties such as Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire, Dunbartonshire and parts of Ayrshire, which formerly came under the single authority of Strathclyde. It is most common in working class people, which can lead to stigma from members of other classes or those outside Glasgow.
Scottish English is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standard English may be defined as "the characteristic speech of the professional class [in Scotland] and the accepted norm in schools". IETF language tag for "Scottish Standard English" is en-scotland.

The history of the Scots language refers to how Anglic varieties spoken in parts of Scotland developed into modern Scots.
Geiriadur Prifysgol Cymru (GPC) is the only standard historical dictionary of the Welsh language, aspiring to be "comparable in method and scope to the Oxford English Dictionary". Vocabulary is defined in Welsh, and English equivalents are given. Detailed attention is given to variant forms, collocations, and etymology.
The Dictionary of the Scots Language (DSL) is an online Scots-English dictionary, now run by Dictionaries of the Scots Language, formerly known as Scottish Language Dictionaries, a registered SCIO charity. Freely available via the Internet, the work comprises the two major dictionaries of the Scots language:
The 'apologetic' or parochial apostrophe is the distinctive use of apostrophes in Modern Scots orthography. Apologetic apostrophes generally occurred where a consonant exists in the Standard English cognate, as in a' (all), gi'e (give) and wi' (with).

Shetland dialect is a dialect of Insular Scots spoken in Shetland, an archipelago to the north of mainland Scotland. It is derived from the Scots dialects brought to Shetland from the end of the fifteenth century by Lowland Scots, mainly from Fife and Lothian, with a degree of Norse influence from the Norn language, which is an extinct North Germanic language spoken on the islands until the late 18th century.

The languages of Scotland are the languages spoken or once spoken in Scotland. Each of the numerous languages spoken in Scotland during its recorded linguistic history falls into either the Germanic or Celtic language families. The classification of the Pictish language was once controversial, but it is now generally considered a Celtic language. Today, the main language spoken in Scotland is English, while Scots and Scottish Gaelic are minority languages. The dialect of English spoken in Scotland is referred to as Scottish English.
The Dictionary of the Older Scottish Tongue (DOST) is a 12-volume dictionary that documents the history of the Scots language covering Older Scots from the earliest written evidence in the 12th century until the year 1700. DOST was compiled over a period of some eighty years, from 1931 to 2002.
The Scottish National Dictionary Association (SNDA) was founded in 1929 to foster and encourage the Scots language, in particular by producing a standard dictionary of modern Scots. This primary aim was fulfilled in 1976 with the completion of the 10-volume Scottish National Dictionary (SND), covering the language from 1700 to 1976. Material for SND is drawn from a wide variety of written and oral sources of Lowland Scots from Shetland to Ulster. SND was produced under the editorial direction of William Grant, and of David Murison.
A Scotticism is a phrase or word which is characteristic of dialects of the Scots language.

Modern Scots comprises the varieties of Scots traditionally spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster, from 1700.
A. F. Murison, MA, LLD, KC. was a professor of Roman law and jurisprudence at University College, London and at the University of Oxford. He was a prolific writer for newspapers and journals in a wide variety of subjects with comparatively few publications in his specialism of Roman Law. He collated the text of Theophilus' Greek paraphrasis of Justinian's Institutes but failed to finish his extensive work in this field. However, his translation of Theophilus was published in 2010 as the parallel English text accompanying the Greek in the new edition. He also wrote two biographical works in Scottish history: Sir William Wallace (1898) and King Robert the Bruce (1899) in the Famous Scots Series published by Oliphant, Anderson and Ferrier. Lack of money took him into journalism and he was editor of the Educational Times from 1902 to 1912 and on the staff of the Daily Chronicle. He even had time to enter politics and he stood as a Liberal Party candidate in at least three General Elections: for the Glasgow and Aberdeen Universities constituency in 1906 and for the Glasgow Central constituency in December 1910 and January 1910 and lost on all three occasions to a Conservative candidate. He died on 8 June 1934 at his home in Clapham Common, London.
The history of Scottish Gaelic dictionaries goes back to the early 17th century. The high-point of Gaelic dictionary production was in the first half of the 19th century, as yet unrivalled even by modern developments in the late 20th and early 21st century. The majority of dictionaries published to date have been Gaelic to English dictionaries.
A historical dictionary or dictionary on historical principles is a dictionary which deals not only with the latterday meanings of words but also the historical development of their forms and meanings. It may also describe the vocabulary of an earlier stage of a language's development without covering present-day usage at all. A historical dictionary is primarily of interest to scholars of language, but may also be used as a general dictionary.

MairiRobinson was best known for her dedication towards the study of the Scottish language and Scottish lexicography. She worked on the later stages of the Scottish National Dictionary and became the editor-in-chief where she oversaw the 1985 publication for the Concise Scots dictionary. She was Scots language consultant for the complete edition of Sir Walter Scott's novels. She was committed to adult learning. Her work has been a noteworthy contribution to the Scots language and to the confidence of the Scottish people about their language.
References
- ↑ "The Confidential Causerie. The Scottish National Dictionary. Canon Wilkinson". The Glasgow Herald . 13 May 1933. p. 4. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ↑ "Scottish National Dictionary. Burns Clubs to raise £20,000". The Glasgow Herald. 1 December 1945. p. 2. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ↑ J. Derrick McClure (27 February 1997). "Obituary: David D. Murison". The Independent . Retrieved 5 July 2016.
- ↑ "Scots wha hae web access". Contact Magazine . May 2002. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- ↑ "MSP supports Scots language project". June 2002. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- ↑ "Online move for Scots language". March 2004. Retrieved 8 July 2020.