
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, burning with urination, pain with sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer.

Streptococcus is a genus of gram-positive coccus or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales, in the phylum Firmicutes. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, so as they grow, they tend to form pairs or chains that may appear bent or twisted.

A group A streptococcal infection is an infection with group A streptococcus (GAS). Streptococcus pyogenes comprises the vast majority of the Lancefield group A streptococci, and is often used as a synonym for GAS. However, S. dysgalactiae can also be group A. S. pyogenes is a beta-hemolytic species of Gram positive bacteria that is responsible for a wide range of both invasive and noninvasive infections.

Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. About 70% of women and men do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms do occur they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms can include itching in the genital area, a bad smelling thin vaginal discharge, burning with urination, and pain with sex. Having trichomoniasis increases the risk of getting HIV/AIDS. It may also cause complications during pregnancy.
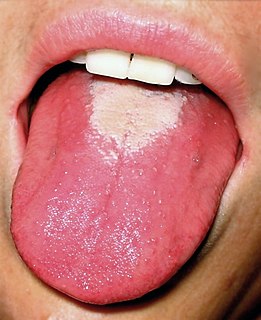
Scarlet fever is a disease which can occur as a result of a group A Streptococcus infection. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age.

Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as strep throat, is an infection of the back of the throat including the tonsils caused by group A streptococcus (GAS). Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, red tonsils, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. A headache, and nausea or vomiting may also occur. Some develop a sandpaper-like rash which is known as scarlet fever. Symptoms typically begin one to three days after exposure and last seven to ten days.

Cefazolin, also known as cefazoline and cephazolin, is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used to treat cellulitis, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, endocarditis, joint infection, and biliary tract infections. It is also used to prevent group B streptococcal disease around the time of delivery and before surgery. It is typically given by injection into a muscle or vein.

Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, typically of rapid onset. It is a type of pharyngitis. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and large lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess.
Preventive healthcare consists of measures taken for disease prevention, as opposed to disease treatment. Just as health comprises a variety of physical and mental states, so do disease and disability, which are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices. Health, disease, and disability are dynamic processes which begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
A vertically transmitted infection is an infection caused by pathogens that uses mother-to-child transmission, that is, transmission directly from the mother to an embryo, fetus, or baby during pregnancy or childbirth. It can occur when the mother gets an infection as an intercurrent disease in pregnancy. Nutritional deficiencies may exacerbate the risks of perinatal infection.

Streptococcus agalactiae is a gram-positive coccus with a tendency to form chains. It is a beta-hemolytic, catalase-negative, and facultative anaerobe. In general, GBS is a harmless commensal bacterium being part of the human microbiota colonizing the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract of up to 30% of healthy human adults. Nevertheless, GBS can cause severe invasive infections.

Group B streptococcus infection, also known as Group B streptococcal disease, is the infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus agalactiae. Group B streptococcal infection can cause serious illness and sometimes death, especially in newborns, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems. GBS was recognized as a pathogen in cattle by Edmond Nocard and Mollereau in the late 1880s, but its significance as a human pathogen was not discovered before 1938, when Fry described three fatal cases of puerperal infections caused by GBS. In the early 1960s, GBS was recognized as a main cause of infections in newborns.

Medical microbiology , the large subset of microbiology that is applied to medicine, is a branch of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. In addition, this field of science studies various clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. There are four kinds of microorganisms that cause infectious disease: bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses, and one type of infectious protein called prion.
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Many of those infected have no symptoms. Men may have burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Women may have burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to joints or heart valves.
Neonatal sepsis is a type of neonatal infection and specifically refers to the presence in a newborn baby of a bacterial blood stream infection (BSI) in the setting of fever. Older textbooks may refer to neonatal sepsis as "sepsis neonatorum". Criteria with regards to hemodynamic compromise or respiratory failure are not useful clinically because these symptoms often do not arise in neonates until death is imminent and unpreventable. Neonatal sepsis is divided into two categories: early-onset sepsis (EOS) and late-onset sepsis (LOS). EOS refers to sepsis presenting in the first 7 days of life, with LOS referring to presentation of sepsis after 7 days. Neonatal sepsis is the single most common cause of neonatal death in hospital as well as community in developing country.
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) are Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to the carbapenem class of antibiotics, considered the drugs of last resort for such infections. They are resistant because they produce an enzyme called a carbapenemase that disables the drug molecule. The resistance can vary from moderate to severe. Enterobacteriaceae are common commensals and infectious agents. Experts fear CRE as the new "superbug". The bacteria can kill up to half of patients who get bloodstream infections. Tom Frieden, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has referred to CRE as "nightmare bacteria". Types of CRE are sometimes known as KPC and NDM. KPC and NDM are enzymes that break down carbapenems and make them ineffective. Both of these enzymes, as well as the enzyme VIM have also been reported in Pseudomonas.
Infectious diseases within American correctional settings are a concern within the public health sector. The corrections population is susceptible to infectious diseases through exposure to blood and other bodily fluids, drug injection, poor health care, prison overcrowding, demographics, security issues, lack of community support for rehabilitation programs, and high-risk behaviors. The spread of infectious diseases, such as HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted diseases, hepatitis C (HCV), hepatitis B (HBV), and tuberculosis result largely from needle-sharing, drug use, and consensual and nonconsensual sex among prisoners. HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C need specific attention because of the specific public health concerns and issues they raise.

Granada medium is a selective and differential culture medium designed to selectively isolate Streptococcus agalactiae and differentiate it from other microorganisms. Granada Medium was developed by Dr. Manuel Rosa-Fraile et al. at the Service of Microbiology in the Hospital Virgen de las Nieves in Granada (Spain).

Neonatal infections are infections of the neonate (newborn) acquired during prenatal development or in the first four weeks of life. Neonatal infections may be contracted by mother to child transmission, in the birth canal during childbirth, or contracted after birth. Some neonatal infections are apparent soon after delivery, while others may develop in the postnatal period. Some neonatal infections such as HIV, hepatitis B, and malaria do not become apparent until much later.
As of 2017 there is no effective vaccine to prevent Group B streptococcal infection, although research is ongoing. Vaccination is considered an ideal solution to prevent not only early- and late-onset disease but also GBS infections in adults at risk.

















