Related Research Articles
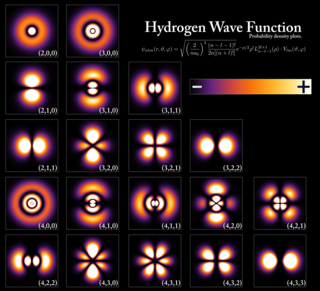
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.
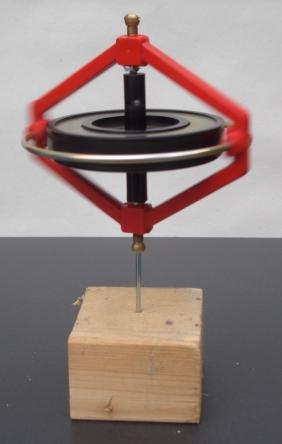
In physics, angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.

The cat, commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae. Recent advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a house pet and farm cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Because of its retractable claws it is adapted to killing small prey like mice and rats. It has a strong flexible body, quick reflexes, sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat communication includes vocalizations like meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting as well as cat body language. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in frequency for human ears, such as those made by small mammals. It also secretes and perceives pheromones.
The centimetre–gram–second system of units is a variant of the metric system based on the centimetre as the unit of length, the gram as the unit of mass, and the second as the unit of time. All CGS mechanical units are unambiguously derived from these three base units, but there are several different ways in which the CGS system was extended to cover electromagnetism.
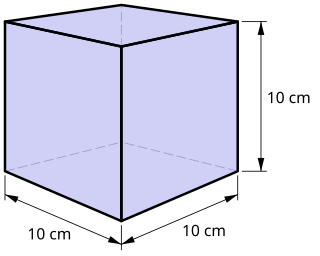
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies that strengthen the immune system and thus reduce the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose.

Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the behavior of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

The lion is a large cat of the genus Panthera native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on large ungulates. The lion is an apex and keystone predator; although some lions scavenge when opportunities occur and have been known to hunt humans, lions typically do not actively seek out and prey on humans.

Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical objects.
In mathematics, the Lp spaces are function spaces defined using a natural generalization of the p-norm for finite-dimensional vector spaces. They are sometimes called Lebesgue spaces, named after Henri Lebesgue, although according to the Bourbaki group they were first introduced by Frigyes Riesz.

The cheetah is a large cat with a tawny to creamy white or pale buff fur that is marked with evenly spaced, solid black spots. Its head is small and rounded, with a short snout and black tear-like facial streaks. It reaches 67–94 cm (26–37 in) at the shoulder, and the head-and-body length is between 1.1 and 1.5 m. Adults weigh between 21 and 72 kg. It is the fastest land animal, capable of running at 80 to 98 km/h ; it has evolved specialized adaptations for speed, including a light build, long thin legs and a long tail.

Samuel Leroy Jackson is an American actor. One of the most widely recognized actors of his generation, the films in which he has appeared have collectively grossed over $27 billion worldwide, making him the second-highest-grossing actor of all time. According to a more recent rating, he is the highest-grossing actor of all time. In 2022, he received the Academy Honorary Award as "a cultural icon whose dynamic work has resonated across genres and generations and audiences worldwide".

Principal component analysis (PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and enabling the visualization of multidimensional data. Formally, PCA is a statistical technique for reducing the dimensionality of a dataset. This is accomplished by linearly transforming the data into a new coordinate system where the variation in the data can be described with fewer dimensions than the initial data. Many studies use the first two principal components in order to plot the data in two dimensions and to visually identify clusters of closely related data points. Principal component analysis has applications in many fields such as population genetics, microbiome studies, and atmospheric science.

Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the electric current, and follows any changes in the magnitude of the current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) (voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called back EMF.
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular, of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per liter, having the unit symbol mol/L or mol/dm3 in SI units. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M or 1 M. Molarity is often depicted with square brackets around the substance of interest; for example, the molarity of the hydrogen ion is depicted as [H+].

Verein für Leibesübungen Bochum 1848 Fußballgemeinschaft, commonly referred to as VfL Bochum or simply Bochum, is a German professional association football club based in the city of Bochum, North Rhine-Westphalia. The club has spent 35 seasons in the Bundesliga.

The Duckworth–Lewis–Stern method (DLS) is a mathematical formulation designed to calculate the target score for the team batting second in a limited overs cricket match interrupted by weather or other circumstances. The method was devised by two English statisticians, Frank Duckworth and Tony Lewis, and was formerly known as the Duckworth–Lewis method (D/L). It was introduced in 1997, and adopted officially by the ICC in 1999. After the retirements of Duckworth and Lewis, Steven Stern became the custodian of the method and it was renamed to its current title in November 2014.

Death Note is a Japanese manga series written by Tsugumi Ohba and illustrated by Takeshi Obata. It was serialized in Shueisha's shōnen manga magazineWeekly Shōnen Jump from December 2003 to May 2006, with its chapters collected in 12 tankōbon volumes. The story follows Light Yagami, a genius high school student who discovers a mysterious notebook: the "Death Note", which belonged to the shinigami Ryuk, and grants the user the supernatural ability to kill anyone whose name is written in its pages. The series centers around Light's subsequent attempts to use the Death Note to carry out a worldwide massacre of individuals whom he deems immoral and to create a crime-free society, using the alias of a god-like vigilante named "Kira", and the subsequent efforts of an elite Japanese police task force, led by enigmatic detective L, to apprehend him.
L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is el, plural els.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 100, 1069, 1070. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.