
Plan 9 from Bell Labs is a distributed operating system which originated from the Computing Science Research Center (CSRC) at Bell Labs in the mid-1980s and built on UNIX concepts first developed there in the late 1960s. Since 2000, Plan 9 has been free and open-source. The final official release was in early 2015.

GNUstep is a free software implementation of the Cocoa Objective-C frameworks, widget toolkit, and application development tools for Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows. It is part of the GNU Project.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

GNU TeXmacs is a scientific word processor and typesetting component of the GNU Project. It originated as a variant of GNU Emacs with TeX functionalities, though it shares no code with those programs, while using TeX fonts. It is written and maintained by Joris van der Hoeven and a group of developers. The program produces structured documents with a WYSIWYG user interface. New document styles can be created by the user. The editor provides high-quality typesetting algorithms and TeX and other fonts for publishing professional looking documents.
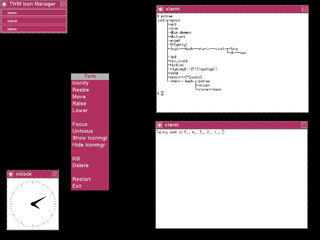
twm is a window manager for the X Window System. Started in 1987 by Tom LaStrange, it has been the standard window manager for the X Window System since version X11R4. The name originally stood for Tom's Window Manager, but the software was renamed Tab Window Manager by the X Consortium when they adopted it in 1989. twm is a stacking window manager that provides title bars, shaped windows and icon management. It is highly configurable and extensible.

The F Virtual Window Manager (FVWM) is a virtual window manager for the X Window System. Originally a twm derivative, FVWM is now a window manager for Unix-like systems.
In artificial intelligence and operations research, constraint satisfaction is the process of finding a solution through a set of constraints that impose conditions that the variables must satisfy. A solution is therefore an assignment of values to the variables that satisfies all constraints—that is, a point in the feasible region.

AMPL is an algebraic modeling language to describe and solve high-complexity problems for large-scale mathematical computing . It was developed by Robert Fourer, David Gay, and Brian Kernighan at Bell Laboratories. AMPL supports dozens of solvers, both open source and commercial software, including CBC, CPLEX, FortMP, MOSEK, MINOS, IPOPT, SNOPT, KNITRO, and LGO. Problems are passed to solvers as nl files. AMPL is used by more than 100 corporate clients, and by government agencies and academic institutions.

SCons is a computer software build tool that automatically analyzes source code file dependencies and operating system adaptation requirements from a software project description and generates final binary executables for installation on the target operating system platform. Its function is analogous to the traditional GNU build system based on the make utility and the autoconf tools.

GNU Ubiquitous Intelligent Language for Extensions is the preferred extension language system for the GNU Project and features an implementation of the programming language Scheme. Its first version was released in 1993. In addition to large parts of Scheme standards, Guile Scheme includes modularized extensions for many different programming tasks.
This article provides basic comparisons for notable text editors. More feature details for text editors are available from the Category of text editor features and from the individual products' articles. This article may not be up-to-date or necessarily all-inclusive.
In computing, minimalism refers to the application of minimalist philosophies and principles in the design and use of hardware and software. Minimalism, in this sense, means designing systems that use the least hardware and software resources possible.

In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with an organization of the screen into mutually non-overlapping frames, as opposed to the more common approach of coordinate-based stacking of overlapping objects (windows) that tries to fully emulate the desktop metaphor.
Cassowary is an incremental constraint solving toolkit that efficiently solves systems of linear equalities and inequalities. Constraints may be either requirements or preferences. Client code specifies the constraints to be maintained, and the solver updates the constrained variables to have values that satisfy the constraints.

Linux is a generic name for a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project.

Gpg4win is an email and file encryption package for most versions of Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Outlook, which utilises the GnuPG framework for symmetric and public-key cryptography, such as data encryption, digital signatures, hash calculations etc.

Maciej Stachowiak is a Polish American software developer currently employed by Apple Inc., where he is a leader of the development team responsible for the WebKit Framework. A longtime proponent of open source software, Stachowiak was involved with the SCWM, GNOME and Nautilus projects for Linux before joining Apple. He is actively involved the development of web standards, served as a co-chair of the World Wide Web Consortium's HTML 5 working group and was a member of the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group steering committee.

GNU Guix is a functional cross-platform package manager and a tool to instantiate and manage Unix-like operating systems, based on the Nix package manager. Configuration and package recipes are written in Guile Scheme. GNU Guix is the default package manager of the GNU Guix System distribution.
Alan H. Borning is an American computer scientist noted for his research on human computer interaction and object-oriented programming. In particular his research in human-computer interaction is on designing for human values. He works on systems to support civic engagement and deliberation, and works on tools to make public transportation easier to use. He has also worked on constraint-based languages and systems, and cooperating constraint languages and solvers.













