
James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 64 km in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
Meade Nunatak is a nunatak 3 nautical miles (6 km) north of Blanchard Hill, rising to 990 metres (3,250 ft) in the Pioneers Escarpment, Shackleton Range, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the U.S. Navy, 1967, and was surveyed by the British Antarctic Survey, 1968–71. In association with the names of pioneers of polar life and travel grouped in this area, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1971 after English mountaineer Charles Francis Meade, the designer of the Meade tent.
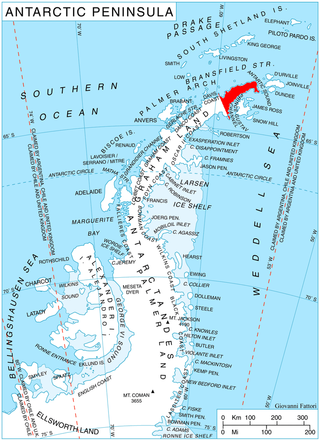
Aitkenhead Glacier is a 10-mile (16 km) long glacier flowing east-southeast from the Detroit Plateau, Graham Land, into Prince Gustav Channel. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) (1960–61), and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Neil Aitkenhead, a FIDS geologist at Hope Bay (1959–60).
Simpson Nunatak is a nunatak, 1,165 metres (3,822 ft), rising 2.5 nautical miles northwest of Mount Roberts, on the south margin of Aitkenhead Glacier, Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Hugh W. Simpson of Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), a member of the Detroit Plateau reconnaissance party from Hope Bay in 1957.
Baines Nunatak is a nunatak rising to 1,020 metres (3,350 ft) to the east of Bernhardi Heights and 10 nautical miles (19 km) northwest of Jackson Tooth, Pioneers Escarpment, in the Shackleton Range. It was photographed from the air by the U.S. Navy, 1967, surveyed by the British Antarctic Survey, 1968–71, and named in 1977 by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Thomas Baines (1822–75), an English explorer and joint author, with William Barry Lord, of Shifts and Expedients of Camp Life, Travel and Exploration.
Brazitis Nunatak is a nunatak, 1,625 metres (5,330 ft) high, along the edge of an ice escarpment 5 nautical miles (9 km) south of DesRoches Nunataks in the southwestern Patuxent Range, Pensacola Mountains. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Peter F. Brazitis, a cosmic ray scientist at South Pole Station, winter 1967.
Cheeks Nunatak is the largest and southernmost of three nunataks located 12 nautical miles (22 km) northwest of the Merrick Mountains, in Palmer Land. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Noble L. Cheeks, aviation electronics technician, member of the R4D party that flew to the vicinity of the eventual Eights Station in 1961 to set up a base camp.
Neff Nunatak is a nunatak rising to about 1,500 m, located 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) southeast of Schmutzler Nunatak in the southeast end of the Grossman Nunataks, Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1965–68. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1988 after Richard J. Neff, USGS cartographer, a member of the winter party at Australia's Casey Station, 1975.
Wagner Nunatak is one of the Rambo Nunataks, 850 m, standing 9 nautical miles (17 km) south of Blackburn Nunatak in the Pensacola Mountains. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for John K. Wagner, radioscientist at Plateau Station, winter 1967.
The Juno Peaks are two steep-sided nunataks with a small rock to the west, forming part of an east–west ridge 6 nautical miles (11 km) southwest of Mimas Peak, lying near the head of Saturn Glacier in southern Alexander Island, Antarctica. They were mapped from trimetrogon air photography taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and from survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1948–50. The nunataks were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Juno, one of the asteroids lying between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter.
Dee Nunatak is a rock nunatak which appears to be within the flow of Garfield Glacier, in the west part of McDonald Heights, Marie Byrd Land. The feature lies 1 nautical mile (2 km) west of Rhodes Icefall. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–65, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Thomas H. Dee, U.S. Navy, Medical Officer at Byrd Station, 1970.
Tuning Nunatak is a small rock nunatak 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) north of Darling Ridge, Ohio Range. Surveyed by the United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) Horlick Mountains Traverse party in December 1958. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Preston O. Tuning, meteorologist at Byrd Station in 1960.

Klinck Nunatak is an isolated nunatak rising to about 1,800 metres (5,900 ft) between the Blanchard Nunataks and the Holmes Hills in south-central Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from aerial photographs taken by the U.S. Navy, 1966–69, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1977 for Jay C. Klinck, U.S. Navy, a construction mechanic at Palmer Station, winter party 1970, who also provided United States Antarctic Research Program operational support at Siple Station, winter party 1973.
Savage Nunatak is a nunatak located 7 nautical miles (13 km) southeast of Hatcher Bluffs, along the east margin of upper Reedy Glacier. Mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–64. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Henry C. Savage, builder at Byrd Station in 1962.
Ray Nunatak is a nunatak, an Eskimo word meaning an isolated rocky peak that projects above the surface of a glacier where the ice cover is relatively thin. Ray Nunatak is 1,630 m, located just north of Beiszer Nunatak and 5 nautical miles (9 km) southwest of Dyrdal Peak in southern Forrestal Range, Pensacola Mountains. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1956–66. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for James A. Ray, utilities man at Ellsworth Station, winter 1957.

The Laputa Nunataks are a range of nunataks and snow-covered hills with minor rock outcrops, rising from about 500 metres (1,600 ft) to over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), and located 6 nautical miles (11 km) northwest of Adie Inlet on the east side of Graham Land, Antarctica. They were first charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Laputa, the flying island in Jonathan Swift's Gulliver's Travels.
Larsen Nunatak is an island called nunatak 2 nautical miles (4 km) north of Murdoch Nunatak in the Seal Nunataks group, off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Seal Nunataks were discovered by a Norwegian whaling expedition under C.A. Larsen in December 1893, and commemoration of Larsen was proposed by Ludwig Friederichsen in 1895. The application of this name is based upon a 1947 survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey.
Lee Nunatak is a nunatak, 1,920 metres (6,300 ft) high, 4 nautical miles (7 km) northwest of Penseroso Bluff in the northwest part of the Daniels Range in the Usarp Mountains of Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Chun Chi Lee, a United States Antarctic Research Program biologist at McMurdo Station, 1967–68.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Seacatch Nunataks". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Seacatch Nunataks". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey. 



