Related Research Articles

School prayer, in the context of religious liberty, is state-sanctioned or mandatory prayer by students in public schools. Depending on the country and the type of school, state-sponsored prayer may be required, permitted, or prohibited. The United Kingdom also requires daily worship by law, but does not enforce it. Countries which prohibit or limit school prayer often differ in their reasons for doing so. In the United States, school prayer cannot be required of students in accordance with the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. This is generally rigorously applied in public schools; the Establishment Clause does not prevent prayer in private schools that have no public funding. In Canada, school-sponsored prayer is disallowed under the concept of freedom of conscience as outlined in the Canadian Charter on Rights & Fundamental Freedoms. School-sponsored prayer is disallowed in France as a byproduct of its status as a secular nation.

The National Secular Society (NSS) is a British campaigning organisation that promotes secularism and the separation of church and state. It holds that no one should gain advantage or disadvantage because of their religion or lack of it. It was founded by Charles Bradlaugh in 1866.

Edmund Campion, SJ was an English Jesuit priest and martyr. While conducting an underground ministry in officially Anglican England, Campion was arrested by priest hunters. Convicted of high treason, he was hanged, drawn and quartered at Tyburn. Campion was beatified by Pope Leo XIII in 1886 and canonised in 1970 by Pope Paul VI as one of the Forty Martyrs of England and Wales. His feast day is celebrated on 1 December.
Ireland is ranked 5th of the countries with the highest education in the world from a new survey on 9th February 2023. The levels of Ireland's education are primary, secondary and higher education. In recent years further education has grown immensely with 51% of working age adults having completed higher education by 2020. Growth in the economy since the 1960s has driven much of the change in the education system. For universities there are student service fees, which students are required to pay on registration, to cover examinations, insurance and registration costs.
A parochial school is a private primary or secondary school affiliated with a religious organization, and whose curriculum includes general religious education in addition to secular subjects, such as science, mathematics and language arts. The word parochial comes from the same root as "parish", and parochial schools were originally the educational wing of the local parish church. Christian parochial schools are called "church schools" or 'Christian schools'. In Ontario, parochial schools are called "separate schools".

Cliffside is a neighbourhood in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located along the Scarborough Bluffs in the district of Scarborough. Its boundaries are Kennedy Road to the west, St. Clair Avenue East to the north, Brimley Road to the east, and the Bluffs on the lakeshore to the south.
Catholic schools are pre-primary, primary and secondary educational institutions administered in association with the Catholic Church. As of 2011, the Catholic Church operates the world's largest religious, non-governmental school system. In 2016, the church supported 43,800 secondary schools and 95,200 primary schools. The schools include religious education alongside secular subjects in their curriculum.
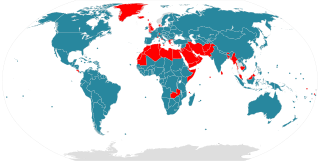
A secular state is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens equally regardless of religion, and claims to avoid preferential treatment for a citizen based on their religious beliefs, affiliation or lack of either over those with other profiles.

Muff is a village and townland in County Donegal, Ireland. It is near the mouth of the River Foyle and sits close to the border between the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. The village of Culmore and the city of Derry are to the south in Northern Ireland.
Nonsectarian institutions are secular institutions or other organizations not affiliated with or restricted to a particular religious group.
Gaelcholáiste Chill Dara is an Irish language secondary level school in Naas, County Kildare, in Ireland.

Michael Nugent is an Irish writer and activist. He has written, co-written or contributed to seven books and the comedy musical play I, Keano. He has campaigned on many political issues, often with his late wife Anne Holliday, and he is chairperson of the advocacy group Atheist Ireland.

Atheist Ireland is an association of atheists based in Ireland. The group was initially founded by members of Atheist.ie, an online community which had been set up by Seamus Murnane in June 2006. Its current chairperson is writer and activist Michael Nugent. Atheist Ireland is a former member of Atheist Alliance International, and a former member of Humanists International, and current member of The Coalition to Repeal the 8th, Children's Rights Alliance, the International Coalition Against Blasphemy Laws and the National Women's Council of Ireland. The group estimates it has about 500 members.

Educate Together is an educational charity in Ireland which is the patron body to "equality-based, co-educational, child centred, and democratically run" schools. It was founded in 1984 to act as the patron body for the new multidenominational schools that opened after the establishment of the Dalkey School Project. As of 2019, Educate Together is the patron of 90 national schools in Ireland. In 2014 three Educate Together Second Level Schools opened in Dublin 15, Drogheda and Lucan along with the first Educate Together school outside Ireland, in Bristol in the United Kingdom. In joint patronage with Kildare and Wicklow ETB, Educate Together opened another second-level school, Celbridge Community School, in 2015.

Old Parish is a village in west County Waterford, Ireland. It is part of the Gaeltacht in Waterford Gaeltacht na nDéise.
An Foras Pátrúnachta na Scoileanna Lán-Ghaeilge Teo. is the largest patron body of gaelscoileanna in the Republic of Ireland. It was founded in 1993 to act as an alternative patron body for gaelscoileanna. The organisation's name is usually abbreviated to An Foras Pátrúnachta. 70 gaelscoileanna, which constitutes as of September 2017 44% of all the gaelscoileanna in the Republic of Ireland, are under the patronage of An Foras. In late 2017, they announced that from September 2018, school students under their patronage in schools would learn a third language alongside Irish and English in both primary and second-level and be taught one subject through that language. Their Ard-Rúnaí is Caoimhín Ó hEaghra. He is a brother of national Irish journalists Cormac Ó hEaghra and Róisín O'Hara.
Catholic education in Australia refers to the education services provided by the Catholic Church in Australia within the Australian education system. From 18th century foundations, the Catholic education system has grown to be the second biggest provider of school-based education in Australia, after government schools. The Catholic Church has established primary, secondary and tertiary educational institutions in Australia. As of 2018, one in five Australian students attend Catholic schools. There are 1,755 Catholic schools in Australia with more than 777,000 students enrolled, employing almost 100,000 staff.
The secular movement refers to a social and political trend in the United States, beginning in the early years of the 20th century, with the founding of the American Association for the Advancement of Atheism in 1925 and the American Humanist Association in 1941, in which atheists, agnostics, secular humanists, freethinkers, and other nonreligious and nontheistic Americans have grown in both numbers and visibility. There has been a sharp increase in the number of Americans who identify as religiously unaffiliated, from under 10 percent in the 1990s to 20 percent in 2013. The trend is especially pronounced among young people, with about one in three Americans younger than 30 identifying as religiously unaffiliated, a figure that has nearly tripled since the 1990s.
Gaelscoil Chill Dara (GSCD) is a coeducational Irish language primary school situated on the Green Road in the Curragh, County Kildare in Ireland.
References
- ↑ "Secular Schools Ireland Ltd". SoloCheck.
- ↑ Ann O'Loughlin (21 July 2015). "Legal challenge over school patronage decision". Irish Examiner.
- ↑ Órla Ryan (14 March 2016). "Secular Schools Ireland to apply to run three new primary schools in Dublin". TheJournal.ie.
- ↑ Ray Managh (5 September 2015). "Secular body's school patronage challenge fails". Irish Times.