
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone through lithification.

Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock.
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation, transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.

Palynology is the study of microorganisms and microscopic fragments of mega-organisms that are composed of acid-resistant organic material and occur in sediments, sedimentary rocks, and even some metasedimentary rocks. Palynomorphs are the microscopic, acid-resistant organic remains and debris produced by a wide variety plants, animals, and Protista that have existed since the late Proterozoic.

A concretion is a hard, compact mass formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular shapes also occur. The word 'concretion' is derived from the Latin concretio "(act of) compacting, condensing, congealing, uniting", itself from con meaning 'together' and crescere meaning "to grow". Concretions form within layers of sedimentary strata that have already been deposited. They usually form early in the burial history of the sediment, before the rest of the sediment is hardened into rock. This concretionary cement often makes the concretion harder and more resistant to weathering than the host stratum.
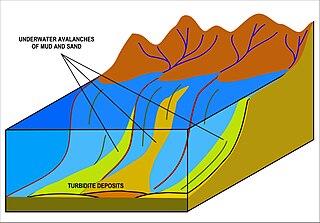
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.

Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the forces acting on them: these forces can be due to gravity, centrifugal acceleration, or electromagnetism. Settling is the falling of suspended particles through the liquid, whereas sedimentation is the final result of the settling process.

In geology, a facies is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks, and the changes that may occur in those attributes over a geographic area. A facies encompasses all of the characteristics of a rock including its chemical, physical, and biological features that distinguish it from adjacent rock.
Detritus is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion. A fragment of detritus is called a clast. Detrital particles can consist of lithic fragments, or of monomineralic fragments. These particles are often transported through sedimentary processes into depositional systems such as riverbeds, lakes or the ocean, forming sedimentary successions. Diagenetic processes can transform these sediments into rock through cementation and lithification, forming sedimentary rocks such as sandstone. These rocks can then in turn again be weathered and eroded to form a second generation of sediment. Detrital grains commonly weather at different rates, according to the Goldich dissolution series, which dictates that early crystallizing minerals are less stable at the earth's surface than late crystallizing minerals.

Aggradation is the term used in geology for the increase in land elevation, typically in a river system, due to the deposition of sediment. Aggradation occurs in areas in which the supply of sediment is greater than the amount of material that the system is able to transport. The mass balance between sediment being transported and sediment in the bed is described by the Exner equation.

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.

In geology, a bed is a layer of sediment, sedimentary rock, or volcanic rock "bounded above and below by more or less well-defined bedding surfaces". Specifically in sedimentology, a bed can be defined in one of two major ways. First, Campbell and Reineck and Singh use the term bed to refer to a thickness-independent layer comprising a coherent layer of sedimentary rock, sediment, or pyroclastic material bounded above and below by surfaces known as bedding planes. By this definition of bed, laminae are small beds that constitute the smallest (visible) layers of a hierarchical succession and often, but not always, internally comprise a bed.
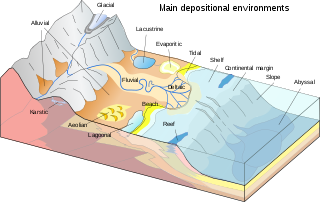
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. In most cases, the environments associated with particular rock types or associations of rock types can be matched to existing analogues. However, the further back in geological time sediments were deposited, the more likely that direct modern analogues are not available.
In sedimentology, compaction is the process by which a sediment progressively loses its porosity due to the effects of pressure from loading. This forms part of the process of lithification. When a layer of sediment is originally deposited, it contains an open framework of particles with the pore space being usually filled with water. As more sediment is deposited above the layer, the effect of the increased loading is to increase the particle-to-particle stresses resulting in porosity reduction primarily through a more efficient packing of the particles and to a lesser extent through elastic compression and pressure solution. The initial porosity of a sediment depends on its lithology. Mudstones start with porosities of >60%, sandstones typically ~40% and carbonates sometimes as high as 70%. Results from hydrocarbon exploration wells show clear porosity reduction trends with depth. Compaction trend estimation and decompaction process are useful for analyzing numerical basin evolution and evaluating hydrocarbon reservoirs and geological storages.
In sedimentary geology and geomorphology, the term progradation refers to the growth of a river delta farther out into the sea over time. This occurs when the volume of incoming sediment is greater than the volume of the delta that is lost through subsidence, sea-level rise, or erosion.

Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentary layers and soft sediment deformation structures formed by shaking. This subtle change in usage accommodates structures that may not remain within a layer.
The geology of Cyprus is part of the regional geology of Europe. Cyprus lies on the southern border of the Eurasian Plate and on the southern margin of the Anatolian Plate. The southern margin of the Anatolian Plate is in collision with the African Plate, which has created the uplift of the Cyprus arc and Cyprus itself.
Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the origin of sediments. The Earth is a dynamic planet, and all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Rocks exposed to the surface are sooner or later broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosional history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.
The Eastern Andes Metamorphic Complex is a large coherent but varied group of metamorphic and sedimentary rocks –in other words a geologic complex– that crops out in the eastern Patagonian Andes in Chile and Argentina. The metamorphic grade of rocks varies but does not exceed greenschist facies, the only exception to this are rocks near plutons affected by contact metamorphism. The sedimentary protoliths sedimented in the Late Paleozoic. The pressures and temperatures of metamorphism of the Eastern Andes Metamorphic Complex are different those usually expected from accretionary complexes. The sedimentary protoliths of the Eastern Andes Metamorphic Complex were likely deposited in a passive continental margin.










