
The Kingdom of Travancore, also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At its zenith, the kingdom covered most of the south of modern-day Kerala, and the southernmost part of modern-day Tamil Nadu with the Thachudaya Kaimal's enclave of Irinjalakuda Koodalmanikyam temple in the neighbouring Kingdom of Cochin. However Tangasseri area of Kollam city and Anchuthengu near Attingal in Thiruvananthapuram district, were British colonies and were part of the Malabar District until 30 June 1927, and Tirunelveli district from 1 July 1927 onwards. Travancore merged with the erstwhile princely state of Cochin to form Travancore-Cochin in 1950. The five Tamil-majority Taluks of Vilavancode, Kalkulam, Thovalai, Agastheeswaram, and Sengottai were transferred from Travancore-Cochin to Madras State in 1956. The Malayalam-speaking regions of Travancore-Cochin merged with the Malabar District and the Kasaragod taluk of the South Canara district in Madras State to form the modern Malayalam-state of Kerala on 1 November 1956, according to the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 passed by the Government of India.

The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including all of the Indian state of Andhra State, almost all of Tamil Nadu and some parts of Kerala, Karnataka, Odisha and the union territory of Lakshadweep. The city of Madras was the winter capital of the presidency and Ooty was the summer capital. The coastal regions and northern part of Island of Ceylon at that time was a part of Madras Presidency from 1793 to 1798, when it became a separate Crown colony. Madras Presidency was neighboured by the Kingdom of Mysore on the northwest, Kingdom of Cochin on the southwest, Kingdom of Pudukkottai in the center, and the Kingdom of Hyderabad on the north. Some parts of the presidency were also flanked by Bombay Presidency (Konkan) and Central Provinces and Berar.

Dr. Ambedkar Government Law College, commonly known by its former name Madras Law College, is a law school, located in Chennai (Madras), Tamil Nadu, India. It is also referred to as Government Law College or GLC, Chennai. It was established in 1891. It was renamed in 1990, as Dr. Ambedkar Government Law College, by the Government of Tamil Nadu in commemoration of the birth centenary of B. R. Ambedkar. In 1997, the Government of Tamil Nadu passed an Act which brought the college under the wings of the newly established Tamil Nadu Dr. Ambedkar Law University, splitting the college from the University of Madras.
The Justice Party, officially the South Indian Liberal Federation, was a political party in the Madras Presidency of British India. It was established on 20 November 1916 in Victoria Public Hall in Madras by Dr C. Natesa Mudaliar and co-founded by T. M. Nair, P. Theagaraya Chetty and Alamelu Mangai Thayarammal as a result of a series of non-Brahmin conferences and meetings in the presidency. Communal division between Brahmins and non-Brahmins began in the presidency during the late-19th and early-20th century, mainly due to caste prejudices and disproportionate Brahminical representation in government jobs. The Justice Party's foundation marked the culmination of several efforts to establish an organisation to represent the non-Brahmins in Madras and is seen as the start of the Dravidian Movement.

Dharmapuri is one of the 38 districts in the state of Tamil-Nadu, India. It is the first district created in Tamil Nadu after the independence of India by splitting it from then-Salem district on 2 October 1965. Dharmapuri District is one of the major producers of mango in the state, fine quality granite is found in the district. It is also one of the main sericulture belts in the state. Around 30 percent of the district's area is under forest cover. Kaveri enters Tamil Nadu through this district. Dharmapuri district had the lowest literacy rate of 74.23% in Tamilnadu during the 2011 census.

Minjur Bhakthavatsalam was an Indian independence activist and politician who served as the chief minister of Madras State from 2 October 1963 to 6 March 1967. He was the last Congress chief minister of Tamil Nadu and the last to have taken part in the Indian independence movement.
Diwan Bahadur Agaram Subbarayalu Reddiar was a landlord and Chief Minister or Premier of Madras Presidency from 17 December 1920 to 11 July 1921.
N. Gopala Menon was a lawyer and an Indian politician of the Indian National Congress, also Member of the Legislative Assembly of Madras state. He served as the Speaker of the Madras Legislative Assembly from 1955 to 1956.
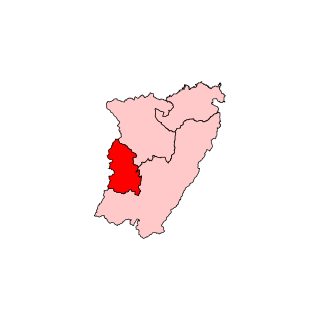
Cumbum is a state assembly constituency in Theni district in Tamil Nadu, part of the Theni Lok Sabha constituency. Elections were not held in 1957 and 1962. It is one of the 234 State Legislative Assembly Constituencies in Tamil Nadu, in India.

The Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It has a strength of 234 members of whom are democratically elected using the First-past-the-post system. The presiding officer of the Assembly is the Speaker. The term of the Assembly is five years unless dissolved earlier.

Thottakurichi Muthuswamy Nallaswamypopularly known as T.M.N was an Indian politician and Member of the Legislative Assembly of Tamil Nadu. He was elected to the 2nd, 3rd & 4th Madras State Legislative Assemblies later renamed Tamil Nadu Legislative Assembly as an Indian National Congress candidate from Karur constituency in the Madras State Legislative Assembly elections in 1957, 1962 and 1967.

The second legislative assembly election for the Madras Presidency after the establishment of a bicameral legislature by the Government of India Act of 1935 was held in 1946. The election was held after 6 years of Governor's rule starting from 1939, when the Indian National Congress government of C. Rajagopalachari resigned protesting Indian involvement in World War II. This was the last election held in the presidency - after Indian independence in 1947, the presidency became the Madras state. The election was held simultaneously with that of the Legislative Council. The Congress swept the polls by winning 163 out of 215 seats. The years after this election saw factionalism in Madras Congress party with divisions across regional and communal lines. Competition among T. Prakasam, C. Rajagopalachari and K. Kamaraj resulted in the election of Prakasam as the Chief Minister initially. But he was later defeated by Omandur Ramaswamy Reddiar with Kamaraj's support. In turn, Reddiar himself was ousted to make way for P. S. Kumaraswamy Raja with the support of Kamaraj.

The second legislative council election to Madras Presidency after the establishment of diarchical system of government by the Government of India Act, 1919 was held in 1923. Voter turnout was higher than the previous election. Swarajists, a breakaway group from Indian National Congress participated in the election. The ruling Justice Party had suffered a split, when a splinter group calling themselves anti-Ministerialists left the party. It won the highest number of seats but fell short of a majority. Nevertheless, Madras Governor Willington invited it to form the government. Incumbent Justice chief minister Panagal Raja was nominated by party leader Theagaraya Chetty to continue as chief minister for a second term. The government survived a no-confidence motion, brought against it on the first day of its tenure by the opposition headed by C. R. Reddy.
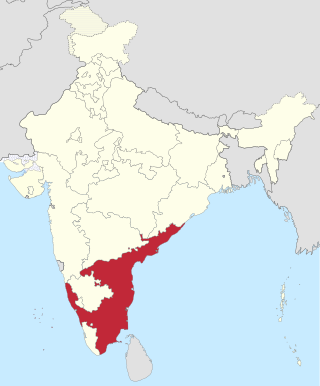
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu, Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and central Kerala, Bellary, South Canara and Kollegal. Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema were separated to form Andhra State in 1953, while South Canara and Bellary districts along with the Kollegalam taluka of Coimbatore district were merged with Mysore State, and Malabar District with the State of Travancore-Cochin to form Kerala in 1956. Post State Reorganization in 1956, the remaining Madras State was renamed to Tamil Nadu on January 14, 1969.

Maniyachchi is a township in the Thoothukudi district of Tamil Nadu situated approximately 40 km west of Thootukudi and some 30 km from Palayamkottai and Kovilpatti.
Broadcasting in the city of Chennai began in 1924 by the Madras Presidency Radio Club. The service was operational till the government-run All India Radio started broadcasting in the city in 1938.
S. Ramanathan was an Indian politician who served as the minister of Madras Presidency in the Congress-led government of 1937. He was the first founder of the Self-Respect Movement.











