View of Selvagem Grande | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
| Coordinates | 30°08′51″N15°51′54″W / 30.14750°N 15.86500°W |
| Archipelago | Savage Islands |
| Highest elevation | 163 m (535 ft) |
| Highest point | Pico da Atalaia |
| Administration | |
| Autonomous Region | |
| Municipality | Funchal |
| Freguesia | Sé |
| Demographics | |
| Population | no permanent residents (2+ rangers and research personnel) |
Selvagem Grande Island is part of the Savage Islands archipelago, which themselves are part of the Portuguese Autonomous Region of Madeira in the North Atlantic Ocean.
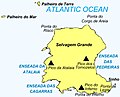
The island (2,000 by 1,700 metres (6,600 ft × 5,600 ft)) belongs to the northeast group of the Savage Islands, which comprises in addition three islets: Sinho Islet, Palheiro de Terra and Palheiro do Mar. [1]
It is generally flat, but has three summits, remnants of former volcanic cones appropriately named Atalaia, Tornozelos and Inferno, Atalaia being the highest of the three, reaching 163 m (535 ft) in altitude. [1]
The island has three residents year-round, two park rangers and a biologist. [1]
The island has a lighthouse, which is automated. [2]
- Nautical chart of the archipelago (1884)
- The Selvagem Grande Island
- Sentinel-2 image of the island (October 2021)
- Northern Island, aerial view
- Side view of the Island
- Warden's base