Related Research Articles
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance.
Middleware in the context of distributed applications is software that provides services beyond those provided by the operating system to enable the various components of a distributed system to communicate and manage data. Middleware supports and simplifies complex distributed applications. It includes web servers, application servers, messaging and similar tools that support application development and delivery. Middleware is especially integral to modern information technology based on XML, SOAP, Web services, and service-oriented architecture.
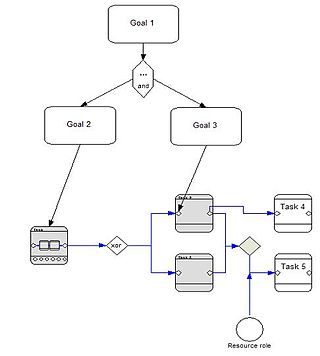
Extended Enterprise Modeling Language (EEML) in software engineering is a modelling language used for Enterprise modelling across a number of layers.

Advanced Resource Connector (ARC) is a grid computing middleware introduced by NorduGrid. It provides a common interface for submission of computational tasks to different distributed computing systems and thus can enable grid infrastructures of varying size and complexity. The set of services and utilities providing the interface is known as ARC Computing Element (ARC-CE). ARC-CE functionality includes data staging and caching, developed in order to support data-intensive distributed computing. ARC is an open source software distributed under the Apache License 2.0.

Copernicus is the Earth observation component of the European Union Space Programme, managed by the European Commission and implemented in partnership with the EU Member States, the European Space Agency (ESA), the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), the Joint Research Centre (JRC), the European Environment Agency (EEA), the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), Frontex, SatCen and Mercator Océan.

The Publications Office of the European Union is the official provider of publishing services to all EU institutions, bodies and agencies. This makes it the central point of access to EU law, publications, open data, research results, procurement notices, and other official information.

The European Institute for Health Records or EuroRec Institute is a non-profit organization founded in 2002 as part of the ProRec initiative. On 13 May 2003, the institute was established as a non-profit organization under French law. Current President of EuroRec is Prof. Dipak Kalra. The institute is involved in the promotion of high quality Electronic Health Record systems in the European Union. One of the main missions of the institute is to support, as the European authorised certification body, EHRs certification development, testing and assessment by defining functional and other criteria.
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator.
The Open Source Observatory and Repository (OSOR) is an online project launched by the European Commission under the IDABC programme, to support the distribution and re-use of software developed by or for public sector administrations across Europe, connecting EU services and Member States.
The Semantic Interoperability Community Europe (SEMIC.EU) was an eGovernment service initiated by the European Commission and managed by the Interoperable Delivery of European eGovernment Services to public Administrations, Businesses and Citizens (IDABC) Unit. As one of the 'horizontal measures' of the IDABC, it was established as a permanent implementation of the principles stipulated in the 'European Interoperability Framework' (EIF). It offered a service for the exchange of semantic interoperability solutions, with a focus on demands of eGovernment in Europe. Through the establishment of a single sharing and collaboration point, the European Union wanted to resolve the problems of semantic interoperability amongst the EU member states. The main idea behind the service was to make visible specifications that already exist, so as to increase their reuse. In this way, governmental agencies and developers benefit as they do not reinvent the wheel, they reduce development costs, and increase the interoperability of their systems.
The Handle System is the Corporation for National Research Initiatives's proprietary registry assigning persistent identifiers, or handles, to information resources, and for resolving "those handles into the information necessary to locate, access, and otherwise make use of the resources".
All European countries show eGovernment initiatives, mainly related to the improvement of governance at the national level. Significant eGovernment activities also take place at the European Commission level as well. There is an extensive list of eGovernment Fact Sheets maintained by the European Commission.
The SHIWA project within grid computing was a project led by the LPDS of MTA Computer and Automation Research Institute. The project coordinator was Prof. Dr. Peter Kacsuk. It started on 1 July 2010 and lasted two years. SHIWA was supported by a grant from the European Commission's FP7 INFRASTRUCTURES-2010-2 call under grant agreement n°261585.
Model Driven Interoperability (MDI) is a methodological framework, which provides a conceptual and technical support to make interoperable enterprises using ontologies and semantic annotations, following model driven development (MDD) principles.

Diplomatic relations between European countries and Indonesia date back to 1949. Initially, European Union (EU)–Indonesia relations were facilitated through the EU–Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) cooperation. Bilateral cooperation was continuously expanded and eventually the EU Delegation to Indonesia was opened in 1988. Economic and political dialogue between Indonesia and the EU takes the form of regular Senior Officials Meetings. In 2000 relations were further reinforced with the release of the European Commission's communication "Developing Closer Relations between Indonesia and the EU". In November 2013, the EU's high representative for foreign and security policy Catherine Ashton made her first official visit to Indonesia.

Joinup is a collaboration platform created by the European Commission. It is funded by the European Union via its Interoperability Solutions for Public Administrations Programme.
The once-only principle is an e-government concept that aims to ensure that citizens, institutions, and companies only have to provide certain standard information to the authorities and administrations once. By incorporating data protection regulations and the explicit consent of the users, the public administration is allowed to re-use and exchange the data with each other. The once-only principle is part of the European Union's (EU) plans to further develop the Digital Single Market by reducing the administrative burden on citizens and businesses.
The National Documentation Centre is a Greek public organisation that promotes knowledge, research, innovation and digital transformation. It was established in 1980 with funding from the United Nations Development Programme with the aim to strengthen the collection and distribution of research-related material, and to ensure full accessibility to it. It has been designated as a National Scientific Infrastructure, a National Authority of the Hellenic Statistical System, and National Contact Point for European Research and Innovation Programmes. Since August 2019, it has been established as a discrete public-interest legal entity under private law, and is supervised by the Ministry of Digital Governance. The management bodies of EKT are the Administrative Board and the Director who, since 2013, has been Dr. Evi Sachini.
D4Science is an organisation operating a Data Infrastructure offering a rich array of services by community-driven virtual research environments. In particular, it supports communities of practice willing to implement open science practices. The infrastructure follows the system of systems approach, where the constituent systems offer “resources” assembled together to implement the overall set of D4Science services. In particular, D4Science aggregates “domain agnostic” service providers as well as community-specific ones to build a unifying space where the aggregated resources can be exploited via Virtual research Environments and their services.
A common data model (CDM) can refer to any standardised data model which allows for data and information exchange between different applications and data sources. Common data models aim to standardise logical infrastructure so that related applications can "operate on and share the same data", and can be seen as a way to "organize data from many sources that are in different formats into a standard structure".
References
- ↑ "SemanticGov" . Retrieved 2007-10-18.
- ↑ Cabral, L.; et al. (2004). "Approaches to Semantic Web Services: an Overview and Comparisons". Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. pp. 225–239.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help)