
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences, such as calculating the distance cost between strings in a natural language or in financial data.

Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by computational biology; and it is important in medicine and biotechnology.

Structural alignment attempts to establish homology between two or more polymer structures based on their shape and three-dimensional conformation. This process is usually applied to protein tertiary structures but can also be used for large RNA molecules. In contrast to simple structural superposition, where at least some equivalent residues of the two structures are known, structural alignment requires no a priori knowledge of equivalent positions. Structural alignment is a valuable tool for the comparison of proteins with low sequence similarity, where evolutionary relationships between proteins cannot be easily detected by standard sequence alignment techniques. Structural alignment can therefore be used to imply evolutionary relationships between proteins that share very little common sequence. However, caution should be used in using the results as evidence for shared evolutionary ancestry because of the possible confounding effects of convergent evolution by which multiple unrelated amino acid sequences converge on a common tertiary structure.

The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine the evolutionary relationship between proteins. Proteins with the same shapes but having little sequence or functional similarity are placed in different superfamilies, and are assumed to have only a very distant common ancestor. Proteins having the same shape and some similarity of sequence and/or function are placed in "families", and are assumed to have a closer common ancestor.

The CATH Protein Structure Classification database is a free, publicly available online resource that provides information on the evolutionary relationships of protein domains. It was created in the mid-1990s by Professor Christine Orengo and colleagues including Janet Thornton and David Jones, and continues to be developed by the Orengo group at University College London. CATH shares many broad features with the SCOP resource, however there are also many areas in which the detailed classification differs greatly.

Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, which are the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a residue, which indicates a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the topic of the scientific field of structural biology, which employs techniques such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and dual polarisation interferometry, to determine the structure of proteins.
A Gap penalty is a method of scoring alignments of two or more sequences. When aligning sequences, introducing gaps in the sequences can allow an alignment algorithm to match more terms than a gap-less alignment can. However, minimizing gaps in an alignment is important to create a useful alignment. Too many gaps can cause an alignment to become meaningless. Gap penalties are used to adjust alignment scores based on the number and length of gaps. The five main types of gap penalties are constant, linear, affine, convex, and profile-based.
In molecular biology, protein threading, also known as fold recognition, is a method of protein modeling which is used to model those proteins which have the same fold as proteins of known structures, but do not have homologous proteins with known structure. It differs from the homology modeling method of structure prediction as it is used for proteins which do not have their homologous protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), whereas homology modeling is used for those proteins which do. Threading works by using statistical knowledge of the relationship between the structures deposited in the PDB and the sequence of the protein which one wishes to model.
Families of Structurally Similar Proteins or FSSP is a database of structurally superimposed proteins generated using the "Distance-matrix ALIgnment" (DALI) algorithm.The database currently contains an extended structural family for each of 330 representative protein chains. Each data set contains structural alignments of one search structure with all other structurally significantly similar proteins in the representative set, as well as all structures in the Protein Data Bank with 70-30% sequence identity relative to the search structure. Very close homologs are excluded as they rarely have marked structural differences. The alignments of remote homologs are the result of pairwise all-against-all structural comparisons in the set of 330 representative protein chains. All such comparisons are based purely on the 3D co-ordinates of the proteins and are derived by automatic (objective) structure comparison programs. The significance of structural similarity is estimated based on statistical criteria. The FSSP database is available electronically from the EMBL file server and by anonymous ftp. The database is helpful for the comparison of protein structures.
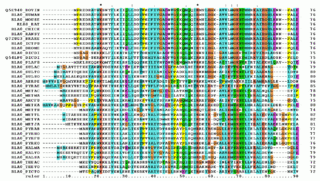
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acids or nucleotides.
T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can also combine multiple sequences alignments obtained previously and in the latest versions can use structural information from PDB files (3D-Coffee). It has advanced features to evaluate the quality of the alignments and some capacity for identifying occurrence of motifs (Mocca). It produces alignment in the aln format (Clustal) by default, but can also produce PIR, MSF, and FASTA format. The most common input formats are supported.
This list of structural comparison and alignment software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used in pairwise or multiple structural comparison and structural alignment.

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein. Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been seen that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.

In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins.
RAPTOR is protein threading software used for protein structure prediction. It has been replaced by RaptorX, which is much more accurate than RAPTOR.
In bioinformatics, the template modeling score or TM-score is a measure of similarity between two protein structures. The TM-score is intended as a more accurate measure of the global similarity of full-length protein structures than the often used RMSD measure. The TM-score indicates the similarity between two structures by a score between , where 1 indicates a perfect match between two structures. Generally scores below 0.20 corresponds to randomly chosen unrelated proteins whereas structures with a score higher than 0.5 assume roughly the same fold. A quantitative study shows that proteins of TM-score = 0.5 have a posterior probability of 37% in the same CATH topology family and of 13% in the same SCOP fold family. The probabilities increase rapidly when TM-score > 0.5. The TM-score is designed to be independent of protein lengths.
Phyre and Phyre2 are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques, it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.

David Tudor Jones is a Professor of Bioinformatics, and Head of Bioinformatics Group in the University College London. He is also the director in Bloomsbury Center for Bioinformatics, which is a joint Research Centre between UCL and Birkbeck, University of London and which also provides bioinformatics training and support services to biomedical researchers. In 2013, he is a member of editorial boards for PLoS ONE, BioData Mining, Advanced Bioinformatics, Chemical Biology & Drug Design, and Protein: Structure, Function and Bioinformatics.
The HH-suite is an open-source software package for sensitive protein sequence searching. It contains programs that can search for similar protein sequences in protein sequence databases. Sequence searches are a standard tool in modern biology with which the function of unknown proteins can be inferred from the functions of proteins with similar sequences. HHsearch and HHblits are two main programs in the package and the entry point to its search function, the latter being a faster iteration. HHpred is an online server for protein structure prediction that uses homology information from HH-suite.
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred. Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent. Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term protein clan is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems.









