Related Research Articles

Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, is a technique in instrumental analysis where two or more mass analyzers are coupled together using an additional reaction step to increase their abilities to analyse chemical samples. A common use of tandem MS is the analysis of biomolecules, such as proteins and peptides.
Protein sequencing is the practical process of determining the amino acid sequence of all or part of a protein or peptide. This may serve to identify the protein or characterize its post-translational modifications. Typically, partial sequencing of a protein provides sufficient information to identify it with reference to databases of protein sequences derived from the conceptual translation of genes.

Peptide mass fingerprinting (PMF) is an analytical technique for protein identification in which the unknown protein of interest is first cleaved into smaller peptides, whose absolute masses can be accurately measured with a mass spectrometer such as MALDI-TOF or ESI-TOF. The method was developed in 1993 by several groups independently. The peptide masses are compared to either a database containing known protein sequences or even the genome. This is achieved by using computer programs that translate the known genome of the organism into proteins, then theoretically cut the proteins into peptides, and calculate the absolute masses of the peptides from each protein. They then compare the masses of the peptides of the unknown protein to the theoretical peptide masses of each protein encoded in the genome. The results are statistically analyzed to find the best match.
Genome-based peptide fingerprint scanning (GFS) is a system in bioinformatics analysis that attempts to identify the genomic origin of sample proteins by scanning their peptide-mass fingerprint against the theoretical translation and proteolytic digest of an entire genome. This method is an improvement from previous methods because it compares the peptide fingerprints to an entire genome instead of comparing it to an already annotated genome. This improvement has the potential to improve genome annotation and identify proteins with incorrect or missing annotations.
The Trans-Proteomic Pipeline (TPP) is an open-source data analysis software for proteomics developed at the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) by the Ruedi Aebersold group under the Seattle Proteome Center. The TPP includes PeptideProphet, ProteinProphet, ASAPRatio, XPRESS and Libra.
A peptide sequence tag is a piece of information about a peptide obtained by tandem mass spectrometry that can be used to identify this peptide in a protein database.
Mascot is a software search engine that uses mass spectrometry data to identify proteins from peptide sequence databases. Mascot is widely used by research facilities around the world. Mascot uses a probabilistic scoring algorithm for protein identification that was adapted from the MOWSE algorithm. Mascot is freely available to use on the website of Matrix Science. A license is required for in-house use where more features can be incorporated.
PEAKS is a proteomics software program for tandem mass spectrometry designed for peptide sequencing, protein identification and quantification.

Protein mass spectrometry refers to the application of mass spectrometry to the study of proteins. Mass spectrometry is an important method for the accurate mass determination and characterization of proteins, and a variety of methods and instrumentations have been developed for its many uses. Its applications include the identification of proteins and their post-translational modifications, the elucidation of protein complexes, their subunits and functional interactions, as well as the global measurement of proteins in proteomics. It can also be used to localize proteins to the various organelles, and determine the interactions between different proteins as well as with membrane lipids.
Shotgun proteomics refers to the use of bottom-up proteomics techniques in identifying proteins in complex mixtures using a combination of high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry. The name is derived from shotgun sequencing of DNA which is itself named after the rapidly expanding, quasi-random firing pattern of a shotgun. The most common method of shotgun proteomics starts with the proteins in the mixture being digested and the resulting peptides are separated by liquid chromatography. Tandem mass spectrometry is then used to identify the peptides.
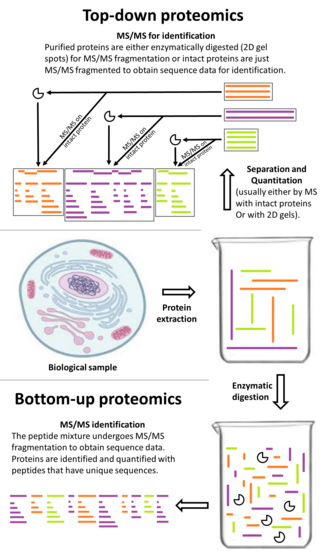
Bottom-up proteomics is a common method to identify proteins and characterize their amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications by proteolytic digestion of proteins prior to analysis by mass spectrometry. The major alternative workflow used in proteomics is called top-down proteomics where intact proteins are purified prior to digestion and/or fragmentation either within the mass spectrometer or by 2D electrophoresis. Essentially, bottom-up proteomics is a relatively simple and reliable means of determining the protein make-up of a given sample of cells, tissues, etc.

Quantitative proteomics is an analytical chemistry technique for determining the amount of proteins in a sample. The methods for protein identification are identical to those used in general proteomics, but include quantification as an additional dimension. Rather than just providing lists of proteins identified in a certain sample, quantitative proteomics yields information about the physiological differences between two biological samples. For example, this approach can be used to compare samples from healthy and diseased patients. Quantitative proteomics is mainly performed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE), preparative one-dimensional gel electrophoresis, or mass spectrometry (MS). However, a recent developed method of quantitative dot blot (QDB) analysis is able to measure both the absolute and relative quantity of an individual proteins in the sample in high throughput format, thus open a new direction for proteomic research. In contrast to 2-DE, which requires MS for the downstream protein identification, MS technology can identify and quantify the changes.

Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) is an isobaric labeling method used in quantitative proteomics by tandem mass spectrometry to determine the amount of proteins from different sources in a single experiment. It uses stable isotope labeled molecules that can be covalent bonded to the N-terminus and side chain amines of proteins.
Label-free quantification is a method in mass spectrometry that aims to determine the relative amount of proteins in two or more biological samples. Unlike other methods for protein quantification, label-free quantification does not use a stable isotope containing compound to chemically bind to and thus label the protein.
A peptide spectral library is a curated, annotated and non-redundant collection/database of LC-MS/MS peptide spectra. One essential utility of a peptide spectral library is to serve as consensus templates supporting the identification of peptide/proteins based on the correlation between the templates with experimental spectra.

Proteogenomics is a field of biological research that utilizes a combination of proteomics, genomics, and transcriptomics to aid in the discovery and identification of peptides. Proteogenomics is used to identify new peptides by comparing MS/MS spectra against a protein database that has been derived from genomic and transcriptomic information. Proteogenomics often refers to studies that use proteomic information, often derived from mass spectrometry, to improve gene annotations. The utilization of both proteomics and genomics data alongside advances in the availability and power of spectrographic and chromatographic technology led to the emergence of proteogenomics as its own field in 2004.
In bio-informatics, a peptide-mass fingerprint or peptide-mass map is a mass spectrum of a mixture of peptides that comes from a digested protein being analyzed. The mass spectrum serves as a fingerprint in the sense that it is a pattern that can serve to identify the protein. The method for forming a peptide-mass fingerprint, developed in 1993, consists of isolating a protein, breaking it down into individual peptides, and determining the masses of the peptides through some form of mass spectrometry. Once formed, a peptide-mass fingerprint can be used to search in databases for related protein or even genomic sequences, making it a powerful tool for annotation of protein-coding genes.
In mass spectrometry, de novo peptide sequencing is the method in which a peptide amino acid sequence is determined from tandem mass spectrometry.
In mass spectrometry, data-independent acquisition (DIA) is a method of molecular structure determination in which all ions within a selected m/z range are fragmented and analyzed in a second stage of tandem mass spectrometry. Tandem mass spectra are acquired either by fragmenting all ions that enter the mass spectrometer at a given time or by sequentially isolating and fragmenting ranges of m/z. DIA is an alternative to data-dependent acquisition (DDA) where a fixed number of precursor ions are selected and analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry.
References
- ↑ Jimmy K. Eng, Ashley L. McCormack, and John R. Yates, III (1994). "An Approach to Correlate Tandem Mass Spectral Data of Peptides with Amino Acid Sequences in a Protein Database". J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 5 (11): 976–989. doi: 10.1016/1044-0305(94)80016-2 . PMID 24226387.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)