
The politics of Pakistan takes place within the framework established by the constitution. The country is a federal parliamentary republic in which provincial governments enjoy a high degree of autonomy and residuary powers. Executive power is vested with the national cabinet which is headed by the prime minister, who works coherently along with the bicameral parliament and the judicature. Stipulations set by the constitution provide a delicate check and balance of sharing powers between executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the government.

The federal government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic in North America, composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court.
The Eighth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan allowed the President to unilaterally dissolve the National Assembly and elected governments. The National Assembly of Pakistan amended the Constitution of Pakistan in 1985 and the law stayed on the books until its repeal in 1997.

The President of Pakistan, is the ceremonial head of state of Pakistan and the Commander-in-Chief of Pakistan Armed Forces.

The Constitution of South Africa is the supreme law of the Republic of South Africa. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the republic, it sets out the rights and duties of its citizens, and defines the structure of the Government. The current constitution, the country's fifth, was drawn up by the Parliament elected in 1994 in the South African general election, 1994. It was promulgated by President Nelson Mandela on 18 December 1996 and came into effect on 4 February 1997, replacing the Interim Constitution of 1993. The first constitution was enacted by the South Africa Act 1909, the longest-lasting to date. Since 1961, the constitutions have promulgated a republican form of government.

Muhammad Rafiq Tarar is a Pakistani politician and a jurist who served as the ninth President of Pakistan from January 1998 until his resignation in June 2001, and prior to that as a senator from Punjab in 1997. Before entering politics, Tarar served as senior justice of the Supreme Court of Pakistan from 1991 to 1994 and as the 28th Chief Justice of Lahore High Court from 1989 to 1991.

The prime minister of Pakistan is the head of government of Pakistan and designated as the "Chief Executive of the Islamic Republic".

Senate of Pakistan or Aiwān-e-Bālā Pākistān is the upper legislative chamber of the bicameral legislature of Pakistan, and together with the National Assembly makes up the Parliament.
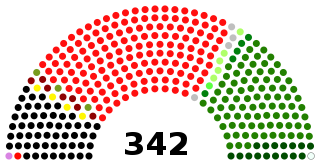
The National Assembly or Aiwān-e-Zairīñ of Pākistān is the lower legislative house of the bicameral Majlis-e-Shura, which also comprises the Senate of Pakistan. The National Assembly and the Senate both convene at Parliament House in Islamabad. The National Assembly is a democratically elected body consisting of a total of 336 members, before 25th amendment they used to be 342 who are referred to as Members of the National Assembly (MNAs), of which 272 are directly elected members and 70 reserved seats for women and religious minorities. A political party must secure 137 seats to obtain and preserve a majority.

Nazim Hussain Siddiqui a Pakistani jurist who served as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of Pakistan, from 31 December 2003 to 29 June 2005.

The Parliament of Pakistan is the federal and supreme legislative body of Pakistan. It is a bicameral federal legislature that consists of the Senate as the upper house and the National Assembly as the lower house. According to the constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, the President of Pakistan is also a component of the Parliament. The National Assembly is elected for a five-year term on the basis of adult franchise and one-man one-vote. The tenure of a Member of the National Assembly is for the duration of the house, or sooner, in case the Member dies or resigns. The tenure of the National Assembly also comes to an end if dissolved on the advice of the Prime Minister or by the president in his discretion under the Constitution.

Since its establishment in 1947, Pakistan has had an asymmetric federal government and is a federal parliamentary democratic republic. At the national level, the people of Pakistan elect a bicameral legislature, the Parliament of Pakistan. The parliament consists of a lower house called the National Assembly, which is elected directly, and an upper house called the Senate, whose members are chosen by elected provincial legislators. The head of government, the Prime Minister, is elected by the majority members of the National Assembly and the head of state, the President, is elected by the Electoral College, which consists of both houses of Parliament together with the four provincial assemblies. In addition to the national parliament and the provincial assemblies, Pakistan also has more than five thousand elected local governments.

Iftikhar Muhammad Chaudhry is a Pakistani jurist who served as the 20th Chief Justice of Pakistan over three non-consecutive terms from 29 June 2005 to 11 December 2013.

The 1999 military takeover in Pakistan was a bloodless coup d'état initiated by the military staff at the Joint Staff HQ working under Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee General Pervez Musharraf seized the control of the civilian government of publicly elected Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif on 12 October 1999. Simultaneously tenuring as the Chief of Army Staff, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs Gen. Musharraf, who then-acted as the country's Chief Executive, declared a state of emergency by issuing a controversial provisional order in a direct violation of that suspended the writ of the Constitution of Pakistan on 14 October 1999 — only two days of seizing the control of the federal government from the legal advise taken from his legal team led by Sharifuddin Pirzada.
This is a brief description of the lawmaking procedure in India.
The Legal Framework Order, 2002 was issued by Pakistani president Pervez Musharraf in August 2002. It provided for the general elections of 2002 and the revival of the 1973 Constitution of Pakistan, and added numerous amendments to the Constitution. The following month, the Supreme Court overruled Musharraf, ruling that the amendments would have to be ratified by Parliament in the manner provided in the unamended 1973 Constitution—the amendments would have to be approved by two-thirds of both houses of the bicameral body.
The Constitution of 1962 was the fundamental law of Islamic Republic of Pakistan from 8 June 1962 until martial law was declared in 26 March 1969. It was abrogated in the same year by President Yahya Khan.
The Eighteenth Amendment of the Constitution of Pakistan was passed by the National Assembly of Pakistan on April 8, 2010, removing the power of the President of Pakistan to dissolve the Parliament unilaterally, turning Pakistan from a semi-presidential to a parliamentary republic, and renaming North-West Frontier Province to Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The package was intended to counter the sweeping powers amassed by the presidency under former presidents General Pervez Musharraf and General Muhammad Zia-ul-Haq and to ease political instability in Pakistan. The bill reversed many infringements on the Constitution of Pakistan over several decades by its military rulers. The amendment bill was passed by the Senate of Pakistan on April 15, 2010 and it became an act of parliament when President Asif Ali Zardari put his signature on the bill on April 19, 2010. It was the first time in Pakistan's history that a president relinquished a significant part of his powers willingly and transferred them to parliament and the office of the prime minister.












