
The administrative units of Pakistan comprise four provinces, one federal territory, and two disputed territories: the provinces of Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan; the Islamabad Capital Territory; and the administrative territories of Azad Jammu and Kashmir and Gilgit–Baltistan. As part of the Kashmir conflict with neighbouring India, Pakistan has also claimed sovereignty over the Indian-controlled territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh since the First Kashmir War of 1947–1948. It also has a territorial dispute with India over Junagadh, but has never exercised administrative authority over either regions. All of Pakistan's provinces and territories are subdivided into divisions, which are further subdivided into districts, and then tehsils, which are again further subdivided into union councils.

The Provincially Administered Tribal Area (PATA) was the former administrative subdivision of Pakistan designated in the Article 246(b) of the Constitution of Pakistan. No Act of Provincial Assembly can be applied to PATA whereas the Governor of the respective province has a mandate parallel to the authority President of Pakistan has over Federally Administered Tribal Areas. In 2018, a Twenty-fifth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan merged PATA, as well as FATA into full control of the Khyber-Paktunkhwa government, thus the PATA designation has no legal standing in the future of Khyber-Paktunkhwa.

The Frontier Crimes Regulations (FCR) were a special set of laws of British India, and which were applicable to the Tribal Areas. They were enacted by the British Empire in the nineteenth century and remained in effect in Pakistan until 2018. They were extended to the Gilgit Agency in Jammu and Kashmir in 1901 and to Baltistan in 1947, remaining in effect till the 1970s.

The Federally Administered Tribal Areas, commonly known as FATA, was a semi-autonomous tribal region in north-western Pakistan that existed from 1947 until being merged with the neighbouring province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in 2018 through the Twenty-fifth amendment to the constitution of Pakistan. It consisted of seven tribal agencies (districts) and six frontier regions, and were directly governed by the federal government through a special set of laws called the Frontier Crimes Regulations.

Senate elections were held in Pakistan on 5 March 2015 to elect the replacements for 52 retiring senators. Those retiring include chairman Nayyar Hussain Bukhari and deputy chairman Sabir Ali Baloch of the upper house. Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP), the majority party in Senate, would lose 21 members, followed by Pakistan Muslim League Nawaz would lose 9 and Awami National Party would lose 6 members.

Triennial Senate elections were in Pakistan held on 3 March 2018 to replace 52 retiring senators - half of the Senate's strength - with the winning candidates serving six-year terms. Overall, Pakistan Muslim League (N) came out as the largest party, followed by the Pakistan Peoples Party and the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf. The results of these elections were steeped in controversy due to rampant allegations of horse trading and vote-buying, which lead to the Prime Minister and opposition leader Imran Khan calling for reforms. Prior to this election, PML (N) candidates were declared as independents by the Election Commission of Pakistan owing to a Supreme Court judgment.
The government of the Federally Administered Tribal Areas was the system by which the former Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) of Pakistan were governed, until its merger with the neighbouring Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. The semi-autonomous region was controlled by the federal government of Pakistan through the Governor of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Constitution of Pakistan contained special provisions for the governing of the FATA, together with the colonial-era Frontier Crimes Regulations (FCR). According to the now–repealed Article 247 of the Constitution of Pakistan, the FATA were outside the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court of Pakistan, the provincial High Courts or indeed the Provincial Assembly of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
Events in the year 2018 in Pakistan.

Barang Tehsil is an administrative subdivision (tehsil) of Bajaur District in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Barang is the sixth largest of Bajaur District's seven tehsils.

Mamund Tehsil is an administrative subdivision (tehsil) of Bajaur District in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Mamund is the largest of Bajaur District's seven tehsils.

Bar Chamarkand Tehsil, alternatively written Bar Chamar Kand is an administrative subdivision (tehsil) of Bajaur District in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Bar Chamarkand is the smallest of Bajaur District's seven tehsils.
The FATA Interim Governance Regulation, 2018 was a law signed by the President of Pakistan on May 28, 2018, which replaces the Frontier Crimes Regulations (FCR) and outline how the Federally Administered Tribal Areas will be governed "within a timeframe of two years" as the region is merged with Khyber Pakhtunkhwa through the passage of the Thirty-first Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan. An official described the regulation as a combination of the FCR and the rejected Tribal Areas Rewaj Act.

Provincial elections were held in the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa's constituencies belonging to areas previously known as the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) on 20 July 2019. After the election, the new members joined the already elected members from the rest of the province to complete the formation of 11th Provincial Assembly of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
The Pakistan Levies, or Federal Levies, are provincial paramilitary forces (gendarmeries) in Pakistan, whose primary missions are law enforcement, assisting the civilian police in maintaining law and order, and conducting internal security operations at the provincial level. The various Levies Forces operate under separate chains of command and wear distinct patches and badges.
On 31 May 2018, with the application of 25th Amendment, Federally Administrated Tribal Areas ceased to exist, and stood merged into neighbouring province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
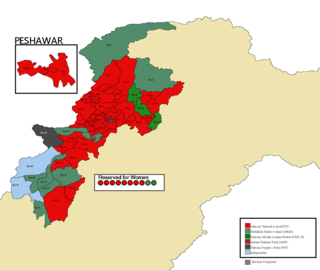
General elections were held in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa on Wednesday, 25 July 2018 to elect the 51 members of 15th National Assembly from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) obtained a landslide victory in the province by winning 37 general seats and increased their margin of victory from 2013. The PTI also won 8 out of 10 reserved seats while the Pakistan Muslim League (N) (PML-N) and Muttahida Majlis-e-Amal (MMA) won 1 reserved seat each.

PK-67 Mohmand-I is a constituency for the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Assembly of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.It was created in 2018 after merger of FATA with Khyber Pakhtunkhwa before 2019 elections.

PK-68 Mohmand-II is a constituency for the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Assembly of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.It was created in 2018 after merger of FATA with Khyber Pakhtunkhwa before 2019 elections.
PK-70 Khyber-II is a constituency for the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Assembly of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.It was created in 2018 after merger of FATA with Khyber Pakhtunkhwa before 2019 elections.

















