
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from her ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Reproductive technology encompasses all current and anticipated uses of technology in human and animal reproduction, including assisted reproductive technology (ART), contraception and others. It is also termed Assisted Reproductive Technology, where it entails an array of appliances and procedures that enable the realization of safe, improved and healthier reproduction. While this is not true of all people, for an array of married couples, the ability to have children is vital. But through the technology, infertile couples have been provided with options that would allow them to conceive children.
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species. It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity.
Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) is a tool of assisted reproductive technology against infertility. Eggs are removed from a woman's ovaries, and placed in one of the fallopian tubes, along with the man's sperm. The technique, first attempted by Steptoe and Edwards and later pioneered by endocrinologist Ricardo Asch, allows fertilization to take place inside the woman's uterus.
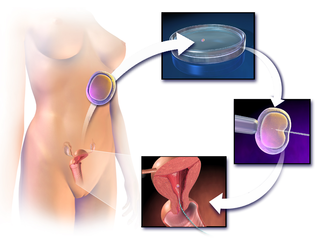
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose. ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits.
Egg donation is the process by which a woman donates eggs to enable another woman to conceive as part of an assisted reproduction treatment or for biomedical research. For assisted reproduction purposes, egg donation typically involves in vitro fertilization technology, with the eggs being fertilized in the laboratory; more rarely, unfertilized eggs may be frozen and stored for later use. Egg donation is a third-party reproduction as part of assisted reproductive technology.

Ovarian reserve is a term that is used to determine the capacity of the ovary to provide egg cells that are capable of fertilization resulting in a healthy and successful pregnancy. With advanced maternal age the number of egg cell that can be successfully recruited for a possible pregnancy declines, constituting a major factor in the inverse correlation between age and female fertility.
Female infertility refers to infertility in women. It affects an estimated 48 million women, with the highest prevalence of infertility affecting women in South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa/Middle East, and Central/Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Infertility is caused by many sources, including nutrition, diseases, and other malformations of the uterus. Infertility affects women from around the world, and the cultural and social stigma surrounding it varies.
Dr Patricia Rashbrook, also known as Patti Farrant, is the oldest woman to give birth in the United Kingdom. It was announced she was pregnant, following IVF treatment, on 4 May 2006, and then gave birth to a son on 5 July at the age of 62 by caesarean section at Sussex County Hospital in Brighton. The baby was healthy and weighed 6 lb 10½oz; he was named Jude. The child was her first with husband John, though she already had three children from a previous marriage. Dr Rashbrook is a child psychiatrist and some criticism has been levelled at her for choosing to become pregnant at such an old age. She claims she will always act in the best interests of her son. She received an IVF treatment from controversial Italian fertility expert Severino Antinori.

Reproductive medicine is a branch of medicine concerning the male and female reproductive systems. It encompasses a variety of reproductive conditions, their prevention and assessment, as well as their subsequent treatment and prognosis.

Oocyte cryopreservation is a procedure to preserve a woman's eggs (oocytes). This technique has been used to enable women to postpone pregnancy to a later date – whether for medical or social reasons. Several studies have shown that most infertility problems are due to germ cell deterioration related to aging. The intention of the procedure is that the woman may choose to have the eggs thawed, fertilized, and transferred to the uterus as embryos to facilitate a pregnancy in the future. The procedure's success rate varies depending on the age of the woman, with odds being higher in younger, adult women.
Poor ovarian reserve is a condition of low fertility characterized by 1): low numbers of remaining oocytes in the ovaries or 2) possibly impaired preantral oocyte development or recruitment. Recent research suggests that premature ovarian aging and premature ovarian failure may represent a continuum of premature ovarian senescence. It is usually accompanied by high FSH levels.

Sherman J. Silber is physician specializing in the field of infertility. He invented many of the infertility treatments in use today in the domain of IVF, sperm retrieval, ICSI, vasectomy reversal, tubal ligation reversal, egg and embryo freezing, ovary transplantation, and the reproductive biological clock. He performed the world's first ovary and testicle transplants, created and popularized the microsurgical vasectomy reversal, and popularized ovarian tissue freezing to preserve female fertility. He was the first to research the genetic causes of infertility in men, and developed the TESE-ICSI technique for extracting sperm from men with low or nonexistent sperm counts and direct injection of the sperm into the egg. Additionally, Silber has studied fertility in animals and performed microscopic surgery on chimpanzees, South American bush dogs, Przewalski's horse, gorillas, wolves, and other endangered species.
Unexplained infertility is infertility that is idiopathic in the sense that its cause remains unknown even after an infertility work-up, usually including semen analysis in the man and assessment of ovulation and fallopian tubes in the woman. It is usually an exercise in excluding all possible causes before making a diagnosis, however the age of the female partner as well as the duration of infertility are often the most scrutinized characteristics of any infertility case.
Partner-assisted reproduction, reception of oocytes from partner (ROPA), reciprocal IVF,shared motherhood, partner IVF or co-IVF is a method of family building that is used by couples who both possess female reproductive organs. The method uses in vitro fertilization (IVF), a method that means eggs are removed from the ovaries, fertilized in a laboratory, and then one or more of the resulting embryos are placed in the uterus to hopefully create a pregnancy. Reciprocal IVF differs from standard IVF in that two partners are involved: the eggs are taken from one partner, and the other partner carries the pregnancy. In this way, the process is mechanically identical to IVF with egg donation. Reciprocal IVF offers the highest chance for pregnancy and a lower risk of a multiple birth. Using this process ensures that each partner is a biological parent of the child. This fertility process is one way that allows lesbian and trans male couples to reproduce and both be involved in the physical process of becoming pregnant.
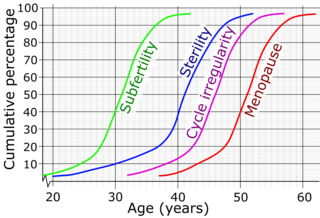
Female fertility is affected by age and is a major fertility factor for women. A woman's fertility is in generally good quality from the late teens to early thirties, although it declines gradually over time. Around 35, fertility is noted to decline at a more rapid rate. While many sources suggest a more dramatic drop at around 35, this is unclear, since few studies have been conducted since the 19th century. One 2004 study of European women found fertility of the 27–34 and the 35–39 groups had only a four-percent difference. At age 45, a woman starting to try to conceive will have no live birth in 50–80 percent of cases. Menopause, or the cessation of menstrual periods, generally occurs in the 40s and 50s and marks the cessation of fertility, although age-related infertility can occur before then. The relationship between age and female fertility is sometimes referred to as a woman's "biological clock."
Endometriosis and its complications are a major cause of female infertility. Endometriosis is a dysfunction characterized by the migration of endometrial tissue to areas outside of the endometrium of the uterus. The most common places to find stray tissue are on ovaries and fallopian tubes, followed by other organs in the lower abdominal cavity such as the bladder and intestines. Typically, the endometrial tissue adheres to the exteriors of the organs, and then creates attachments of scar tissue called adhesions that can join adjacent organs together. The endometrial tissue and the adhesions can block a fallopian tube and prevent the meeting of ovum and sperm cells, or otherwise interfere with fertilization, implantation and, rarely, the carrying of the fetus to term.
John Jin Zhang is a medical scientist who has made contributions in fertility research, and particularly in in vitro fertilization. He made headlines in September 2016 for successfully producing the world's first three-parent baby using the spindle transfer technique of mitochondrial replacement. Having obtained an M.D. from Zhejiang University School of Medicine, an M.Sc. from University of Birmingham, and a Ph.D. from University of Cambridge, he became the founder-director of New Hope Fertility Center in New York, USA.
Miriam Friedman Menkin, née Miriam Friedman, was an American scientist who was most famous for her in vitro fertilization (IVF) research with John Rock. In February 1944, she became the first person to conceive human life outside of the body.

Fertility fraud is the failure on the part of a fertility doctor to obtain consent from a patient before inseminating her with his own sperm. This normally occurs in the context of people using assisted reproductive technology (ART) to address fertility issues.






