Related Research Articles

The Underground Railroad was a network of secret routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early to mid-19th century, and used by enslaved African-Americans to escape into free states and Canada. The scheme was assisted by abolitionists and others sympathetic to the cause of the escapees. Not literally but metaphorically a railroad, the workers who secretly aided the fugitives are also collectively referred to as the "Underground Railroad". Various other routes led to Mexico, where slavery had been abolished, or overseas. An earlier escape route running south toward Florida, then a Spanish possession, existed from the late 17th century until Florida became a United States territory in 1821. One of the main reasons Florida was purchased by the United States was to end its function as a safe haven for escaped slaves. However, the network now generally known as the Underground Railroad was formed in the late 1700s. It ran north and grew steadily until the Civil War began. One estimate suggests that by 1850, 100,000 slaves had escaped via the "Railroad".

The First Transcontinental Railroad was a 1,912-mile (3,077 km) continuous railroad line constructed between 1863 and 1869 that connected the existing eastern U.S. rail network at Council Bluffs, Iowa with the Pacific coast at the Oakland Long Wharf on San Francisco Bay. The rail line was built by three private companies over public lands provided by extensive US land grants. Construction was financed by both state and US government subsidy bonds as well as by company issued mortgage bonds. The Western Pacific Railroad Company built 132 mi (212 km) of track from the road's western terminus at Alameda/Oakland to Sacramento, California. The Central Pacific Railroad Company of California (CPRR) constructed 690 mi (1,110 km) eastward from Sacramento to Promontory Summit, Utah Territory. The Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) built 1,085 mi (1,746 km) from the road's eastern terminus at the Missouri River settlements of Council Bluffs and Omaha, Nebraska westward to Promontory Summit.

A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is a contiguous network railroad trackage that crosses a continental land mass with terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single railroad or over those owned or controlled by multiple railway companies along a continuous route. Although Europe is crisscrossed by railways, the railroads within Europe are usually not considered transcontinental, with the possible exception of the historic Orient Express. Transcontinental railroads helped open up unpopulated interior regions of continents to exploration and settlement that would not otherwise have been feasible. In many cases they also formed the backbones of cross-country passenger and freight transportation networks. Many of them continue to have an important role in freight transportation and some like the Transsiberian Railroad even have passenger trains going from one end to the other.
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak, is a passenger railroad service that provides medium and long-distance intercity service in the contiguous United States and to nine Canadian cities.

The Union Pacific Railroad, legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over 32,200 miles (51,800 km) routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. The Union Pacific Railroad system is the second largest in the United States after BNSF and is one of the world's largest transportation companies. The Union Pacific Railroad is the principal operating company of the Union Pacific Corporation, both headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. The president of Union Pacific since 2015 is Lance Fritz.

The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from the city of Baltimore, which had benefitted to some extent from the construction of the National Road early in the century, wanted to continue to compete for trade with trans-Appalachian settlers with the newly constructed Erie Canal, another canal being proposed by Pennsylvania, the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, and the James River Canal, which directed traffic toward Richmond and Norfolk, Virginia. At first the B&O was located entirely in the state of Maryland, its original line extending from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook.
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American railroad name that was used at the Class I railroad level from 1968 until 1976. The railroad system that applied the Penn Central name was a combination of railroad systems from three railroads: the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR), New York Central Railroad (NYC) and the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (NH). The railroad system started off as a combination of the PRR and New York Central systems first as the system began as a merger between the PRR and the New York Central in 1968, the New York, New Haven and Hartford was added in 1969.

The Boston and Maine Corporation, known as the Boston and Maine Railroad (B&M), was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. It became part of what is now the Pan Am Railways network in 1983.
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was so named because it was established in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.
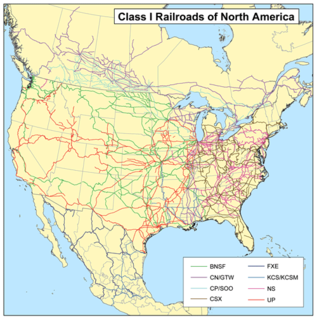
In the United States, railroads are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to size criteria first established by the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) in 1911. Since the ICC was abolished on January 1, 1996, railroads have been governed by the Surface Transportation Board.

The Southern Pacific was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company.

The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), often referred to as the "Milwaukee Road", was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.

The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States, named after the cities and towns of Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe. Chartered in February 1859, the railroad reached the Kansas–Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farmland from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress. Despite the namesake, its mainline did not directly serve Santa Fe, due to the mountainous terrain, the metropolitan city of Albuquerque instead served New Mexico and the Santa Fe area.
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the northeastern United States, originally connecting New York City — more specifically Jersey City, New Jersey, where Erie's former terminal, long demolished, used to stand — with Lake Erie. It expanded west to Chicago with its 1941 merger with the former Atlantic and Great Western Railroad, also known as the New York, Pennsylvania and Ohio Railroad. Its mainline route proved influential in the development and economic growth of the Southern Tier of New York State, including cities such as Binghamton, Elmira, and Hornell. The Erie Railroad repair shops were located in Hornell, and were Hornell's largest employer. Hornell was also where Erie's main line split into two routes, one north to Buffalo and the other west to Cleveland.

The Reading Company was a company that was involved in the railroad industry in southeast Pennsylvania and neighboring states from 1924 until 1976.

The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines, was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It filed for bankruptcy three times; in 1939, 1947 and on March 22, 1967, the CNJ filed for bankruptcy for the final time. It foreshadowed the rest of New Jersey's railroads, but not by much. It then pulled out of Pennsylvania completely in 1972. While most of the passenger services, structures and equipment were picked up by the State of New Jersey, later NJ Transit, it was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of the northeastern United States. Only two of the railroad's steam locomotives were preserved: CNJ No. 592 & CNJ No. 113; the latter is the only one that is still operational.

The Southern Railway is a name of a class 1 railroad that was based in the Southern United States. The railroad is the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.

The Illinois Central Railroad, sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, was a railroad in the central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa (1870). There was a significant branch to Omaha, Nebraska (1899), west of Fort Dodge, Iowa, and another branch reaching Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), starting from Cherokee, Iowa. The Sioux Falls branch has been abandoned in its entirety.

Conrail, formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name, and while it no longer operates trains, it continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway.
References
| This Kings County, California-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |